Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
You can connect Excel to a database and then import data and create tables and charts based on values in the database. In this tutorial you will set up the connection between Excel and a database table, save the file that stores data and the connection information for Excel, and then create a pivot chart from the database values.
You'll need to create a database before you get started. If you don't have one:
- You can create a database in Azure SQL Database and Create server-level IP firewall to get a database with sample data up and running in a few minutes.
- You can also try Azure SQL Managed Instance.
In this article, you'll import sample data into Excel from that article, but you can follow similar steps with your own data.
You'll also need a copy of Excel. This article uses Microsoft Excel 2016.
Connect Excel and load data
To connect Excel to a database in SQL Database, open Excel and then create a new workbook or open an existing Excel workbook.
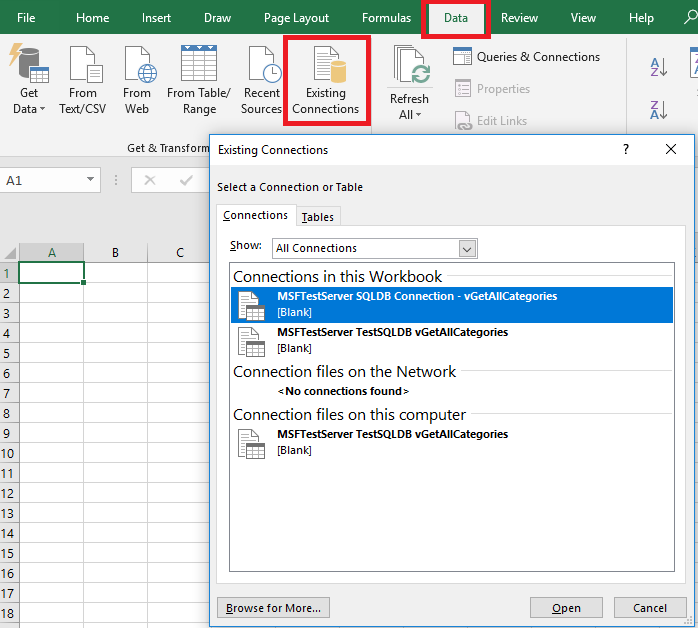
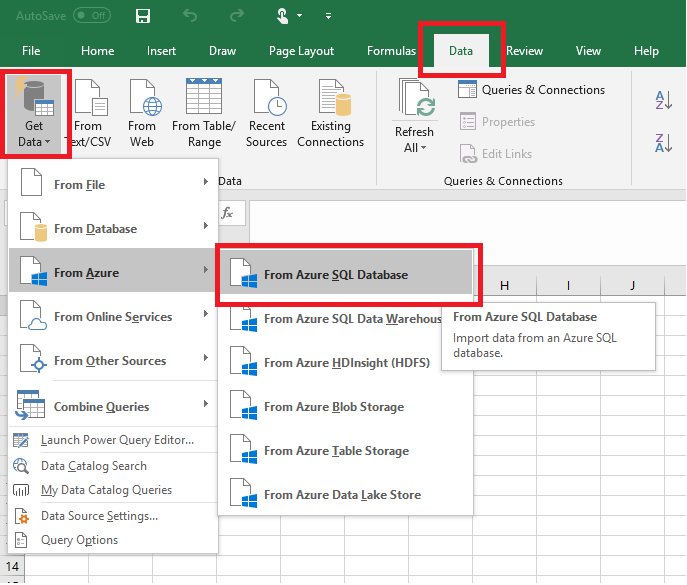
In the menu bar at the top of the page, select the Data tab, select Get Data, select From Azure, and then select From Azure SQL Database.
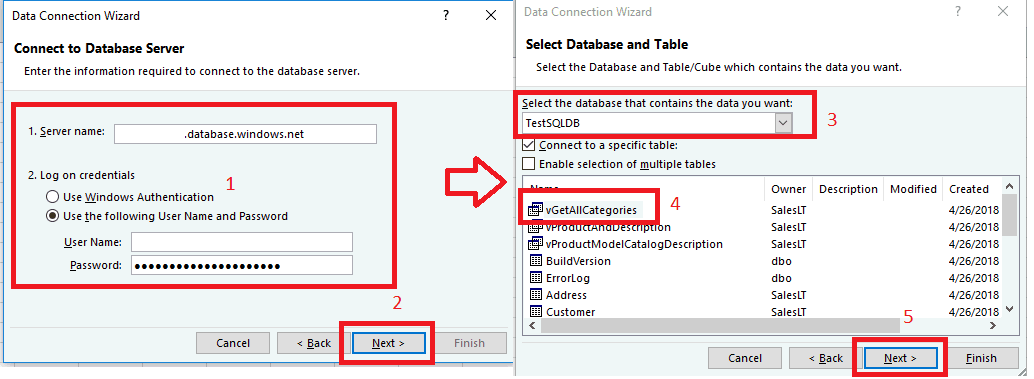
In the SQL Server database dialog box, type the Server name you want to connect to.
