Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Learn how to access Microsoft Graph from a web app running on Azure App Service.
You want to add access to Microsoft Graph from your web app and perform some action as the signed-in user. This section describes how to grant delegated permissions to the web app and get the signed-in user's profile information from Microsoft Entra ID.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Grant delegated permissions to a web app.
- Call Microsoft Graph from a web app for a signed-in user.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a trial account before you begin.
Prerequisites
- A web application running on Azure App Service that has the App Service authentication/authorization module enabled.
Grant front-end access to call Microsoft Graph
Now that you've enabled authentication and authorization on your web app, the web app is registered with the Microsoft identity platform and is backed by a Microsoft Entra application. In this step, you give the web app permissions to access Microsoft Graph for the user. (Technically, you give the web app's Microsoft Entra application the permissions to access the Microsoft Graph Microsoft Entra application for the user.)
In the Azure portal menu, select Microsoft Entra ID or search for and select Microsoft Entra ID from any page.
Select App registrations > Owned applications > View all applications in this directory. Select your web app name, and then select API permissions.
Select Add a permission, and then select Microsoft APIs and Microsoft Graph.
Select Delegated permissions, and then select User.Read from the list. Select Add permissions.
Configure App Service to return a usable access token
The web app now has the required permissions to access Microsoft Graph as the signed-in user. In this step, you configure App Service authentication and authorization to give you a usable access token for accessing Microsoft Graph. For this step, you need to add the User.Read scope for the downstream service (Microsoft Graph): https://microsoftgraph.chinacloudapi.cn/User.Read.
Important
If you don't configure App Service to return a usable access token, you receive a CompactToken parsing failed with error code: 80049217 error when you call Microsoft Graph APIs in your code.
Use the Azure CLI to call the App Service Web App REST APIs to get and update the auth configuration settings so your web app can call Microsoft Graph.
Open a command window and login to Azure CLI:
az loginGet your existing 'config/authsettingsv2' settings and save to a local authsettings.json file.
az rest --method GET --url '/subscriptions/{SUBSCRIPTION_ID}/resourceGroups/{RESOURCE_GROUP}/providers/Microsoft.Web/sites/{WEBAPP_NAME}/config/authsettingsv2/list?api-version=2020-06-01' > authsettings.jsonOpen the authsettings.json file using your preferred text editor.
Find the login section of identityProviders -> azureActiveDirectory.
Add the following loginParameters settings:
"loginParameters":[ "response_type=code id_token","scope=openid offline_access profile https://microsoftgraph.chinacloudapi.cn/User.Read" ]."identityProviders": { "azureActiveDirectory": { "enabled": true, "login": { "loginParameters":[ "response_type=code id_token", "scope=openid offline_access profile https://microsoftgraph.chinacloudapi.cn/User.Read" ] } } } },Save your changes to the authsettings.json file and upload the local settings to your web app:
az rest --method PUT --url '/subscriptions/{SUBSCRIPTION_ID}/resourceGroups/{RESOURCE_GROUP}/providers/Microsoft.Web/sites/{WEBAPP_NAME}/config/authsettingsv2?api-version=2020-06-01' --body @./authsettings.json
Call Azure Graph with .NET
Your web app now has the required permissions and also adds Microsoft Graph's client ID to the login parameters.
Using the Microsoft.Identity.Web library, the web app gets an access token for authentication with Microsoft Graph. In version 1.2.0 and later, the Microsoft.Identity.Web library integrates with and can run alongside the App Service authentication/authorization module. Microsoft.Identity.Web detects that the web app is hosted in App Service and automatically retrieves the access token from the X-MS-TOKEN-AAD-ACCESS-TOKEN request header that App Service injects. You don't need to manually access this header in your code. The access token is then passed along to authenticated requests with the Microsoft Graph API.
To see this code as part of a sample application, see the:
Note
The Microsoft.Identity.Web library isn't required in your web app for basic authentication/authorization or to authenticate requests with Azure Graph.
However, the App Service authentication/authorization is designed for more basic authentication scenarios. For more complex scenarios (handling custom claims, for example), you need the Microsoft.Identity.Web library or Microsoft Authentication Library. There's a little more setup and configuration work in the beginning, but the Microsoft.Identity.Web library can run alongside the App Service authentication/authorization module. Later, when your web app needs to handle more complex scenarios, you can disable the App Service authentication/authorization module and Microsoft.Identity.Web will already be a part of your app.
Install client library packages
Install the Microsoft.Identity.Web and Microsoft.Identity.Web.MicrosoftGraph NuGet packages in your project by using the .NET Core command-line interface or the Package Manager Console in Visual Studio.
.NET Core command line
Open a command line, and switch to the directory that contains your project file.
Run the install commands.
dotnet add package Microsoft.Identity.Web.MicrosoftGraph
dotnet add package Microsoft.Identity.Web
Package Manager Console
Open the project/solution in Visual Studio, and open the console by using the Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console command.
