Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a managed Kubernetes service that lets you quickly deploy and manage clusters. In this quickstart, you learn how to:
- Create an AKS cluster using Flatcar Container Linux for AKS (preview).
- Deploy an AKS cluster using the Azure CLI.
- Run a sample multi-container application with a group of microservices and web front ends that simulate a retail scenario.
Note
This article includes steps to deploy a cluster with default settings for evaluation purposes only.
Before you begin
This quickstart assumes a basic understanding of Kubernetes concepts. For more information, see Kubernetes core concepts for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
- If you don't have an Azure trial subscription, create an Azure trial subscription before you begin.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
- Make sure that the identity you're using to create your cluster has the appropriate minimum permissions. For more information on access and identity for AKS, see Access and identity options for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
- If you have multiple Azure subscriptions, select the appropriate subscription ID in which the resources should be billed using the
az account setcommand. For more information, see How to manage Azure subscriptions – Azure CLI.
Register resource providers
You might need to register resource providers in your Azure subscription. For example, Microsoft.ContainerService is required.
Check the registration status using the az provider show command.
az provider show --namespace Microsoft.ContainerService --query registrationState
If necessary, register the resource provider using the az provider register command.
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.ContainerService
Install aks-preview extension
Important
AKS preview features are available on a self-service, opt-in basis. Previews are provided "as is" and "as available," and they're excluded from the service-level agreements and limited warranty. AKS previews are partially covered by customer support on a best-effort basis. As such, these features aren't meant for production use. For more information, see the following support articles:
Install the
aks-previewAzure CLI extension using theaz extension addcommand.az extension add --name aks-previewUpdate to the latest version of the extension using the
az extension updatecommand. Flatcar Container Linux requires a minimum of 18.0.0b42.az extension update --name aks-preview
Register AKSFlatcarPreview feature flag
Register the
AKSFlatcarPreviewfeature flag using theaz feature registercommand.az feature register --namespace "Microsoft.ContainerService" --name "AKSFlatcarPreview"Verify the registration status using the
az feature showcommand. It takes a few minutes for the status to show Registered.az feature show --namespace Microsoft.ContainerService --name AKSFlatcarPreviewWhen the status reflects Registered, refresh the registration of the Microsoft.ContainerService resource provider using the
az provider registercommand.az provider register --namespace Microsoft.ContainerService
Define environment variables
- Define the following environment variables for use throughout this quickstart:
export RANDOM_ID="$(openssl rand -hex 3)"
export MY_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME="myAKSResourceGroup$RANDOM_ID"
export REGION="chinanorth3"
export MY_AKS_CLUSTER_NAME="myAKSCluster$RANDOM_ID"
The RANDOM_ID variable's value is a six-character alphanumeric value appended to the resource group and cluster name so that the names are unique. Use the echo command to view variable values like echo $RANDOM_ID.
Create a resource group
An Azure resource group is a logical group in which Azure resources are deployed and managed. When you create a resource group, you're prompted to specify a location. This location is the storage location of your resource group metadata and where your resources run in Azure if you don't specify another region during resource creation.
- Create a resource group using the
az group createcommand.
az group create \
--name $MY_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME \
--location $REGION
Example output:
{
"id": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/myAKSResourceGroup<randomIDValue>",
"location": "chinanorth3",
"managedBy": null,
"name": "myAKSResourceGroup<randomIDValue>",
"properties": {
"provisioningState": "Succeeded"
},
"tags": null,
"type": "Microsoft.Resources/resourceGroups"
}
Create an AKS cluster
- Create an AKS cluster using the
az aks createcommand. The following example creates a cluster with one node and enables a system-assigned managed identity:
az aks create \
--resource-group $MY_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME \
--name $MY_AKS_CLUSTER_NAME \
--os-sku flatcar \
--node-count 1 \
--generate-ssh-keys
Note
When you create a new cluster, AKS automatically creates a second resource group to store the AKS resources. For more information, see Why are two resource groups created with AKS?
Connect to the cluster
To manage a Kubernetes cluster, use the Kubernetes command-line client, kubectl. To install kubectl locally, use the az aks install-cli command.