- In Azure SQL Database, this looks like:
<servername>.database.chinacloudapi.cn. - In Azure SQL Managed Instance, this looks like:
<your-instance-name>.<unique-dns-prefix>.database.chinacloudapi.cn.
- In Azure SQL Database, this looks like:
Optionally, enter in the name of your database. Select OK to open the credentials window.
In the SQL Server database dialog box, select Database on the left side, and then enter in your User Name and Password for the server you want to connect to. Select Connect to open the Navigator.
Tip
Depending on your network environment, you might not be able to connect if the server doesn't allow traffic from your client IP address. Go to the Azure portal, select SQL servers, select your server, select firewall under settings and add your client IP address. For more information, see IP firewall rules.
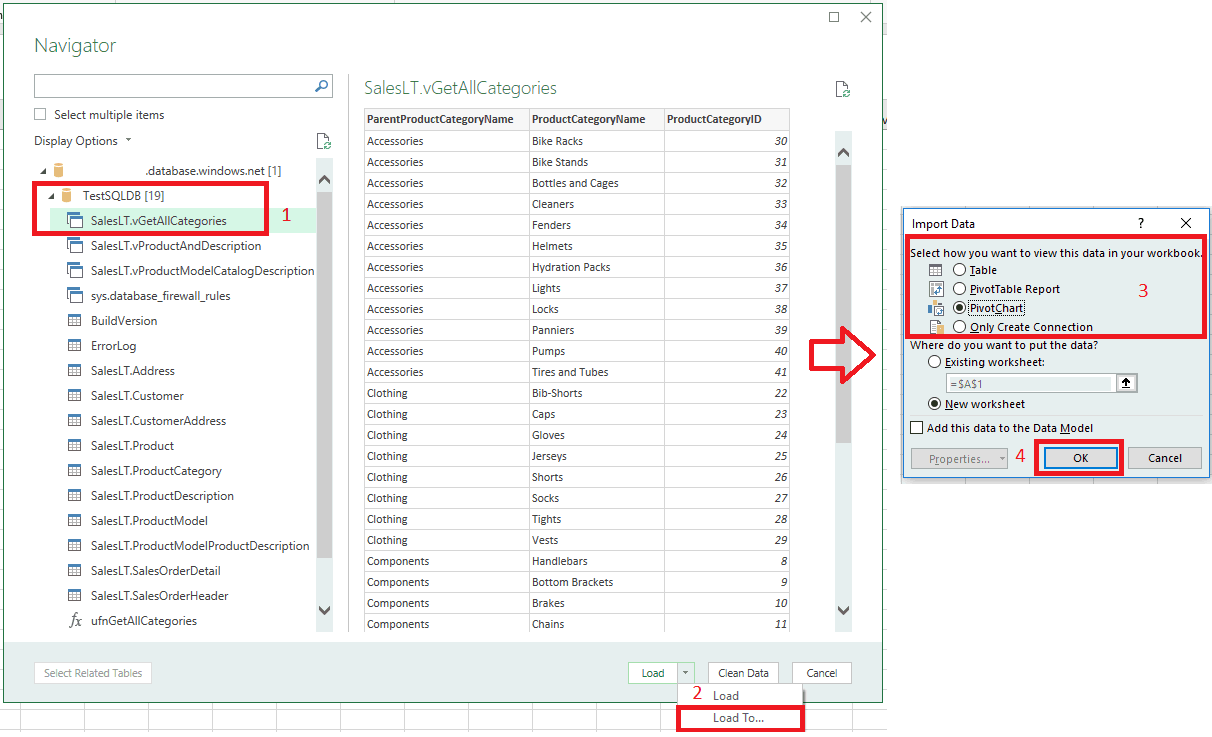
In the Navigator, select the database you want to work with from the list, select the tables or views you want to work with (we chose
vGetAllCategories), and then select Load to move the data from your database to your Excel spreadsheet.
Import the data into Excel and create a pivot chart
Now that you've established the connection, you have several different options with how to load the data. For example, the following steps create a pivot chart based on the data found in your database in SQL Database.
