Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
To run Get-AzureStackLog on an integrated system, you need to have access to the privileged endpoint (PEP). Here's an example script you can run using the PEP to collect logs. If you are canceling a running log collection to start a new one, please wait 5 minutes Before starting new log collection and enter Remove-PSSession -Session $session.
$ipAddress = "<IP ADDRESS OF THE PEP VM>" # You can also use the machine name instead of IP here.
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString "<CLOUD ADMIN PASSWORD>" -AsPlainText -Force
$cred = New-Object -TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("<DOMAIN NAME>\CloudAdmin", $password)
$shareCred = Get-Credential
$session = New-PSSession -ComputerName $ipAddress -ConfigurationName PrivilegedEndpoint -Credential $cred -SessionOption (New-PSSessionOption -Culture en-US -UICulture en-US)
$fromDate = (Get-Date).AddHours(-8)
$toDate = (Get-Date).AddHours(-2) # Provide the time that includes the period for your issue
Invoke-Command -Session $session { Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSharePath "<EXTERNAL SHARE ADDRESS>" -OutputShareCredential $using:shareCred -FilterByRole Storage -FromDate $using:fromDate -ToDate $using:toDate}
if ($session) {
Remove-PSSession -Session $session
}
Examples
Collect all logs for all roles:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSharePath "<path>" -OutputShareCredential $credCollect logs from VirtualMachines and BareMetal roles:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSharePath "<path>" -OutputShareCredential $cred -FilterByRole VirtualMachines,BareMetalCollect logs from VirtualMachines and BareMetal roles, with date filtering for log files for the past 8 hours:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSharePath "<path>" -OutputShareCredential $cred -FilterByRole VirtualMachines,BareMetal -FromDate (Get-Date).AddHours(-8)Collect logs from VirtualMachines and BareMetal roles, with date filtering for log files for the time period between 8 hours ago and 2 hours ago:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSharePath "<path>" -OutputShareCredential $cred -FilterByRole VirtualMachines,BareMetal -FromDate (Get-Date).AddHours(-8) -ToDate (Get-Date).AddHours(-2)Collect logs from tenant deployments running self-managed Kubernetes clusters (AKS engine) on Azure Stack. Kubernetes logs should be stored in a tenant storage account in a format that will enable the collection time range to be applied to them as well.
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputPath <Path> -InputSasUri "<Blob Service Sas URI>" -FromDate "<Beginning of the time range>" -ToDate "<End of the time range>"For example:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputPath C:\KubernetesLogs -InputSasUri "https://<storageAccountName>.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<ContainerName><SAS token>" -FromDate (Get-Date).AddHours(-8) -ToDate (Get-Date).AddHours(-2)Collect logs for the value-add RPs. The general syntax is:
Get-AzureStackLog -FilterByResourceProvider <<value-add RP name>>To collect logs for SQL RP:
Get-AzureStackLog -FilterByResourceProvider SQLAdapterTo collect logs for MySQL RP:
Get-AzureStackLog -FilterByResourceProvider MySQLAdapterTo collect logs for Event Hubs:
Get-AzureStackLog -FilterByResourceProvider eventhubCollect logs and store them in the specified Azure Storage blob container. The general syntax for this operation is as follows:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSasUri "<Blob service SAS Uri>"For example:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSasUri "https://<storageAccountName>.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<ContainerName><SAS token>"Note
This procedure is useful for uploading logs. Even if you don't have an SMB share accessible or internet access, you can create a blob storage account on your Azure Stack Hub to transfer the logs, and then use your client to retrieve those logs.
To generate the SAS token for the storage account, the following permissions are required:
- Access to the Blob Storage service.
- Access to the container resource type.
To generate a SAS Uri value to be used for the
-OutputSasUriparameter, follow these steps:- Create a storage account, following the steps in this article.
- Open an instance of the Azure Storage Explorer.
- Connect to the storage account created in step 1.
- Navigate to Blob Containers in Storage Services.
- Select Create a new container.
- Right-click the new container, then click Get Shared Access Signature.
- Select a valid Start Time and End Time, depending on your requirements.
- For the required permissions, select Read, Write, and List.
- Select Create.
- You'll get a Shared Access Signature. Copy the URL portion and provide it to the
-OutputSasUriparameter.
Parameter considerations
The parameters OutputSharePath and OutputShareCredential are used to store logs in a user specified location.
The FromDate and ToDate parameters can be used to collect logs for a particular time period. If these parameters aren't specified, logs are collected for the past four hours by default.