Run the install commands.
Install-Package Microsoft.Identity.Web.GraphServiceClient
Install-Package Microsoft.Identity.Web
Startup.cs
In the Startup.cs file, the AddMicrosoftIdentityWebApp method adds Microsoft.Identity.Web to your web app. The AddMicrosoftGraph method adds Azure Graph support. For info on managing incremental consent and conditional access, read this.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.OpenIdConnect;
// Some code omitted for brevity.
public class Startup
{
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddOptions();
string[] initialScopes = Configuration.GetValue<string>("DownstreamApi:Scopes")?.Split(' ');
services.AddAuthentication(OpenIdConnectDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddMicrosoftIdentityWebApp(Configuration.GetSection("AzureAd"))
.EnableTokenAcquisitionToCallDownstreamApi(initialScopes)
.AddMicrosoftGraph(Configuration.GetSection("DownstreamApi"))
.AddInMemoryTokenCaches();
services.AddAuthorization(options =>
{
// By default, all incoming requests will be authorized according to the default policy
options.FallbackPolicy = options.DefaultPolicy;
});
services.AddRazorPages()
.AddMvcOptions(options => {})
.AddMicrosoftIdentityUI();
services.AddControllersWithViews()
.AddMicrosoftIdentityUI();
}
}
appsettings.json
AzureAd specifies the configuration for the Microsoft.Identity.Web library. In the Azure portal, select Microsoft Entra ID from the portal menu and then select App registrations. Select the app registration created when you enabled the App Service authentication/authorization module. (The app registration should have the same name as your web app.) You can find the tenant ID and client ID in the app registration overview page. The domain name can be found in the Azure AD overview page for your tenant.
Graph specifies the Azure Graph endpoint and the initial scopes needed by the app.
{
"AzureAd": {
"Instance": "https://login.chinacloudapi.cn/",
"Domain": "[Enter the domain of your tenant, e.g. contoso.partner.onmschina.cn]",
"TenantId": "[Enter 'common', or 'organizations' or the Tenant Id (Obtained from the Azure portal. Select 'Endpoints' from the 'App registrations' blade and use the GUID in any of the URLs), e.g. da41245a5-11b3-996c-00a8-4d99re19f292]",
"ClientId": "[Enter the Client Id (Application ID obtained from the Azure portal), e.g. ba74781c2-53c2-442a-97c2-3d60re42f403]",
"ClientSecret": "[Copy the client secret added to the app from the Azure portal]",
"ClientCertificates": [
],
// the following is required to handle Continuous Access Evaluation challenges
"ClientCapabilities": [ "cp1" ],
"CallbackPath": "/signin-oidc"
},
"DownstreamApis": {
"MicrosoftGraph": {
// Specify BaseUrl if you want to use Microsoft graph in a national cloud.
// See https://learn.microsoft.com/graph/deployments#microsoft-graph-and-graph-explorer-service-root-endpoints
// "BaseUrl": "https://microsoftgraph.chinacloudapi.cn/v1.0",
// Set RequestAppToken this to "true" if you want to request an application token (to call graph on
// behalf of the application). The scopes will then automatically
// be ['https://microsoftgraph.chinacloudapi.cn/.default'].
// "RequestAppToken": false
// Set Scopes to request (unless you request an app token).
"Scopes": [ "User.Read" ]
// See https://aka.ms/ms-id-web/downstreamApiOptions for all the properties you can set.
}
},
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
Call Microsoft Graph on behalf of the user
The following example shows how to call Azure Graph as the signed-in user and get some user information. The GraphServiceClient object is injected into the controller, and authentication has been configured for you by the Microsoft.Identity.Web library.
// Index.cshtml.cs
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using Microsoft.Graph;
using System.IO;
using Microsoft.Identity.Web;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
// Some code omitted for brevity.
[AuthorizeForScopes(Scopes = new[] { "User.Read" })]
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ILogger<IndexModel> _logger;
private readonly GraphServiceClient _graphServiceClient;
public IndexModel(ILogger<IndexModel> logger, GraphServiceClient graphServiceClient)
{
_logger = logger;
_graphServiceClient = graphServiceClient;
}
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
try
{
var user = await _graphServiceClient.Me.GetAsync();
ViewData["Me"] = user;
ViewData["name"] = user.DisplayName;
using (var photoStream = await _graphServiceClient.Me.Photo.Content.GetAsync())
{
byte[] photoByte = ((MemoryStream)photoStream).ToArray();
ViewData["photo"] = Convert.ToBase64String(photoByte);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ViewData["photo"] = null;
}
}
}
Clean up resources
If you completed all the steps in this multipart tutorial, you created an app service, app service hosting plan, and a storage account in a resource group. You also created an app registration in Microsoft Entra ID. When no longer needed, delete these resources and app registration so that you don't continue to accrue charges.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Delete the Azure resources created while following the tutorial.
Delete the resource group
In the Azure portal, select Resource groups from the portal menu and select the resource group that contains your App Service and App Service plan.