Follow the steps in the previous section, but this time, instead of selecting Load, select Load to from the Load dropdown list.
Next, select how you want to view this data in your workbook. We chose PivotChart. You can also choose to create a New worksheet or to Add this data to a Data Model. For more information on Data Models, see Create a data model in Excel.
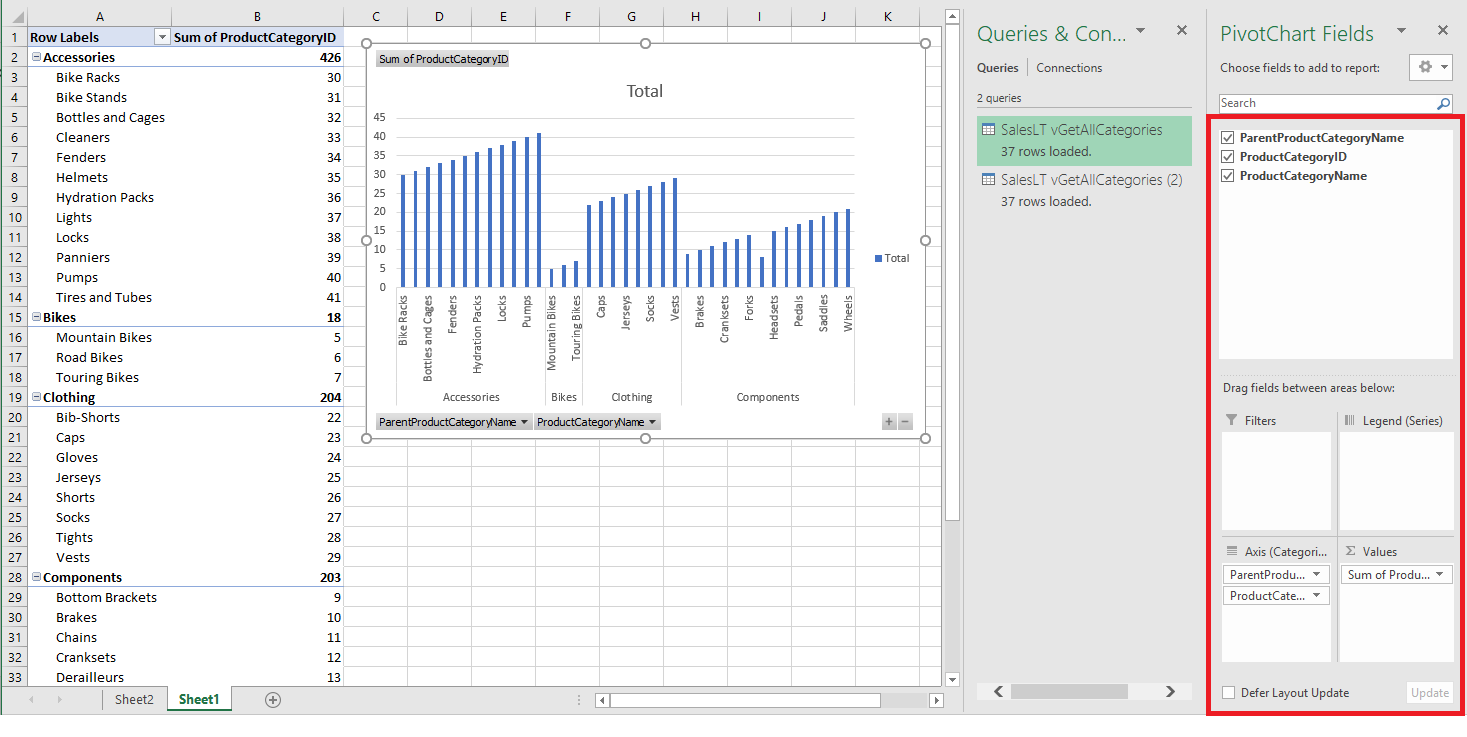
The worksheet now has an empty pivot table and chart.
Under PivotTable Fields, select all the check-boxes for the fields you want to view.
Tip
If you want to connect other Excel workbooks and worksheets to the database, select the Data tab, and select Recent Sources to launch the Recent Sources dialog box. From there, choose the connection you created from the list, and then select Open.
Create a permanent connection using .odc file
To save the connection details permanently, you can create an .odc file and make this connection a selectable option within the Existing Connections dialog box.