Configure
kubectlto connect to your Kubernetes cluster using theaz aks get-credentialscommand. This command downloads credentials and configures the Kubernetes CLI to use them.az aks get-credentials \ --resource-group $MY_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME \ --name $MY_AKS_CLUSTER_NAMEVerify the connection to your cluster using the
kubectl getcommand. This command returns a list of the cluster nodes.kubectl get nodes
Deploy the application
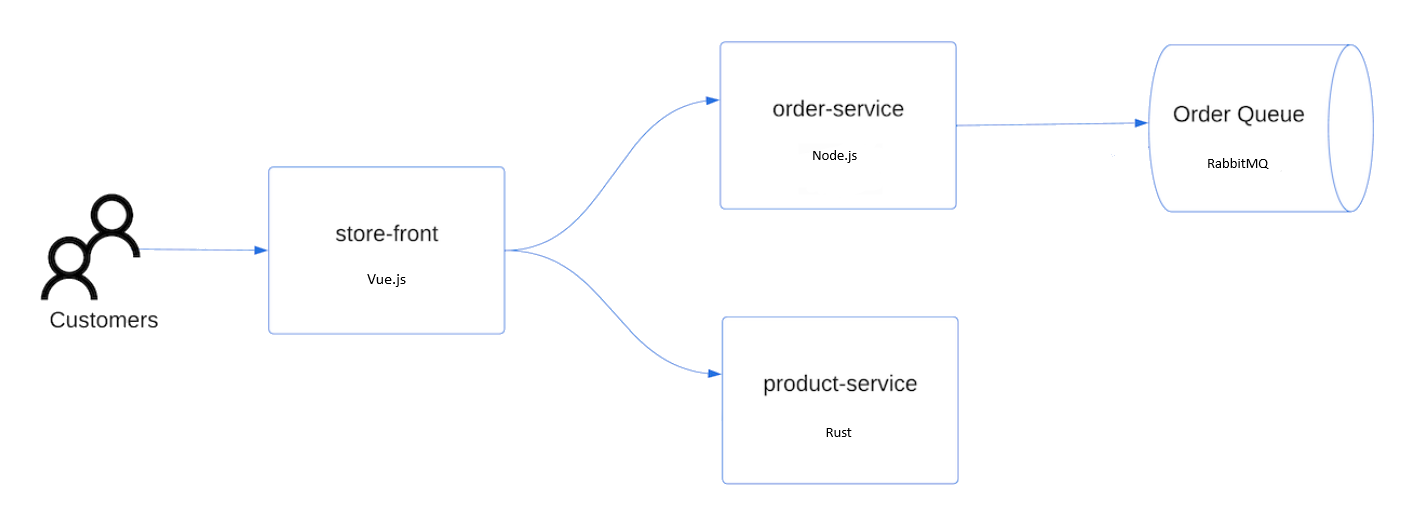
To deploy the application, you use a manifest file to create all the objects required to run the AKS Store application. A Kubernetes manifest file defines a cluster's desired state, such as which container images to run. The manifest includes the following Kubernetes deployments and services:
- Store front: Web application for customers to view products and place orders.
- Product service: Shows product information.
- Order service: Places orders.
RabbitMQ: Message queue for an order queue.
Note
We don't recommend running stateful containers, such as RabbitMQ, without persistent storage for production. We use it here for simplicity, but we recommend using managed services, such as Azure Cosmos DB or Azure Service Bus.
