Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO: Premium
This article provides an overview of API Management workspaces and how they empower decentralized API development teams to manage and productize their APIs in a common service infrastructure.
Why should organizations federate API management?
Today, organizations increasingly face challenges in managing a proliferation of APIs. As the number of APIs and API development teams grows, so does the complexity of managing them. This complexity can lead to increased operational overhead, security risks, and reduced agility. On the one hand, organizations want to establish a centralized API infrastructure to ensure API governance, security, and compliance. On the other hand, they want their API teams to innovate and respond quickly to business needs, without the overhead of managing an API platform.
A federated model of API management addresses these needs. Federated API management allows decentralized API management by development teams with appropriate isolation of control and data planes, while maintaining centralized governance, monitoring, and API discovery managed by an API platform team. This model overcomes the limitations of alternative approaches such as fully centralized API management by the platform team or siloed API management by each development team.
Federated API management provides:
- Centralized API governance and observability
- A unified developer portal for effective API discovery and onboarding
- Segregated administrative permissions between API teams, enhancing productivity and security
- Segregated API runtime between API teams, improving reliability, resiliency, and security
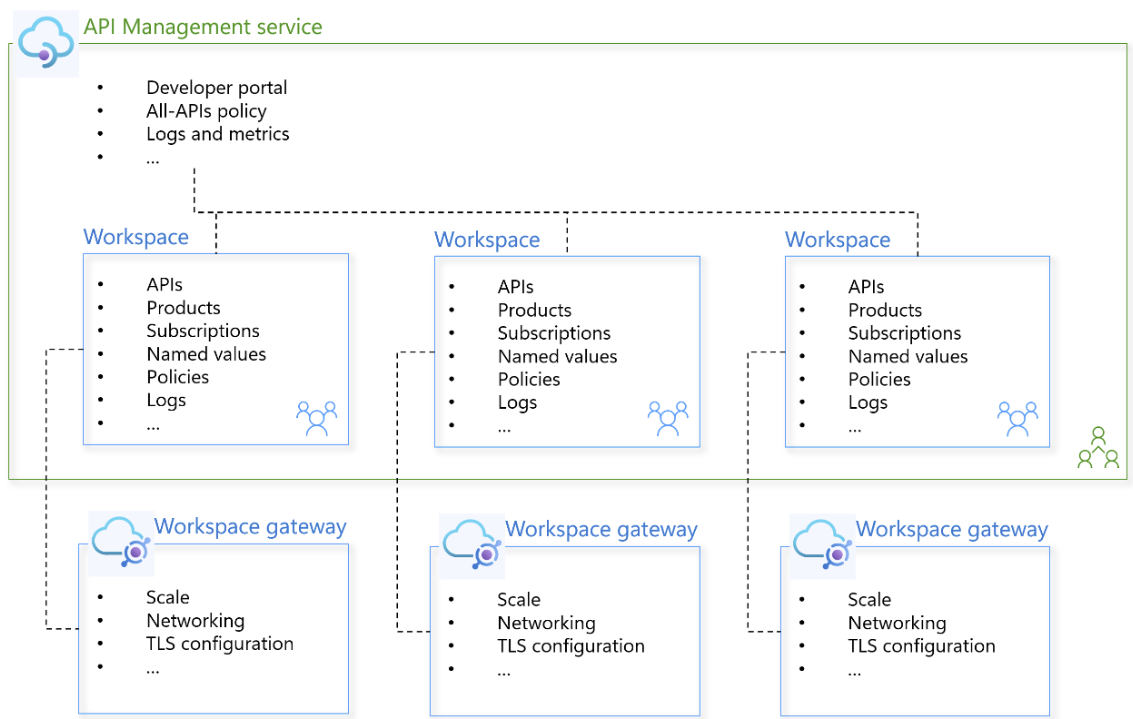
How workspaces enable federated API management
In Azure API Management, use workspaces to implement federated API management. Workspaces function like "folders" within an API Management service:
- Each workspace contains APIs, products, subscriptions, named values, and related resources. See the API Management REST API reference for a full list of resources and operations supported in workspaces.
