Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
As an extension of the Azure location construct, the custom locations feature provides a way for tenant administrators to use their Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters as target locations for deploying Azure services instances.
Similar to Azure locations, end users within the tenant who have access to Custom Locations can deploy resources there using their company's private compute.

You can visualize custom locations as an abstraction layer on top of Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters, cluster connect, and cluster extensions. Custom locations create the granular RoleBindings and ClusterRoleBindings necessary for other Azure services to access the cluster. These other Azure services require cluster access to manage deployed resources.
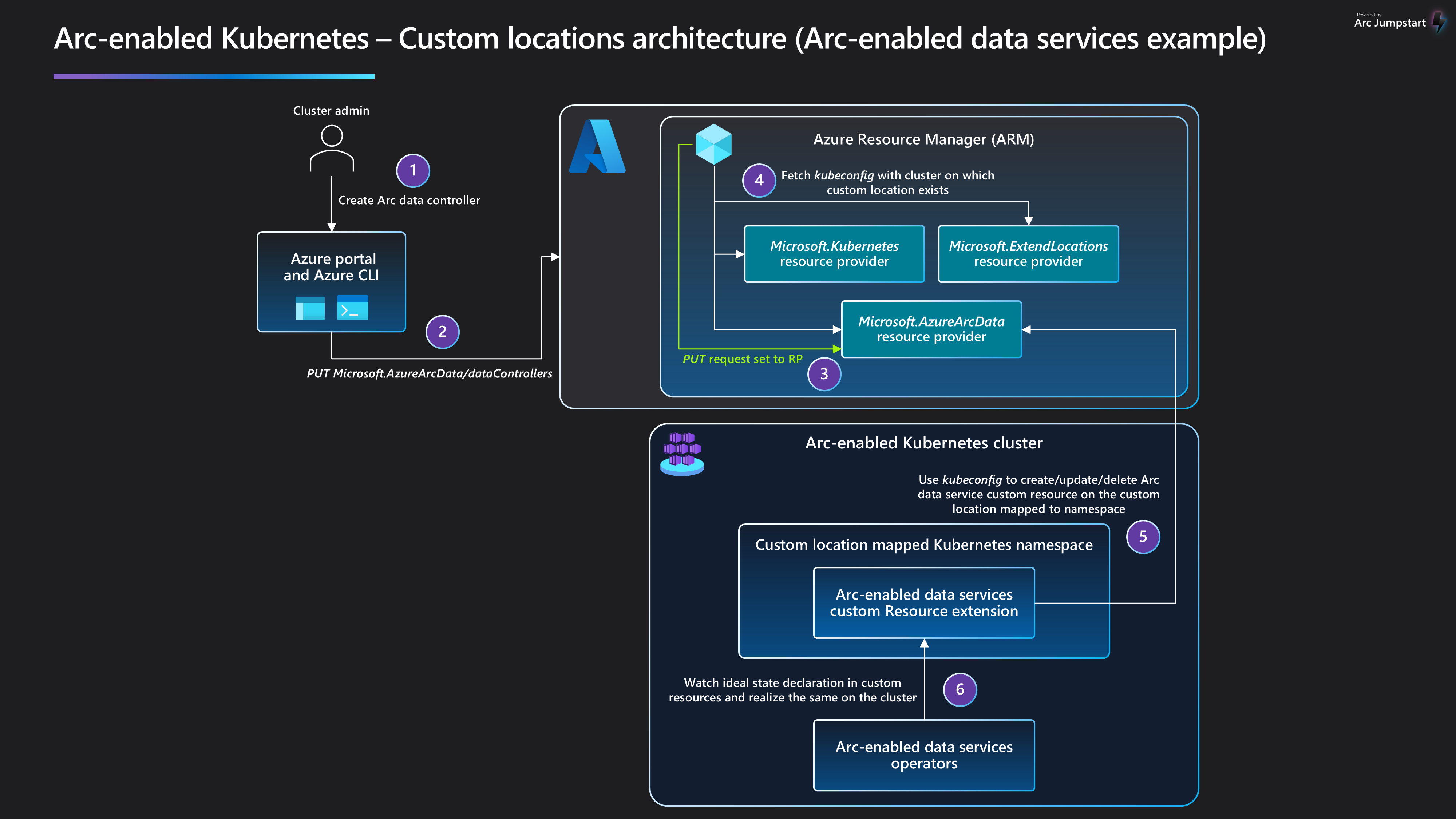
Architecture
When the admin enables the custom locations feature on the cluster, a ClusterRoleBinding is created on the cluster, authorizing the Microsoft Entra application used by the custom locations resource provider. Once authorized, the custom locations resource provider can create ClusterRoleBinding or RoleBinding objects that are needed by other Azure resource providers to create custom resources on this cluster. The cluster extensions installed on the cluster determine the list of resource providers to authorize.
Note
To download Arc diagrams in high resolution, visit Jumpstart Gems.
When the user creates a data service instance on the cluster:
The PUT request is sent to Azure Resource Manager.
The PUT request is forwarded to the Azure Arc-enabled data services resource provider.
The RP fetches the
kubeconfigfile associated with the Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster on which the custom location exists.- Custom location is referenced as
extendedLocationin the original PUT request.
- Custom location is referenced as
The Azure Arc-enabled data services resource provider uses the
kubeconfigto communicate with the cluster to create a custom resource of the Azure Arc-enabled data services type on the namespace mapped to the custom location.- The Azure Arc-enabled data services operator was deployed via cluster extension creation before the custom location existed.
The Azure Arc-enabled data services operator reads the new custom resource created on the cluster and creates the data controller, translating into realization of the desired state on the cluster.
Next steps
- Use our quickstart to connect a Kubernetes cluster to Azure Arc.
- Create a custom location on your Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster.