Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to use the Azure portal to configure an Azure Application Gateway v2 SKU instance to perform parameter-based path selection by combining the capabilities of URL Rewrite with path-based routing.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a Trial before you begin.
Before you begin
You need to have an Application Gateway v2 SKU instance to finish the steps in this article. URL Rewrite and rewriting headers aren't supported in the v1 SKU. If you don't have the v2 SKU, create an Application Gateway v2 SKU instance before you begin.
Sign in to Azure
Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure account.
Configure parameter-based path selection
For this example, you have a shopping website. The product category is passed as a query string in the URL. To route the request to the backend based on the query string, follow these steps.
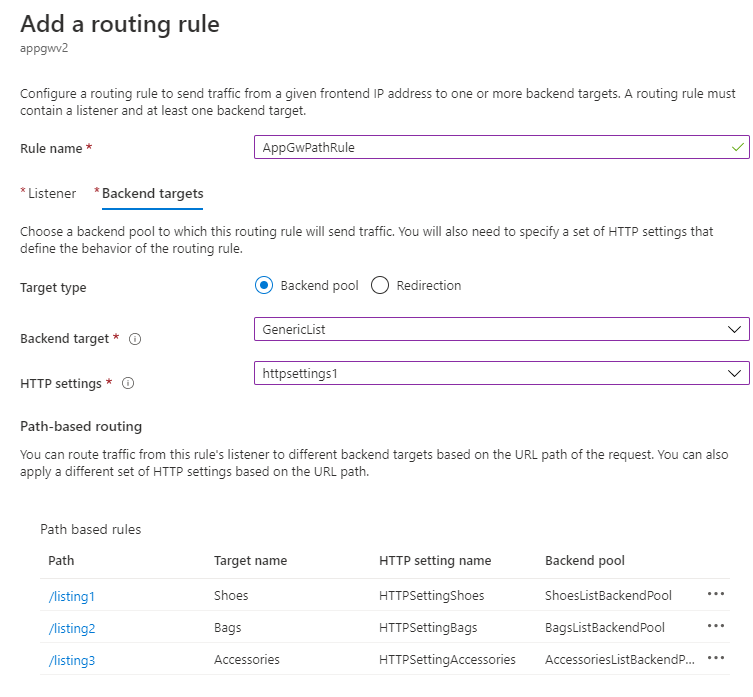
Create a path map.
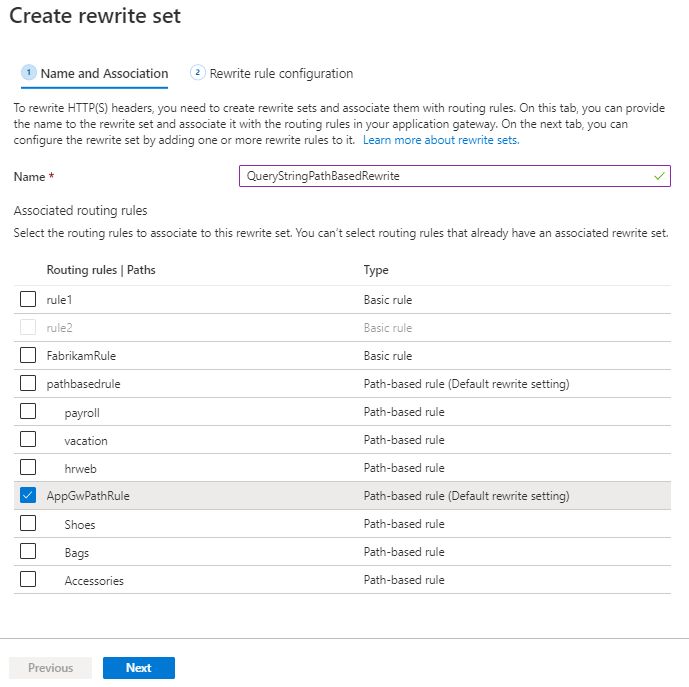
Create a rewrite set that has three rewrite rules:
The first rule has a condition that checks the
query_stringvariable forcategory=shoes. An action rewrites the URL path to/listing1. Reevaluate path map is enabled.The second rule has a condition that checks the
query_stringvariable forcategory=bags. An action rewrites the URL path to/listing2. Reevaluate path map is enabled.The third rule has a condition that checks the
query_stringvariable forcategory=accessories. An action rewrites the URL path to/listing3. Reevaluate path map is enabled.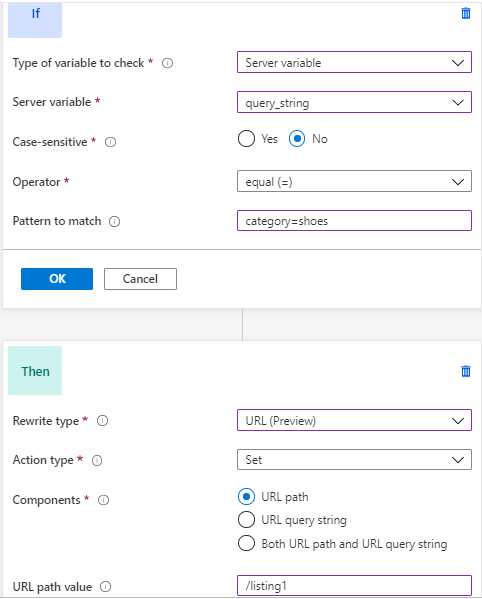
Associate this rewrite set with the default path of the previous path-based rule.
If the user requests contoso.com/listing?category=any, it's matched with the default path because the path patterns in the path map (/listing1, /listing2, /listing3) don't match. Because you associated the previous rewrite set with this path, this rewrite set is evaluated. The query string doesn't match the condition in any of the three rewrite rules in this rewrite set, so no rewrite action takes place. The request is routed unchanged to the backend associated with the default path (which is GenericList).
If the user requests contoso.com/listing?category=shoes, the default path is matched. In this case, the condition in the first rule matches. The action associated with the condition is executed, which rewrites the URL path to /listing1 and reevaluates the path map. When the path map is reevaluated, the request matches the path associated with the pattern /listing1. The request is routed to the backend associated with this pattern (ShoesListBackendPool).
Note
You can extend this scenario to any header or cookie value, URL path, query string, or server variables based on the conditions defined. You can then route requests based on those conditions.
Related content
To learn more about how to set up some common use cases, see Common header rewrite scenarios.