Select Delete resource group to delete the resource group and all the resources.
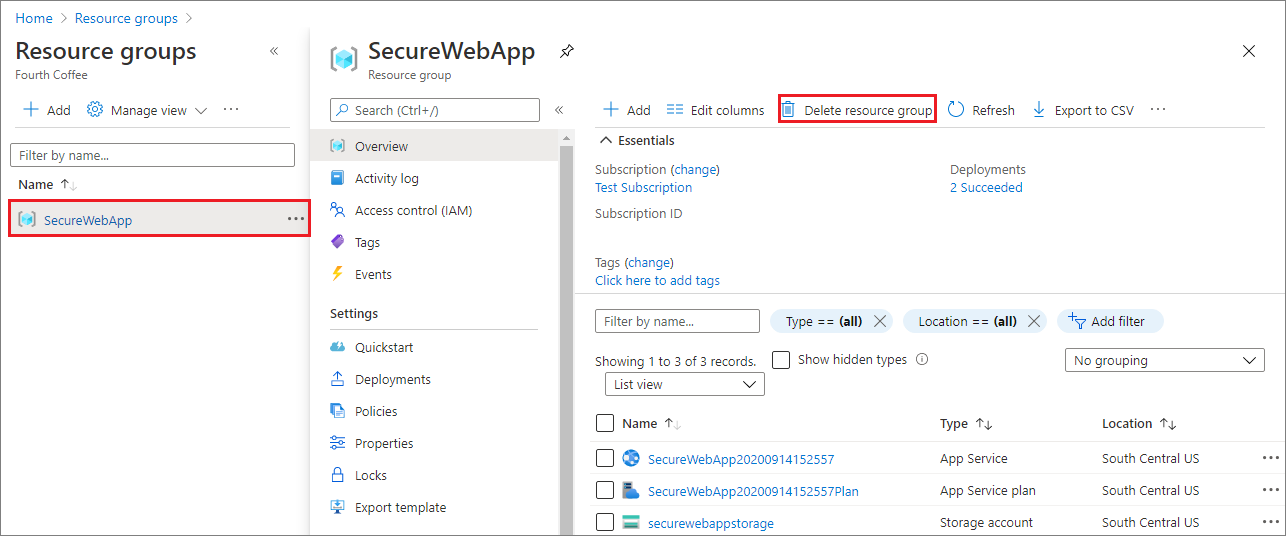
This command might take several minutes to run.
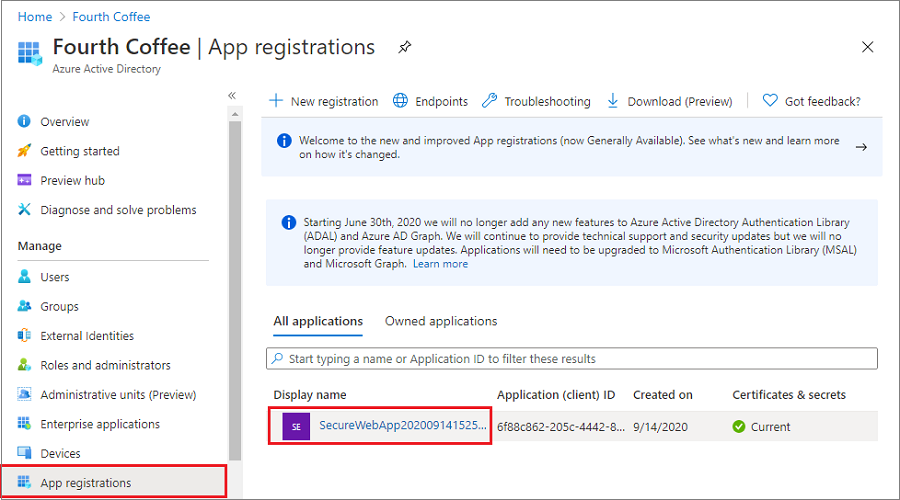
Delete the app registration
From the portal menu, select Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations. Then select the application you created.
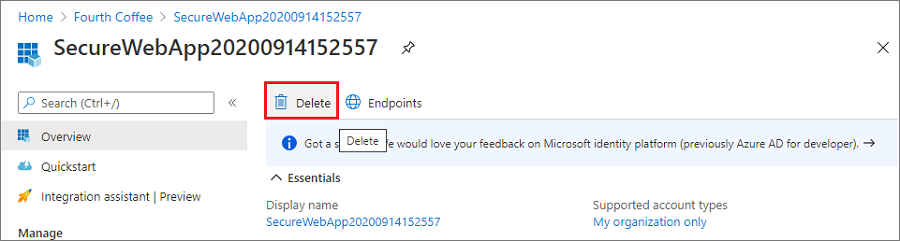
In the app registration overview, select Delete.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Grant delegated permissions to a web app.
- Call Microsoft Graph from a web app for a signed-in user.