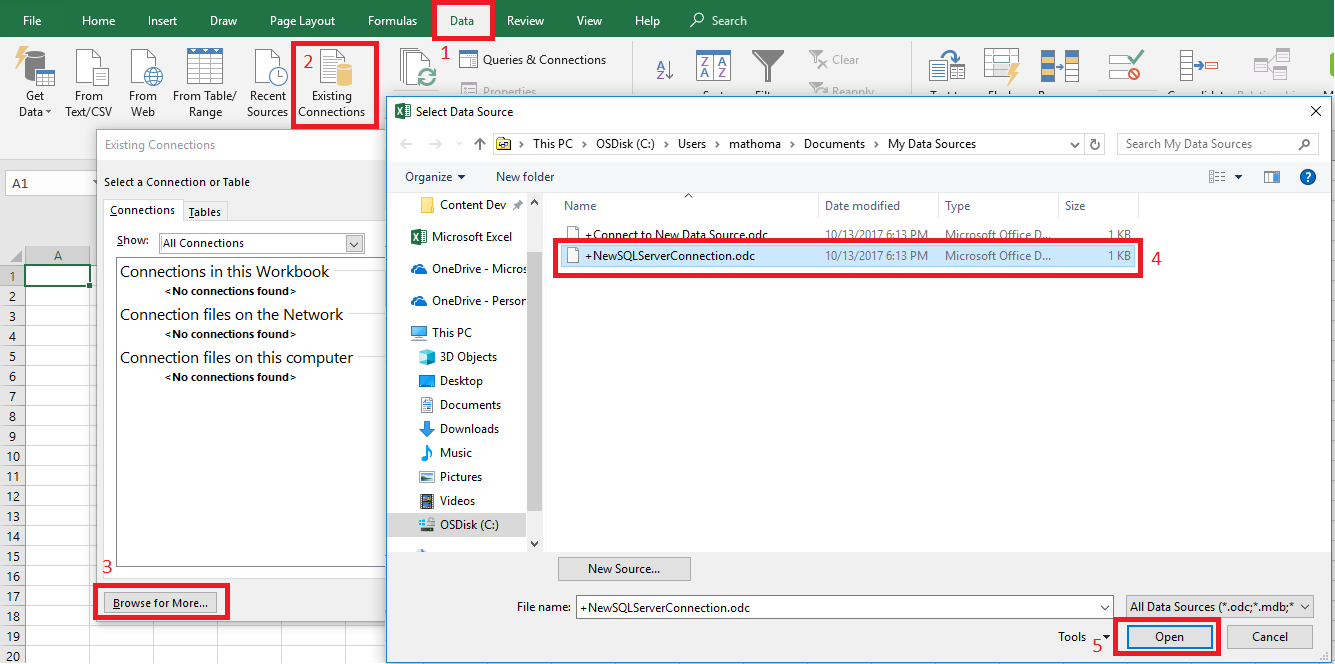
In the menu bar at the top of the page, select the Data tab, and then select Existing Connections to launch the Existing Connections dialog box.
In the Data Connection Wizard, type in your server name and your SQL Database credentials. Select Next.
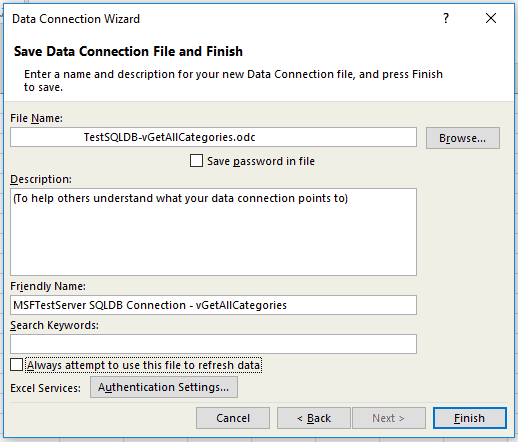
Select the location of your file, the File Name, and the Friendly Name in the next screen of the Data Connection Wizard. You can also choose to save the connection string password in the file, though this can potentially expose your data to unwanted access. Select Finish when ready.
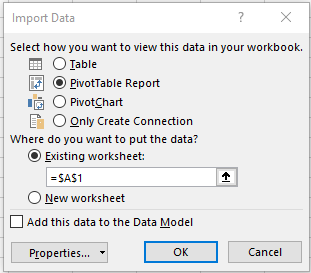
Select how you want to import your data. We chose to do a PivotTable. You can also modify the properties of the connection by selecting Properties. Select OK when ready. If you did not choose to save the password with the file, then you will be prompted to enter your credentials.
Verify that your new connection has been saved by expanding the Data tab, and selecting Existing Connections.