Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The upstream endpoints feature allows Azure SignalR Service to send messages and connection events to a set of endpoints in serverless mode. You can use upstream endpoints to invoke a hub method from clients in serverless mode to notify endpoints when client connections are connected or disconnected.
Note
Upstream endpoints can only be configured in serverless mode.
Upstream endpoint settings
An upstream endpoint's settings consist of a list of order-sensitive items:
- A URL template, which specifies where messages send to.
- A set of rules.
- Authentication configurations.
When an event is fired, an item's rules are checked one by one in order. Messages will be sent to the first matching item's upstream endpoint URL.
URL template settings
You can parameterize the upstream endpoint URL to support various patterns. There are three predefined parameters:
| Predefined parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| {hub} | A hub is a concept of Azure SignalR Service. A hub is a unit of isolation. The scope of users and message delivery is constrained to a hub. |
| {category} | A category can be one of the following values:
|
| {event} | For the messages category, an event is the target in an invocation message that clients send. For the connections category, only connected and disconnected are used. |
These predefined parameters can be used in the URL pattern. Parameters will be replaced with a specified value when you're evaluating the upstream endpoint URL. For example:
http://host.com/{hub}/api/{category}/{event}
When a client connection in the "chat" hub is connected, a message will be sent to this URL:
http://host.com/chat/api/connections/connected
When a client in the "chat" hub invokes the hub method broadcast, a message will be sent to this URL:
http://host.com/chat/api/messages/broadcast
Key Vault secret reference in URL template settings
The upstream endpoint URL isn't encrypted. You can secure sensitive upstream endpoints using Key Vault and access them with a managed identity.
To enable managed identity in your SignalR service instance and grant it Key Vault access:
Add a system-assigned identity or user-assigned identity. See How to add managed identity in Azure portal.
Grant secret read permission for the managed identity in the Access policies in the Key Vault. See Assign a Key Vault access policy using the Azure portal
Replace your sensitive text with the below syntax in the upstream endpoint URL Pattern:
{@Microsoft.KeyVault(SecretUri=<secret-identity>)}<secret-identity>is the full data-plane URI of a secret in Key Vault, optionally including a version, e.g.,https://myvault.vault.azure.cn/secrets/mysecret/orhttps://myvault.vault.azure.cn/secrets/mysecret/ec96f02080254f109c51a1f14cdb1931For example, a complete reference would look like the following:
{@Microsoft.KeyVault(SecretUri=https://myvault.vault.azure.cn/secrets/mysecret/)}An upstream endpoint URL to Azure Function would look like the following:
https://contoso.chinacloudsites.cn/runtime/webhooks/signalr?code={@Microsoft.KeyVault(SecretUri=https://myvault.vault.azure.cn/secrets/mysecret/)}
Note
Every 30 minutes, or whenever the upstream endpoint settings or managed identity change, the service rereads the secret content. You can immediately trigger an update by changing the upstream endpoint settings.
Rule settings
You can set hub rules, category rules, and event rules separately. The matching rule supports three formats:
- Use an asterisk (*) to match any event.
- Use a comma (,) to join multiple events. For example,
connected, disconnectedmatches the connected and disconnected events. - Use the full event name to match the event. For example,
connectedmatches the connected event.
Note
If you're using Azure Functions with SignalR trigger, SignalR trigger will expose a single endpoint in the following format: <Function_App_URL>/runtime/webhooks/signalr?code=<API_KEY>.
You can just configure URL template settings to this url and keep Rule settings default. See SignalR Service integration for details about how to find <Function_App_URL> and <API_KEY>.
Authentication settings
You can configure authentication for each upstream endpoint setting separately. When you configure authentication, a token is set in the Authentication header of the upstream message. Currently, Azure SignalR Service supports the following authentication types:
NoneManagedIdentity
When you select ManagedIdentity, you must first enable a managed identity in Azure SignalR Service and optionally, specify a resource. See Managed identities for Azure SignalR Service for details.
Configure upstream endpoint settings via the Azure portal
Note
Integration with App Service Environment is currently not supported.
- Go to Azure SignalR Service.
- Select Settings.
- Switch Service Mode to Serverless.
- Add URLs under Upstream URL Pattern.
