Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft Entra Domain Services provides managed domain services such as domain join, group policy, LDAP, Kerberos/NTLM authentication that is fully compatible with Windows Server Active Directory. You consume these domain services without deploying, managing, and patching domain controllers yourself. Domain Services integrates with your existing Microsoft Entra tenant. This integration lets users sign in using their corporate credentials, and you can use existing groups and user accounts to secure access to resources.
You can create a managed domain using default configuration options for networking and synchronization, or manually define these settings. This tutorial shows you how to define those advanced configuration options to create and configure a Domain Services managed domain using the Microsoft Entra admin center.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Configure DNS and virtual network settings for a managed domain
- Create a managed domain
- Add administrative users to domain management
- Enable password hash synchronization
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an account before you begin.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need the following resources and privileges:
- An active Azure subscription.
- If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an account.
- A Microsoft Entra tenant associated with your subscription, either synchronized with an on-premises directory or a cloud-only directory.
- You need Application Administrator and Groups Administrator Microsoft Entra roles in your tenant to enable Domain Services.
- You need Domain Services Contributor Azure role to create the required Domain Services resources.
Although not required for Domain Services, it's recommended to configure self-service password reset (SSPR) for the Microsoft Entra tenant. Users can change their password without SSPR, but SSPR helps if they forget their password and need to reset it.
Important
After you create a managed domain, you can't move it to a different subscription, resource group, or region. Take care to select the most appropriate subscription, resource group, and region when you deploy the managed domain.
Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center
In this tutorial, you create and configure the managed domain using the Microsoft Entra admin center. To get started, first sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center.
Create a managed domain and configure basic settings
To launch the Enable Microsoft Entra Domain Services wizard, complete the following steps:
- On the Microsoft Entra admin center menu or from the Home page, select Create a resource.
- Enter Domain Services into the search bar, then choose Microsoft Entra Domain Services from the search suggestions.
- On the Microsoft Entra Domain Services page, select Create. The Enable Microsoft Entra Domain Services wizard is launched.
- Select the Azure Subscription in which you would like to create the managed domain.
- Select the Resource group to which the managed domain should belong. Choose to Create new or select an existing resource group.
When you create a managed domain, you specify a DNS name. There are some considerations when you choose this DNS name:
- Built-in domain name: By default, the built-in domain name of the directory is used (a .partner.onmschina.cn suffix). If you wish to enable secure LDAP access to the managed domain over the internet, you can't create a digital certificate to secure the connection with this default domain. Microsoft owns the .partner.onmschina.cn domain, so a Certificate Authority (CA) won't issue a certificate.
- Custom domain names: The most common approach is to specify a custom domain name, typically one that you already own and is routable. When you use a routable, custom domain, traffic can correctly flow as needed to support your applications.
- Non-routable domain suffixes: We generally recommend that you avoid a non-routable domain name suffix, such as contoso.local. The .local suffix isn't routable and can cause issues with DNS resolution.
Tip
If you create a custom domain name, take care with existing DNS namespaces. It's recommended to use a domain name separate from any existing Azure or on-premises DNS name space.
For example, if you have an existing DNS name space of contoso.com, create a managed domain with the custom domain name of aaddscontoso.com. If you need to use secure LDAP, you must register and own this custom domain name to generate the required certificates.
You may need to create some additional DNS records for other services in your environment, or conditional DNS forwarders between existing DNS name spaces in your environment. For example, if you run a webserver that hosts a site using the root DNS name, there can be naming conflicts that require additional DNS entries.
In these tutorials and how-to articles, the custom domain of aaddscontoso.com is used as a short example. In all commands, specify your own domain name.
The following DNS name restrictions also apply:
- Domain prefix restrictions: You can't create a managed domain with a prefix longer than 15 characters. The prefix of your specified domain name (such as aaddscontoso in the aaddscontoso.com domain name) must contain 15 or fewer characters.
- Network name conflicts: The DNS domain name for your managed domain shouldn't already exist in the virtual network. Specifically, check for the following scenarios that would lead to a name conflict:
- If you already have an Active Directory domain with the same DNS domain name on the Azure virtual network.
- If the virtual network where you plan to enable the managed domain has a VPN connection with your on-premises network. In this scenario, ensure you don't have a domain with the same DNS domain name on your on-premises network.
- If you have an existing Azure cloud service with that name on the Azure virtual network.