Create a file named aks-store-quickstart.yaml and copy in the following manifest.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: rabbitmq spec: serviceName: rabbitmq replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: rabbitmq template: metadata: labels: app: rabbitmq spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": linux containers: - name: rabbitmq image: mcr.microsoft.com/mirror/docker/library/rabbitmq:3.10-management-alpine ports: - containerPort: 5672 name: rabbitmq-amqp - containerPort: 15672 name: rabbitmq-http env: - name: RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER value: "username" - name: RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS value: "password" resources: requests: cpu: 10m memory: 128Mi limits: cpu: 250m memory: 256Mi volumeMounts: - name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins mountPath: /etc/rabbitmq/enabled_plugins subPath: enabled_plugins volumes: - name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins configMap: name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins items: - key: rabbitmq_enabled_plugins path: enabled_plugins --- apiVersion: v1 data: rabbitmq_enabled_plugins: | [rabbitmq_management,rabbitmq_prometheus,rabbitmq_amqp1_0]. kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: rabbitmq spec: selector: app: rabbitmq ports: - name: rabbitmq-amqp port: 5672 targetPort: 5672 - name: rabbitmq-http port: 15672 targetPort: 15672 type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: order-service spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: order-service template: metadata: labels: app: order-service spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": linux containers: - name: order-service image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/order-service:latest ports: - containerPort: 3000 env: - name: ORDER_QUEUE_HOSTNAME value: "rabbitmq" - name: ORDER_QUEUE_PORT value: "5672" - name: ORDER_QUEUE_USERNAME value: "username" - name: ORDER_QUEUE_PASSWORD value: "password" - name: ORDER_QUEUE_NAME value: "orders" - name: FASTIFY_ADDRESS value: "0.0.0.0" resources: requests: cpu: 1m memory: 50Mi limits: cpu: 75m memory: 128Mi startupProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 3000 failureThreshold: 5 initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 10 readinessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 3000 failureThreshold: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 3 periodSeconds: 5 livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 3000 failureThreshold: 5 initialDelaySeconds: 3 periodSeconds: 3 initContainers: - name: wait-for-rabbitmq image: busybox command: ['sh', '-c', 'until nc -zv rabbitmq 5672; do echo waiting for rabbitmq; sleep 2; done;'] resources: requests: cpu: 1m memory: 50Mi limits: cpu: 75m memory: 128Mi --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: order-service spec: type: ClusterIP ports: - name: http port: 3000 targetPort: 3000 selector: app: order-service --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: product-service spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: product-service template: metadata: labels: app: product-service spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": linux containers: - name: product-service image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/product-service:latest ports: - containerPort: 3002 env: - name: AI_SERVICE_URL value: "http://ai-service:5001/" resources: requests: cpu: 1m memory: 1Mi limits: cpu: 2m memory: 20Mi readinessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 3002 failureThreshold: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 3 periodSeconds: 5 livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 3002 failureThreshold: 5 initialDelaySeconds: 3 periodSeconds: 3 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: product-service spec: type: ClusterIP ports: - name: http port: 3002 targetPort: 3002 selector: app: product-service --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: store-front spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: store-front template: metadata: labels: app: store-front spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": linux containers: - name: store-front image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/store-front:latest ports: - containerPort: 8080 name: store-front env: - name: VUE_APP_ORDER_SERVICE_URL value: "http://order-service:3000/" - name: VUE_APP_PRODUCT_SERVICE_URL value: "http://product-service:3002/" resources: requests: cpu: 1m memory: 200Mi limits: cpu: 1000m memory: 512Mi startupProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 8080 failureThreshold: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 5 periodSeconds: 5 readinessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 8080 failureThreshold: 3 initialDelaySeconds: 3 periodSeconds: 3 livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 8080 failureThreshold: 5 initialDelaySeconds: 3 periodSeconds: 3 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: store-front spec: ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 8080 selector: app: store-front type: LoadBalancerFor a breakdown of YAML manifest files, see Deployments and YAML manifests.
If you create and save the YAML file locally, then you can upload the manifest file to your default directory in Cli by selecting the Upload/Download files button and selecting the file from your local file system.
Deploy the application using the
kubectl applycommand and specify the name of your YAML manifest.kubectl apply -f aks-store-quickstart.yamlThe following example output shows the deployments and services:
deployment.apps/rabbitmq created service/rabbitmq created deployment.apps/order-service created service/order-service created deployment.apps/product-service created service/product-service created deployment.apps/store-front created service/store-front created
Test the application
When the application runs, a Kubernetes service exposes the application front end to the internet. This process can take a few minutes to complete.