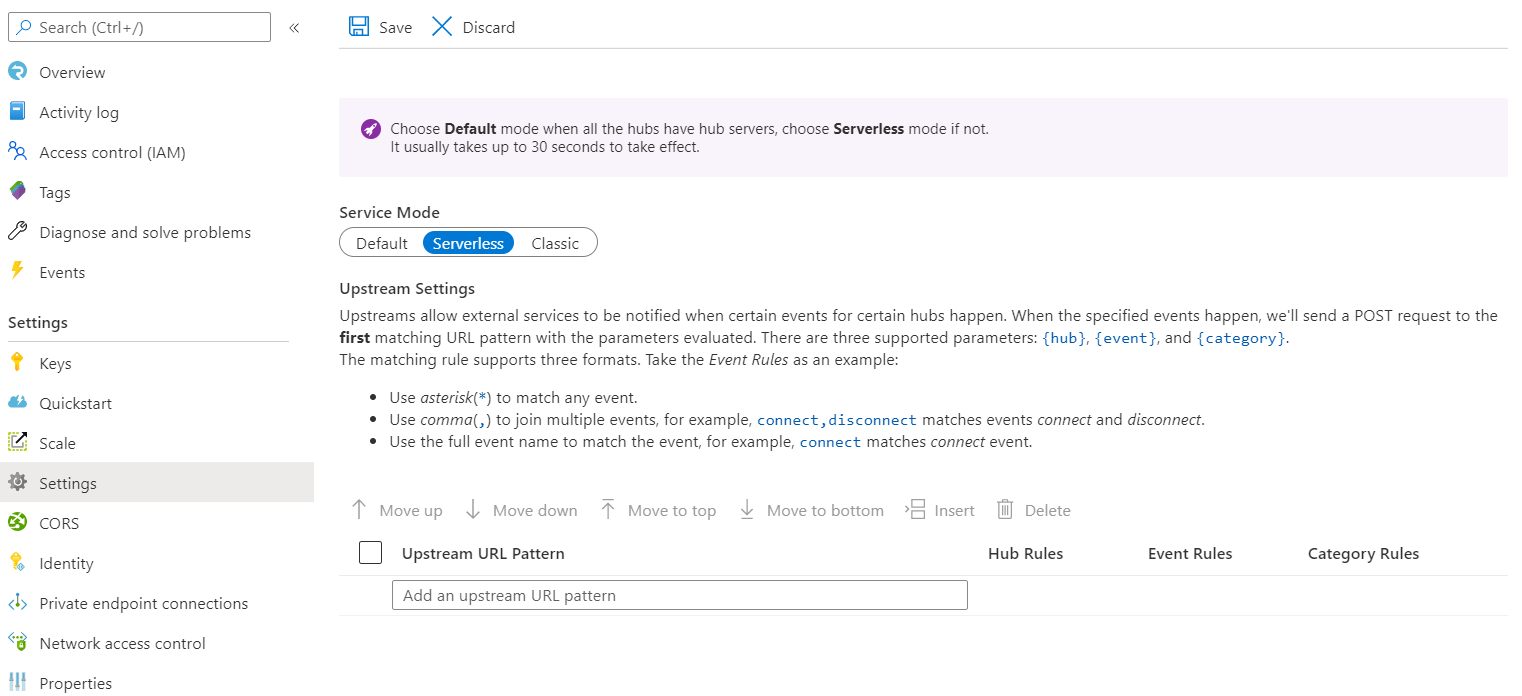
- Select Hub Rules to open Upstream Settings.
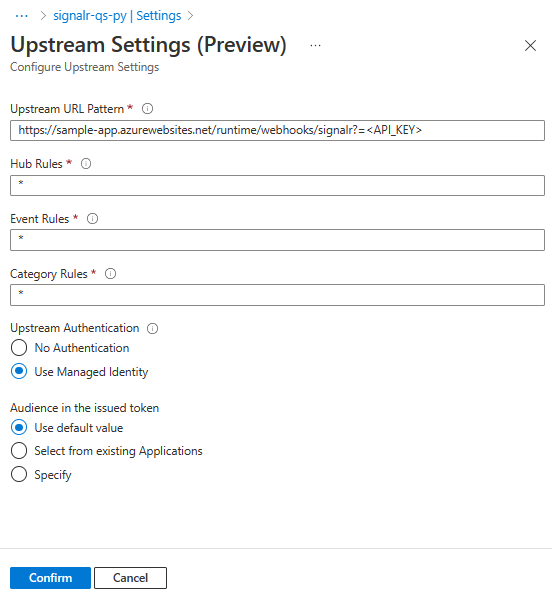
- Change Hub Rules, Event Rules and Category Rules by entering rule value in the corresponding field.
- Under Upstream Authentication select
- Use Managed Identity. (Ensure that you've enabled managed identity)
- Choose any options under Audience in the issued token. See Managed identities for Azure SignalR Service for details.
Configure upstream endpoint settings via Resource Manager template
To configure upstream endpoint settings by using an Azure Resource Manager template, set the upstream property in the properties property. The following snippet shows how to set the upstream property for creating and updating upstream endpoint settings.
{
"properties": {
"upstream": {
"templates": [
{
"UrlTemplate": "http://host.com/{hub}/api/{category}/{event}",
"EventPattern": "*",
"HubPattern": "*",
"CategoryPattern": "*",
"Auth": {
"Type": "ManagedIdentity",
"ManagedIdentity": {
"Resource": "<resource>"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
Serverless protocols
Azure SignalR Service sends messages to endpoints that follow the following protocols. You can use SignalR Service trigger binding with Function App, which handles these protocols for you.
Method
POST
Request header
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| X-ASRS-Connection-Id | The connection ID for the client connection. |
| X-ASRS-Hub | The hub that the client connection belongs to. |
| X-ASRS-Category | The category that the message belongs to. |
| X-ASRS-Event | The event that the message belongs to. |
| X-ASRS-Signature | A hash-based message authentication code (HMAC) that's used for validation. See Signature for details. |
| X-ASRS-User-Claims | A group of claims of the client connection. |
| X-ASRS-User-Id | The user identity of the client that sends the message. |
| X-ASRS-Client-Query | The query of the request when clients connect to the service. |
| Authentication | An optional token when you're using ManagedIdentity. |
Request body
Connected
Content-Type: application/json
Disconnected
Content-Type: application/json
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Error | string | The error message of a closed connection. Empty when connections close with no error. |
Invocation message
Content-Type: application/json or application/x-msgpack
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| InvocationId | string | An optional string that represents an invocation message. Find details in Invocations. |
| Target | string | The same as the event and the same as the target in an invocation message. |
| Arguments | Array of object | An array that contains arguments to apply to the method referred to in Target. |
Signature
The service will calculate SHA256 code for the X-ASRS-Connection-Id value by using both the primary access key and the secondary access key as the HMAC key. The service will set it in the X-ASRS-Signature header when making HTTP requests to an upstream endpoint:
Hex_encoded(HMAC_SHA256(accessKey, connection-id))