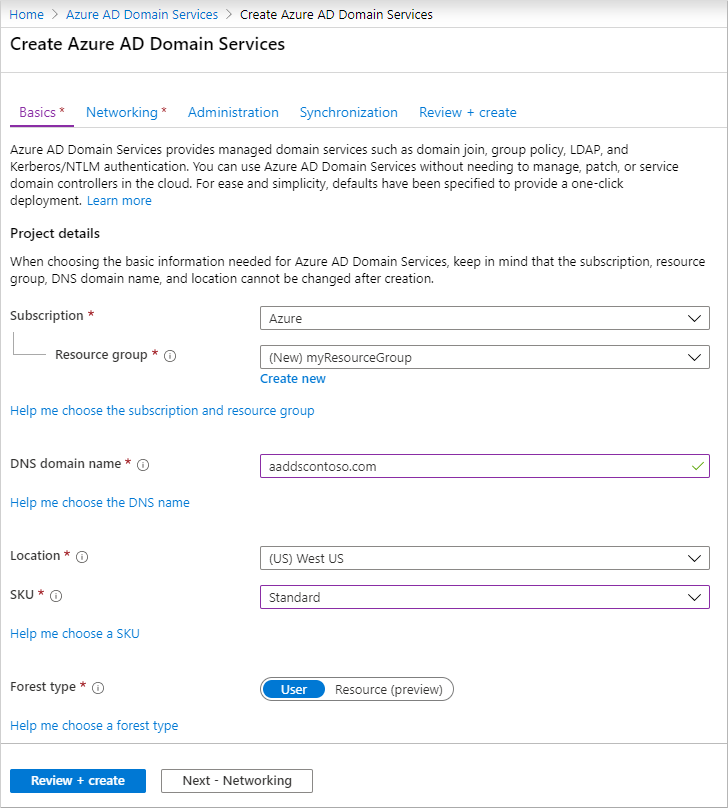
To create a managed domain, complete the fields in the Basics window of the Microsoft Entra admin center:
Enter a DNS domain name for your managed domain, taking into consideration the previous points.
Choose the Azure Location in which the managed domain should be created. If you choose a region that supports Availability Zones, the Domain Services resources are distributed across zones for additional redundancy.
Tip
Availability Zones are unique physical locations within an Azure region. Each zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. To ensure resiliency, there's a minimum of three separate zones in all enabled regions.
There's nothing for you to configure for Domain Services to be distributed across zones. The Azure platform automatically handles the zone distribution of resources. For more information and to see region availability, see What are Availability Zones in Azure?
The SKU determines the performance and backup frequency. You can change the SKU after creating the managed domain if your business demands or requirements change. For more information, see Domain Services SKU concepts.
For this tutorial, select the Standard SKU.
A forest is a logical construct used by Active Directory Domain Services to group one or more domains.
To manually configure additional options, choose Next - Networking. Otherwise, select Review + create to accept the default configuration options, then skip to the section to Deploy your managed domain. The following defaults are configured when you choose this create option:
- Creates a virtual network named aadds-vnet that uses the IP address range of 10.0.1.0/24.
- Creates a subnet named aadds-subnet using the IP address range of 10.0.1.0/24.
- Synchronizes All users from Microsoft Entra ID into the managed domain.
Create and configure the virtual network
To provide connectivity, an Azure virtual network and a dedicated subnet are needed. Domain Services is enabled in this virtual network subnet. In this tutorial, you create a virtual network, though you could instead choose to use an existing virtual network. In either approach, you must create a dedicated subnet for use by Domain Services.
Tip
Because you must use the Microsoft Entra Domain Services deployment IPs as the DNS resolver in the VNET in which it resides, we recommend a dedicated Azure virtual network if using a different DNS service and configuring conditional forwarders on Microsoft Entra Domain Services itself.
Some considerations for this dedicated virtual network subnet include the following areas:
- The subnet must have at least 3-5 available IP addresses in its address range to support the Domain Services resources.
- Don't select the Gateway subnet for deploying Domain Services. It's not supported to deploy Domain Services into a Gateway subnet.
- Don't deploy any other virtual machines to the subnet. Applications and VMs often use network security groups to secure connectivity. Running these workloads in a separate subnet lets you apply those network security groups without disrupting connectivity to your managed domain.
For more information on how to plan and configure the virtual network, see networking considerations for Microsoft Entra Domain Services.