- Teams' access to resources within a workspace is managed through Azure's role-based access control (RBAC) with built-in or custom roles assignable to Microsoft Entra accounts and scoped to a workspace.
- Each workspace is associated with one or more workspace gateways for routing API traffic to the backend services of APIs in the workspace.
- The platform team can apply policies spanning APIs and products in workspaces to govern API runtime across the organization. A built-in Azure Policy definition (
API Management policies should inherit parent scope policies using <base/>) lets you audit or enforce that these policies are applied across all workspace resources. - The platform team can implement a centralized API discovery experience with a developer portal.
- Each workspace team can gather and analyze gateway resource logs to monitor their own workspace APIs, while the platform team has federated access to logs across all workspaces in the API Management service, providing oversight, security, and compliance across their API ecosystem.
Note
- The latest workspace features are supported in API Management REST API version 2023-09-01-preview or later.
- For pricing considerations, see API Management pricing.
While workspaces are managed independently from the API Management service and other workspaces, by design they can reference selected service-level resources. See Workspaces and other API Management features, later in this article.
Example scenario overview
An organization that manages APIs using Azure API Management may have multiple development teams that develop, define, maintain, and productize different sets of APIs. Workspaces allow these teams to use API Management to manage, access, and secure their APIs separately, and independently of managing the service infrastructure.
The following is a sample workflow for creating and using a workspace.
A central API platform team that manages the API Management instance creates a workspace and assigns permissions to workspace collaborators using RBAC roles - for example, permissions to create or read resources in the workspace. A workspace-scoped API gateway is also created for the workspace.
A central API platform team uses DevOps tools to create a DevOps pipeline for APIs in that workspace.
Workspace members develop, publish, productize, and maintain APIs in the workspace.
The central API platform team manages the infrastructure of the service, such as monitoring, resiliency, and enforcement of all-APIs policies.
RBAC roles for workspaces
Azure RBAC is used to configure workspace collaborators' permissions to read and edit entities in the workspace. For a list of roles, see How to use role-based access control in API Management.
To manage APIs and other resources in the workspace, workspace members must be assigned roles (or equivalent permissions using custom roles) scoped to the API Management service, the workspace, and the workspace gateway. The service-scoped role enables referencing certain service-level resources from workspace-level resources. For example, organize a user into a workspace-level group to control API and product visibility.
Note
For easier management, set up Microsoft Entra groups to assign workspace permissions to multiple users.
Workspaces and other API Management features
Workspaces are designed to be self-contained to maximize segregation of administrative access and API runtime. There are several exceptions to ensure higher productivity and enable platform-wide governance, observability, reusability, and API discovery.
Resource references - Resources in a workspace can reference other resources in the workspace and selected resources from the service level, such as users, authorization servers, or built-in user groups. They can't reference resources from another workspace.
For security reasons, it's not possible to reference service-level resources from workspace-level policies (for example, named values) or by resource names, such as
backend-idin the set-backend-service policy.Important
All resources in an API Management service (for example, APIs, products, tags, or subscriptions) need to have unique names, even if they're located in different workspaces. There can't be any resources of the same type and with the same Azure resource name in the same workspace, in other workspaces, or on the service level.
Developer portal - Workspaces are an administrative concept and aren't surfaced as such to developer portal consumers, including through the developer portal UI and the underlying API. APIs and products within a workspace can be published to the developer portal, just like APIs and products on the service level.
Note
API Management supports assigning authorization servers defined on the service level to APIs within workspaces.
Migrate from preview workspaces
If you created preview workspaces in Azure API Management and want to continue using them, migrate your workspaces to the generally available version by associating a workspace gateway with each workspace.
Deleting a workspace
Deleting a workspace deletes all its child resources (APIs, products, and so on) and its associated gateway, if you're deleting the workspace using the Azure portal interface. It doesn't delete the API Management instance or other workspaces.