Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Durable Task Scheduler offers two pricing models to accommodate different workload requirements, usage patterns, and preferred billing models:
In this article, you learn about actions, the available SKU options, and their pricing structures.
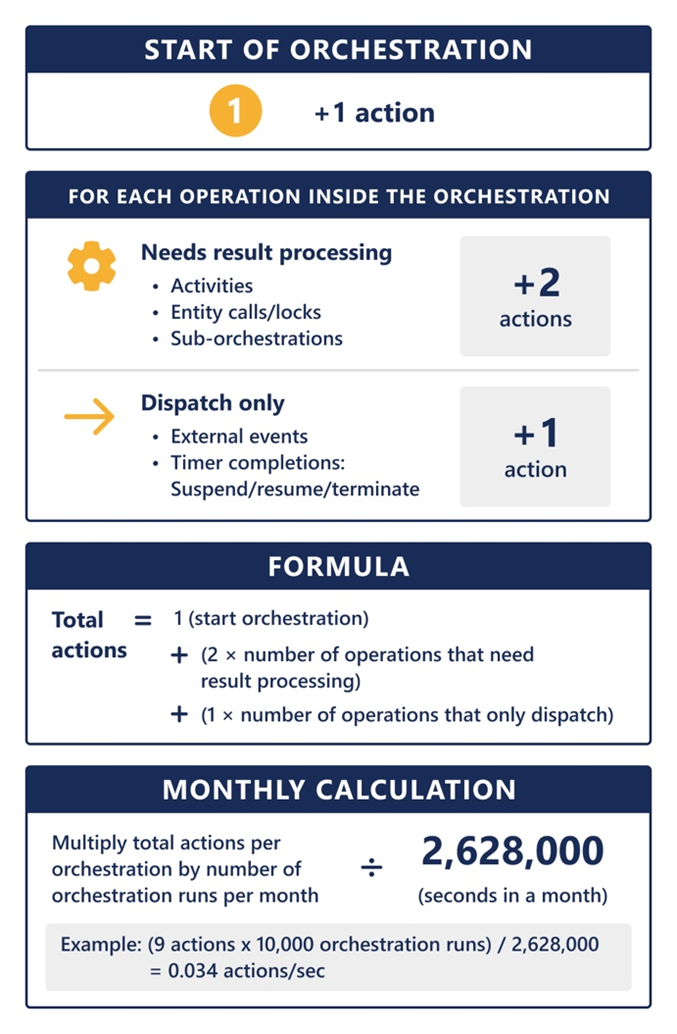
What is an action?
An action is a message dispatched by the Durable Task Scheduler to your application, triggering the execution of an orchestrator, activity, or entity functions. Functions triggered by an action include:
- Starting an orchestration or suborchestration
- Starting an activity
- Completing a timer
- Triggering an external event
- Executing an entity operation
- Suspending, resuming, or terminating an orchestration
- Processing the result of an activity, entity call, entity lock, or suborchestration
The following diagram explains how to calculate actions in your orchestration.
Example
Let's say you have an orchestration that calls three different activities.
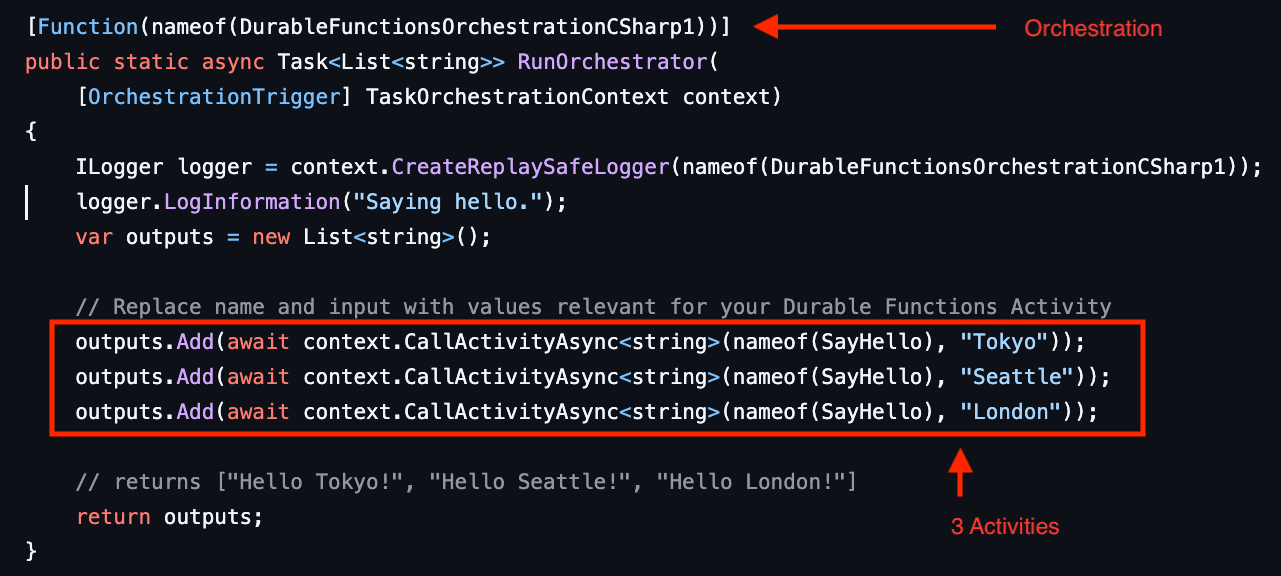
In this example, you can see how Durable Task Scheduler processes each action:
- Orchestrator start (
RunOrchestrator) uses one action - Activity 1 (
(nameof(SayHello), "Tokyo")) uses two actions:- Scheduling the activity
- Processing the result
- Activity 2 (
(nameof(SayHello), "Seattle")) uses two actions:- Scheduling the activity
- Processing the result
- Activity 3 (
(nameof(SayHello), "London")) uses two actions:- Scheduling the activity
- Processing the result
Available SKUs
Durable Task Scheduler offers two SKU options: Dedicated and Consumption (preview).
Dedicated SKU
The Dedicated SKU provides performance and pricing through preallocated Capacity Units (CUs). You can purchase up to three CUs.
Currently, you're limited to 25 task hubs when using the Dedicated SKU. For more quota, contact support.
Key features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Base cost | Fixed monthly cost per CU (regional pricing). Not "per action" billing. |
| Performance | Each CU supports up to 2,000 actions per second and 50GB of orchestration data storage |
| Orchestration data retention | Up to 90 days |
| Custom scaling | Configure CUs to match your workload needs. 1 CU required per deployment. |
| High availability | High availability with multi-CU deployments. A minimum of 3 CUs is required. |
Calculating Capacity Units for the Dedicated SKU
Example 1
You have an orchestration with 5 activities, plus error handling, and averaging 12 actions per orchestration (orchestrator and activity invocations). Let's calculate running 20 million orchestrations per month.