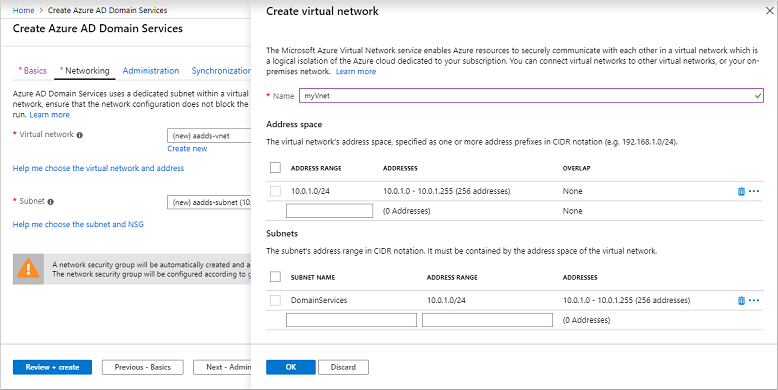
Complete the fields in the Network window as follows:
On the Network page, choose a virtual network to deploy Domain Services into from the drop-down menu, or select Create new.
- If you choose to create a virtual network, enter a name for the virtual network, such as myVnet, then provide an address range, such as 10.0.1.0/24.
- Create a dedicated subnet with a clear name, such as DomainServices. Provide an address range, such as 10.0.1.0/24.
Make sure to pick an address range that is within your private IP address range. IP address ranges you don't own that are in the public address space cause errors within Domain Services.
Select a virtual network subnet, such as DomainServices.
When ready, choose Next - Administration.
Configure an administrative group
A special administrative group named AAD DC Administrators is used for management of the Domain Services domain. Members of this group are granted administrative permissions on VMs that are domain-joined to the managed domain. On domain-joined VMs, this group is added to the local administrators group. Members of this group can also use Remote Desktop to connect remotely to domain-joined VMs.
Important
You don't have Domain Administrator or Enterprise Administrator permissions on a managed domain using Domain Services. The service reserves these permissions and doesn't make them available to users within the tenant.
Instead, the AAD DC Administrators group lets you perform some privileged operations. These operations include belonging to the administration group on domain-joined VMs, and configuring Group Policy.
The wizard automatically creates the AAD DC Administrators group in your Microsoft Entra directory. If you have an existing group with this name in your Microsoft Entra directory, the wizard selects this group. You can optionally choose to add additional users to this AAD DC Administrators group during the deployment process. These steps can be completed later.
To add additional users to this AAD DC Administrators group, select Manage group membership.
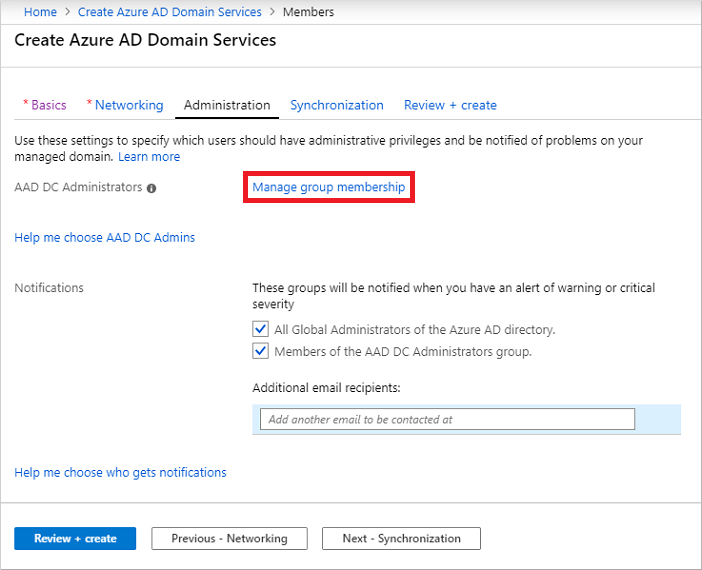
Select the Add members button, then search for and select users from your Microsoft Entra directory. For example, search for your own account, and add it to the AAD DC Administrators group.
If desired, change or add additional recipients for notifications when there are alerts in the managed domain that require attention.
When ready, choose Next - Synchronization.
Configure synchronization
Domain Services lets you synchronize all users and groups available in Microsoft Entra ID, or a scoped synchronization of only specific groups. You can change the synchronize scope now, or once the managed domain is deployed. For more information, see Microsoft Entra Domain Services scoped synchronization.
For this tutorial, choose to synchronize All users and groups. This synchronization choice is the default option.
