Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Test with a simple Kubernetes app
The following steps assume:
- You have an AKS cluster, with Advanced Networking enabled
- AGIC has been installed on the AKS cluster
- You already have an Application Gateway on a VNET shared with your AKS cluster
To verify that the Application Gateway + AKS + AGIC installation is set up correctly, deploy the simplest possible app:
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-agic-app-pod
labels:
app: test-agic-app
spec:
containers:
- image: "mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/samples:aspnetapp"
name: aspnetapp-image
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: test-agic-app-service
spec:
selector:
app: test-agic-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-agic-app-ingress
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway
spec:
#ingressClassName: azure-application-gateway # according to the AGIC setup guide, annotations are the approach to set the class
rules:
- host: test.agic.contoso.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
name: test-agic-app-service
port:
number: 80
EOF
Copy and paste all lines at once from the previous script. Verify that the entire command is copied - starting with cat and including the last EOF.
After a successful deployment of the app your AKS cluster has a new Pod, Service, and Ingress.
Get the list of pods: kubectl get pods -o wide. We expect for a pod named test-agic-app-pod to have been created with an IP address. This address must be within the VNET of the Application Gateway, which is used with AKS.
Get the list of services: kubectl get services -o wide. We expect to see a service named test-agic-app-service.
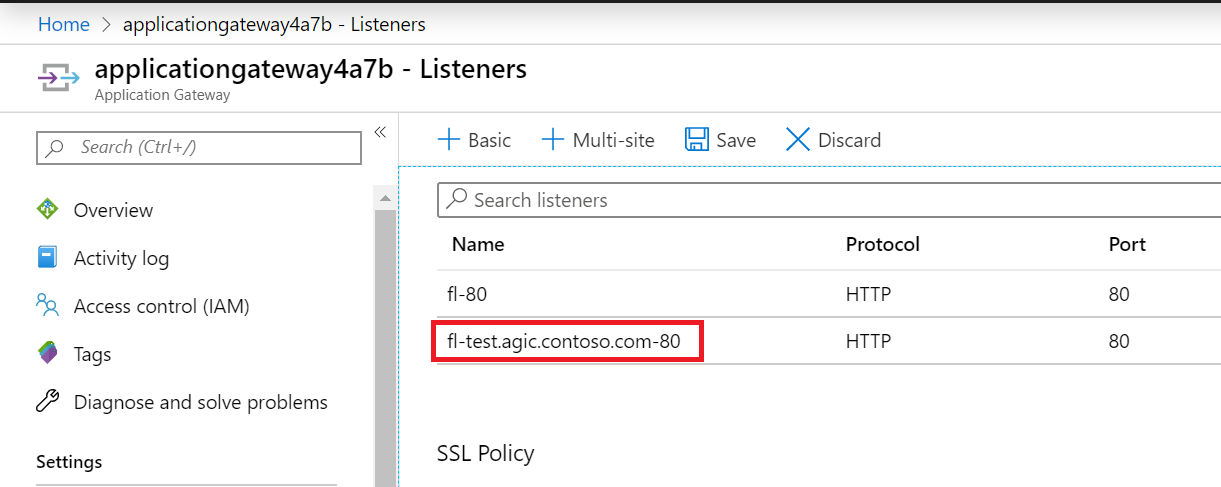
Get the list of the ingresses: kubectl get ingress. We expect an Ingress resource named test-agic-app-ingress to have been created. The resource has a host name test.agic.contoso.com.
One of the pods is AGIC. kubectl get pods shows a list of pods, one of which begins with 'ingress-azure.' Get all logs of that pod with kubectl logs <name-of-ingress-controller-pod> to verify that we've had a successful deployment. A successful deployment would have added the following lines to the log:
I0927 22:34:51.281437 1 process.go:156] Applied Application Gateway config in 20.461335266s
I0927 22:34:51.281585 1 process.go:165] cache: Updated with latest applied config.
I0927 22:34:51.282342 1 process.go:171] END AppGateway deployment
Alternatively, we can retrieve only the lines indicating successful Application Gateway configuration with kubectl logs <ingress-azure-....> | grep 'Applied App Gateway config in', where <ingress-azure....> should be the exact name of the AGIC pod.
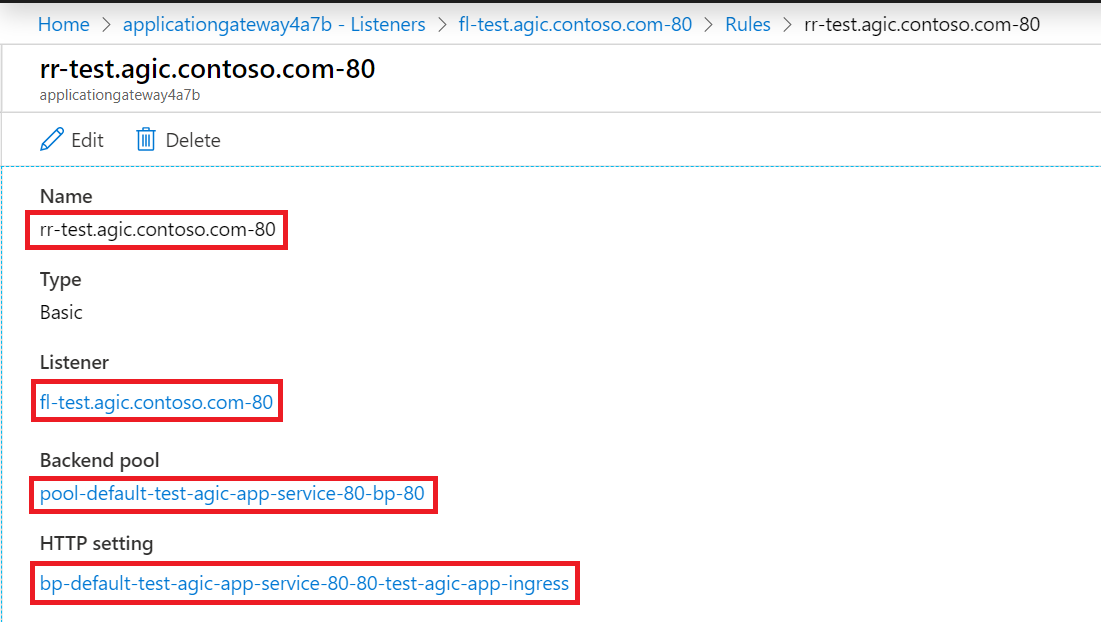
Application Gateway has the following configuration applied:
Listener:
Routing Rule:
Backend Pool:
- There's one IP address in the backend address pool and it matches the IP address of the Pod we observed earlier with
kubectl get pods -o wide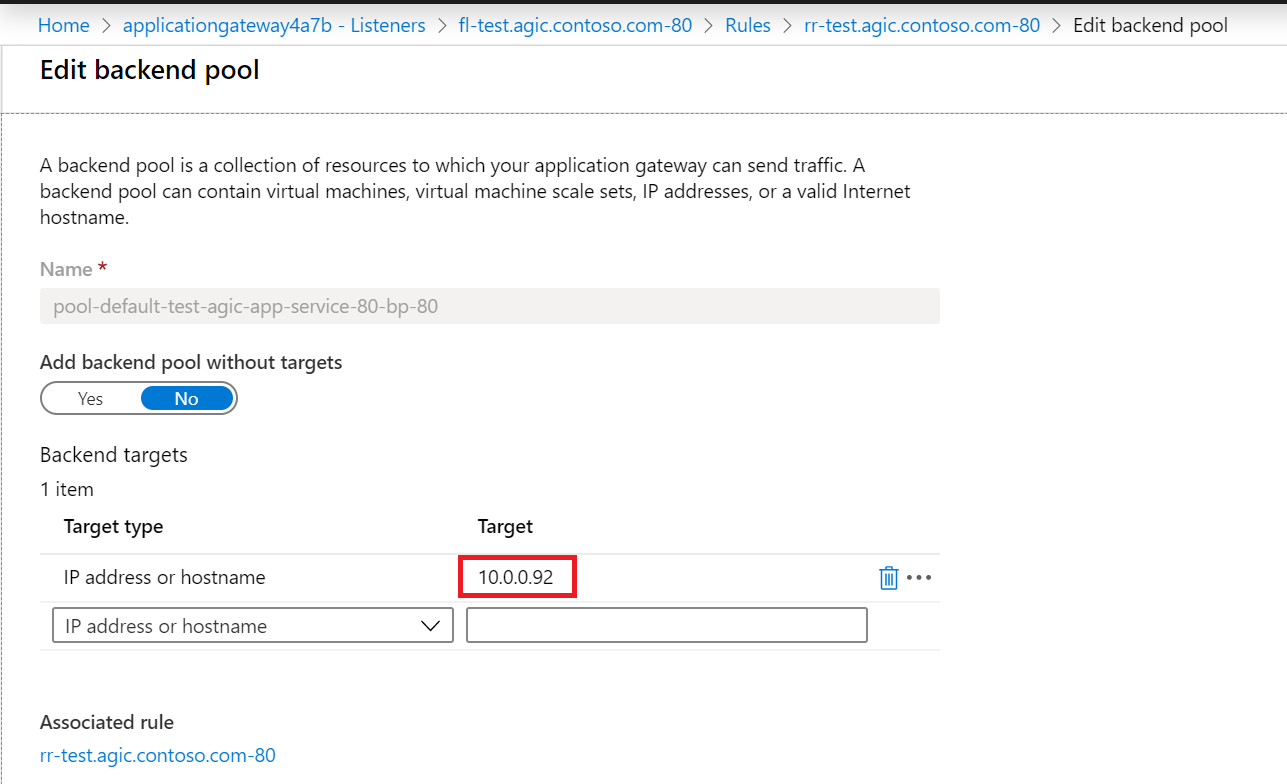
- There's one IP address in the backend address pool and it matches the IP address of the Pod we observed earlier with
Finally we can use the cURL command to establish an HTTP connection to the newly deployed app:
- Use
kubectl get ingressto get the Public IP address of Application Gateway - Use
curl -I -H 'test.agic.contoso.com' <public-ip-address-from-previous-command>
A result of HTTP/1.1 200 OK indicates that the Application Gateway + AKS + AGIC system is working as expected.
Inspect Kubernetes Installation
Pods, Services, Ingress
Application Gateway Ingress Controller (AGIC) continuously monitors the following Kubernetes resources: Deployment or Pod, Service, Ingress
The following conditions must be in place for AGIC to function as expected:
AKS must have one or more healthy pods. Verify this configuration with
kubectl get pods -o wide --show-labelsIf you have a Pod with anapsnetapp, your output may look like this:delyan@Azure:~$ kubectl get pods -o wide --show-labels NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES LABELS aspnetapp 1/1 Running 0 17h 10.0.0.6 aks-agentpool-35064155-1 <none> <none> app=aspnetappOne or more services, referencing these pods via matching
selectorlabels. Verify this configuration withkubectl get services -o widedelyan@Azure:~$ kubectl get services -o wide --show-labels NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR LABELS aspnetapp ClusterIP 10.2.63.254 <none> 80/TCP 17h app=aspnetapp <none>Ingress, annotated with
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway, referencing the previous service. Verify this configuration withkubectl get ingress -o wide --show-labelsdelyan@Azure:~$ kubectl get ingress -o wide --show-labels NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE LABELS aspnetapp * 80 17h <none>View annotations of the previous ingress:
kubectl get ingress aspnetapp -o yaml(substituteaspnetappwith the name of your ingress)delyan@Azure:~$ kubectl get ingress aspnetapp -o yaml apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway name: aspnetapp spec: backend: serviceName: aspnetapp servicePort: 80The ingress resource must be annotated with
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway.
Verify Observed Namespace
Get the existing namespaces in Kubernetes cluster. What namespace is your app running in? Is AGIC watching that namespace? Refer to the Multiple Namespace Support documentation on how to properly configure observed namespaces.