| Activity | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly actions | 20,000,000 × 12 | 240,000,000 actions |
| Actions per second | 240,000,000 ÷ 2,628,000 (seconds in a month) | ≈ 91 actions/second |
| Required CUs | 91 ÷ 2,000 | 240,000,000 actions CUs needed: 0.046 → 1 CU sufficient |
Example 2
A large enterprise runs 500 million complex orchestrations monthly, with an average of 15 actions per orchestration (multiple activities with orchestrator coordination).
| Activity | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly actions | 500 million × 13 | 6.5 billion actions |
| Actions per second | 6.5 billion ÷ 2,628,000 | ≈ 2,473 actions/second |
| Required CUs | 2,473 ÷ 2,000 | 240,000,000 actions CUs needed: 1.23 → 2 CUs sufficient |
Example 3
A Software as a Service (SaaS) platform supports 800 million orchestrations monthly, each with an average of 15 actions (user interactions, background processing, and external API calls).
| Activity | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly actions | 800 million × 15 | 12 billion actions |
| Actions per second | 12 billion ÷ 2,628,000 | ≈ 4,571 actions/second |
| Required CUs | 4,571 ÷ 2,000 | 240,000,000 actions CUs needed: 2.29 → 3 CUs sufficient |
Consumption SKU (preview)
Note
The Consumption SKU is currently in preview. Learn more about the SKU and orchestration framework recommended for production use.
The Consumption SKU offers a pay-as-you-use model, ideal for variable workloads and development scenarios.
Currently, you're limited to 5 task hubs when using the Consumption SKU. For more quota, contact support.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Pay-Per-Use | Only pay for actions dispatched. No upfront costs, minimum commitments, or base fees |
| Performance | Up to 500 actions per second. |
| Data retention | 30-day maximum retention |
Example 1
A development team is testing simple orchestrations, each with three actions (using the "Hello City" pattern), and runs 10,000 orchestrations per month.
| Activity | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly actions | 10,000 × 3 | 30,000 actions |
| Cost | 30,000 × $0.003 | $90/month |
Example 2
An e-commerce application experiences dynamic workload scaling during promotional sales events, especially on weekends. It uses an orchestration comprising seven total actions, which executes approximately 20,000 times per month.
| Activity | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly actions | 20,000 × 7 | 140,000 actions |
| Cost | 140,000 × $0.003 | $420/month |