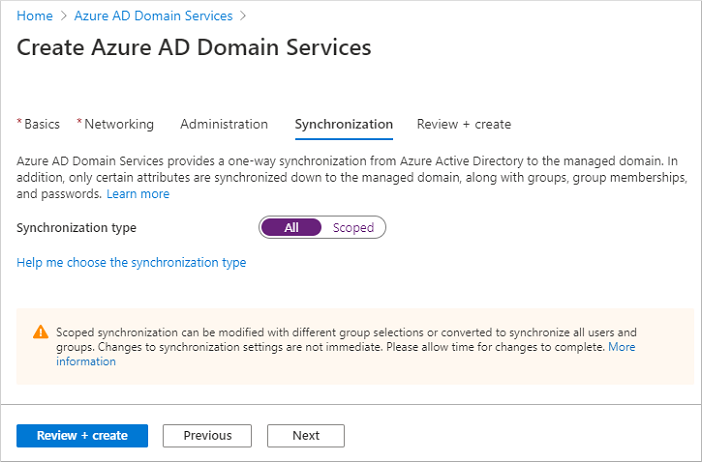
Select Review + create.
Deploy the managed domain
On the Summary page of the wizard, review the configuration settings for your managed domain. You can go back to any step of the wizard to make changes. To redeploy a managed domain to a different Microsoft Entra tenant in a consistent way using these configuration options, you can also Download a template for automation.
To create the managed domain, select Create. A note displays that certain configuration options like DNS name or virtual network can't be changed once the Domain Services managed is created. To continue, select OK.
The process of provisioning your managed domain can take up to an hour. A notification is displayed in the portal that shows the progress of your Domain Services deployment. Select the notification to see detailed progress for the deployment.
Select your resource group, such as myResourceGroup, then choose your managed domain from the list of Azure resources, such as aaddscontoso.com. The Overview tab shows that the managed domain is currently Deploying. You can't configure the managed domain until it's fully provisioned.

When the managed domain is fully provisioned, the Overview tab shows the domain status as Running.

Important
The managed domain is associated with your Microsoft Entra tenant. During the provisioning process, Domain Services creates two Enterprise Applications named Domain Controller Services and AzureActiveDirectoryDomainControllerServices in the Microsoft Entra tenant. These Enterprise Applications are needed to service your managed domain. Don't delete these applications.
Update DNS settings for the Azure virtual network
With Domain Services successfully deployed, now configure the virtual network to allow other connected VMs and applications to use the managed domain. To provide this connectivity, update the DNS server settings for your virtual network to point to the two IP addresses where the managed domain is deployed.
The Overview tab for your managed domain shows some Required configuration steps. The first configuration step is to update DNS server settings for your virtual network. Once the DNS settings are correctly configured, this step is no longer shown.
The addresses listed are the domain controllers for use in the virtual network. In this example, those addresses are 10.0.1.4 and 10.0.1.5. You can later find these IP addresses on the Properties tab.
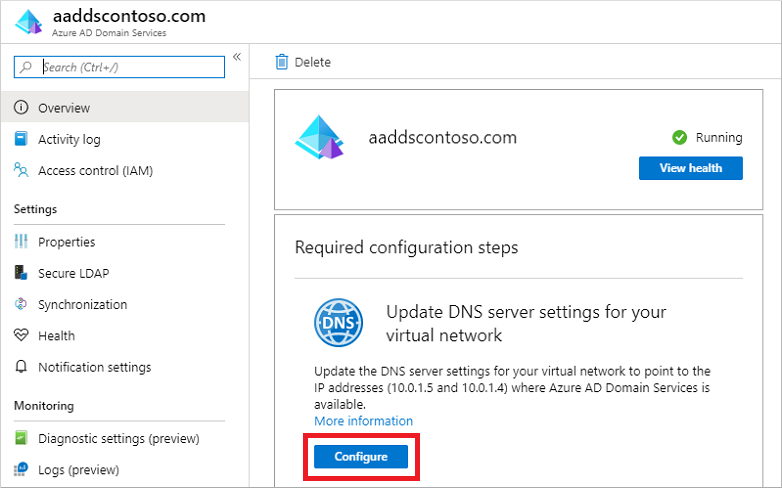
To update the DNS server settings for the virtual network, select the Configure button. The DNS settings are automatically configured for your virtual network.