Check the status of the deployed pods using the
kubectl get podscommand. Make sure all pods areRunningbefore proceeding.kubectl get podsCheck for a public IP address for the
store-frontapplication. Monitor progress using thekubectl get servicecommand with the--watchargument.kubectl get service store-front --watchThe EXTERNAL-IP output for the
store-frontservice initially shows as pending:NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE store-front LoadBalancer 10.0.100.10 <pending> 80:30025/TCP 4h4mOnce the EXTERNAL-IP address changes from pending to an actual public IP address, use
CTRL-Cto stop thekubectlwatch process.The following example output shows a valid public IP address assigned to the service:
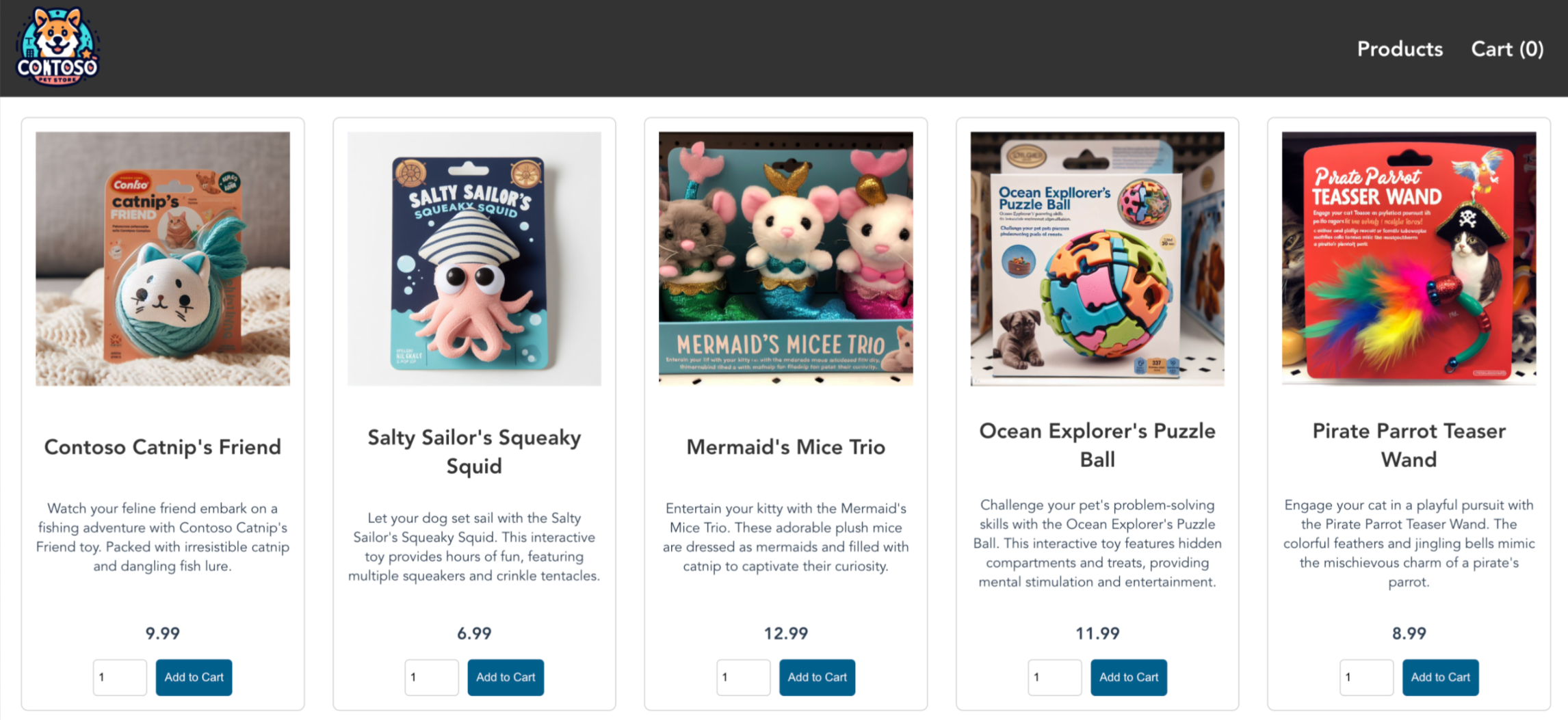
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE store-front LoadBalancer 10.0.100.10 20.62.159.19 80:30025/TCP 4h5mOpen a web browser to the external IP address of your service to see the Azure Store app in action.
Delete the cluster
If you don't plan on going through the AKS tutorial, clean up unnecessary resources to avoid Azure billing charges.
Remove the resource group, container service, and all related resources using the
az group deletecommand.az group delete --name $MY_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAMEThe AKS cluster was created with a system-assigned managed identity, which is the default identity option used in this quickstart. The platform manages this identity so you don't need to manually remove it.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you deployed a Kubernetes cluster and then deployed a simple multi-container application to it. This sample application is for demo purposes only and doesn't represent all the best practices for Kubernetes applications.
To learn more about AKS and do a complete code-to-deployment example, continue to the Kubernetes cluster tutorial.