# What namespaces exist on your cluster kubectl get namespaces # What pods are currently running kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -o wideThe AGIC pod should be in the
defaultnamespace (see columnNAMESPACE). A healthy pod would haveRunningin theSTATUScolumn. There should be at least one AGIC pod.# Get a list of the Application Gateway Ingress Controller pods kubectl get pods --all-namespaces --selector app=ingress-azureIf the AGIC pod isn't healthy (
STATUScolumn from the previous command isn'tRunning), then:- get logs to understand why:
kubectl logs <pod-name> - get logs for the previous instance of the pod:
kubectl logs <pod-name> --previous - describe the pod to get more context:
kubectl describe pod <pod-name>
- get logs to understand why:
Do you have a Kubernetes Service and Ingress resources?
# Get all services across all namespaces kubectl get service --all-namespaces -o wide # Get all ingress resources across all namespaces kubectl get ingress --all-namespaces -o wideIs your Ingress annotated with:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway? AGIC only watches for Kubernetes Ingress resources that have this annotation.# Get the YAML definition of a particular ingress resource kubectl get ingress --namespace <which-namespace?> <which-ingress?> -o yamlAGIC emits Kubernetes events for certain critical errors. You can view these events:
- in your terminal via
kubectl get events --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp - in your browser using the Kubernetes Web UI (Dashboard)
- in your terminal via
Logging Levels
AGIC has three logging levels. Level 1 is the default one and it shows minimal number of log lines. Level 5, on the other hand, would display all logs, including sanitized contents of config applied to ARM.
The Kubernetes community has established nine levels of logging for the kubectl tool. In this repository, we're utilizing three of these levels, with similar semantics:
| Verbosity | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Default log level; shows startup details, warnings and errors |
| 3 | Extended information about events and changes; lists of created objects |
| 5 | Logs marshaled objects; shows sanitized JSON config applied to ARM |
The verbosity levels are adjustable via the verbosityLevel variable in the
helm-config.yaml file. Increase verbosity level to 5 to get
the JSON config dispatched to
ARM:
- add
verbosityLevel: 5on a line by itself in helm-config.yaml and reinstall - get logs with
kubectl logs <pod-name>
Sample Helm config file
# This file contains the essential configs for the ingress controller helm chart
# Verbosity level of the App Gateway Ingress Controller
verbosityLevel: 3
################################################################################
# Specify which application gateway the ingress controller manages
#
appgw:
subscriptionId: <subscriptionId>
resourceGroup: <resourceGroupName>
name: <applicationGatewayName>
# Setting appgw.shared to "true" creates an AzureIngressProhibitedTarget CRD.
# This prohibits AGIC from applying config for any host/path.
# Use "kubectl get AzureIngressProhibitedTargets" to view and change this.
shared: false
################################################################################
# Specify which kubernetes namespace the ingress controller watches
# Default value is "default"
# Leaving this variable out or setting it to blank or empty string would
# result in Ingress Controller observing all accessible namespaces.
#
# kubernetes:
# watchNamespace: <namespace>
################################################################################
# Specify the authentication with Azure Resource Manager
#
# Two authentication methods are available:
# - Option 1: AAD-Pod-Identity (https://github.com/Azure/aad-pod-identity)
armAuth:
type: aadPodIdentity
identityResourceID: <identityResourceId>
identityClientID: <identityClientId>
## Alternatively you can use Service Principal credentials
# armAuth:
# type: servicePrincipal
# secretJSON: <<Generate this value with: "az ad sp create-for-rbac --subscription <subscription-uuid> --role Contributor --sdk-auth | base64 -w0" >>
################################################################################
# Specify if the cluster is Kubernetes RBAC enabled or not
rbac:
enabled: false # true/false
# Specify aks cluster related information. THIS IS BEING DEPRECATED.
aksClusterConfiguration:
apiServerAddress: <aks-api-server-address>
Review Application Gateway Activity Log
When troubleshooting Application Gateway Ingress Controller issues, it's good practice to check the Application Gateway's Activity Log in addition to Kubernetes resources. Every time AGIC applies a new configuration, a corresponding entry is recorded in the Activity Log in the Azure portal. Reviewing these entries helps to confirm whether configuration updates were successfully applied and can often reveal gateway-related issues that aren't visible from the Kubernetes side.