Tip
If you selected an existing virtual network in the previous steps, any VMs connected to the network only get the new DNS settings after a restart. You can restart VMs using the Microsoft Entra admin center, Microsoft Graph PowerShell, or the Azure CLI.
Enable user accounts for Domain Services
To authenticate users on the managed domain, Domain Services needs password hashes in a format that's suitable for NT LAN Manager (NTLM) and Kerberos authentication. Microsoft Entra ID doesn't generate or store password hashes in the format that's required for NTLM or Kerberos authentication until you enable Domain Services for your tenant. For security reasons, Microsoft Entra ID also doesn't store any password credentials in clear-text form. Therefore, Microsoft Entra ID can't automatically generate these NTLM or Kerberos password hashes based on users' existing credentials.
Note
Once appropriately configured, the usable password hashes are stored in the managed domain. If you delete the managed domain, any password hashes stored at that point are also deleted.
Synchronized credential information in Microsoft Entra ID can't be re-used if you later create a managed domain - you must reconfigure the password hash synchronization to store the password hashes again. Previously domain-joined VMs or users can't immediately authenticate - Microsoft Entra ID needs to generate and store the password hashes in the new managed domain.
For more information, see Password hash sync process for Domain Services and Microsoft Entra Connect.
The steps to generate and store these password hashes are different for two types of user accounts:
- Cloud-only user accounts created in Microsoft Entra ID.
- User accounts that are synchronized from your on-premises directory using Microsoft Entra Connect.
A cloud-only user account is an account that was created in your Microsoft Entra directory using either the Microsoft Entra admin center or Microsoft Graph PowerShell cmdlets. These user accounts aren't synchronized from an on-premises directory.
In this tutorial, let's work with a basic cloud-only user account. For more information on the additional steps required to use Microsoft Entra Connect, see Synchronize password hashes for user accounts synced from your on-premises AD to your managed domain.
Tip
If your Microsoft Entra tenant has a combination of cloud-only users and users from your on-premises AD, you need to complete both sets of steps.
For cloud-only user accounts, users must change their passwords before they can use Domain Services. This password change process causes the password hashes for Kerberos and NTLM authentication to be generated and stored in Microsoft Entra ID. The account isn't synchronized from Microsoft Entra ID to Domain Services until the password is changed. Either expire the passwords for all cloud users in the tenant who need to use Domain Services, which forces a password change on next sign-in, or instruct cloud users to manually change their passwords. For this tutorial, let's manually change a user password.
Before a user can reset their password, the Microsoft Entra tenant must be configured for self-service password reset.
To change the password for a cloud-only user, the user must complete the following steps:
Go to the Microsoft Entra ID Access Panel page at https://myapplications.windowsazure.cn.
In the top-right corner, select your name, then choose Profile from the drop-down menu.
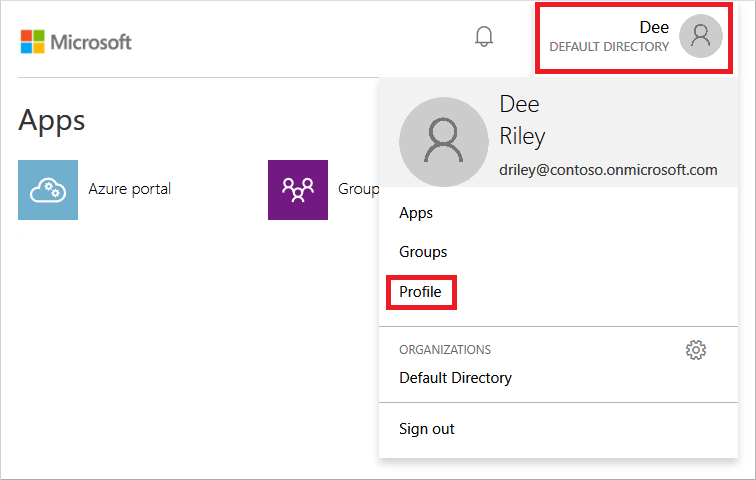
On the Profile page, select Change password.
On the Change password page, enter your existing (old) password, then enter and confirm a new password.
Select Submit.
It takes a few minutes after you've changed your password for the new password to be usable in Domain Services and to successfully sign in to computers joined to the managed domain.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Configure DNS and virtual network settings for a managed domain
- Create a managed domain
- Add administrative users to domain management
- Enable user accounts for Domain Services and generate password hashes
To see this managed domain in action, create and join a virtual machine to the domain.