Use the FilterByNode parameter to filter logs by computer name. For example:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSharePath "<path>" -OutputShareCredential $cred -FilterByNode azs-xrp01Use the FilterByLogType parameter to filter logs by type. You can choose to filter by File, Share, or WindowsEvent. For example:
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSharePath "<path>" -OutputShareCredential $cred -FilterByLogType FileYou can use the TimeOutInMinutes parameter to set the timeout for log collection. It's set to 150 (2.5 hours) by default.
Dump file log collection is disabled by default. To enable it, use the IncludeDumpFile switch parameter.
Currently, you can use the FilterByRole parameter to filter log collection by the following roles:
ACS
ACSBlob
ACSDownloadService
ACSFabric
ACSFrontEnd
ACSMetrics
ACSMigrationService
ACSMonitoringService
ACSSettingsService
ACSTableMaster
ACSTableServer
ACSWac
ADFS
ApplicationController
ASAppGateway
AzureBridge
AzureMonitor
BareMetal
BRP
CA
CacheService
Compute
CPI
CRP
DeploymentMachine
DiskRP
Domain
ECE
EventAdminRP
EventRP
ExternalDNS
FabricRing
FabricRingServices
FirstTierAggregationService
FRP
Gateway
HealthMonitoring
HintingServiceV2
HRP
IBC
InfraServiceController
KeyVaultAdminResourceProvider
KeyVaultControlPlane
KeyVaultDataPlane
KeyVaultInternalControlPlane
KeyVaultInternalDataPlane
KeyVaultNamingService
MDM
MetricsAdminRP
MetricsRP
MetricsServer
MetricsStoreService
MonAdminRP
MonRP
NC
NonPrivilegedAppGateway
NRP
OboService
OEM
OnboardRP
PXE
QueryServiceCoordinator
QueryServiceWorker
SeedRing
SeedRingServices
SLB
SQL
SRP
Storage
StorageController
URP
SupportBridgeController
SupportRing
SupportRingServices
SupportBridgeRP
UsageBridge
VirtualMachines
WAS
WASPUBLIC
Additional considerations on diagnostic logs
The command takes some time to run based on which role(s) the logs are collecting. Contributing factors also include the time duration specified for log collection, and the numbers of nodes in the Azure Stack Hub environment.
As log collection runs, check the new folder created in the OutputSharePath parameter specified in the command.
Each role has its logs inside individual zip files. Depending on the size of the collected logs, a role may have its logs split into multiple zip files. For such a role, if you want to have all the log files unzipped into a single folder, use a tool that can unzip in bulk. Select all the zipped files for the role and select extract here. All the log files for that role will be unzipped into a single merged folder.
A file called Get-AzureStackLog_Output.log is also created in the folder that contains the zipped log files. This file is a log of the command output, which can be used for troubleshooting problems during log collection. Sometimes the log file includes
PS>TerminatingErrorentries which can be safely ignored, unless expected log files are missing after log collection runs.To investigate a specific failure, logs may be needed from more than one component.
- System and event logs for all infrastructure VMs are collected in the VirtualMachines role.
- System and event logs for all hosts are collected in the BareMetal role.
- Failover cluster and Hyper-V event logs are collected in the Storage role.
- ACS logs are collected in the Storage and ACS roles.
Note
Size and age limits are enforced on the logs collected as it's essential to ensure efficient utilization of your storage space and to avoid getting flooded with logs. However, when diagnosing a problem, you sometimes need logs that don't exist anymore because of these limits. Thus, it's highly recommended that you offload your logs to an external storage space (a storage account in Azure, an additional on premises storage device, etc.) every 8 to 12 hours and keep them there for 1 - 3 months, depending on your requirements. You should also ensure this storage location is encrypted.
Invoke-AzureStackOnDemandLog
You can use the Invoke-AzureStackOnDemandLog cmdlet to generate on-demand logs for certain roles (see the list at the end of this section). The logs generated by this cmdlet aren't present by default in the log bundle you receive when you execute the Get-AzureStackLog cmdlet. Also, it's recommended that you collect these logs only when requested by the Azure support team.
Currently, you can use the -FilterByRole parameter to filter log collection by the following roles:
- OEM
- NC
- SLB
- Gateway
Example of collecting on-demand diagnostic logs
$ipAddress = "<IP ADDRESS OF THE PEP VM>" # You can also use the machine name instead of IP here.
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString "<CLOUD ADMIN PASSWORD>" -AsPlainText -Force
$cred = New-Object -TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("<DOMAIN NAME>\CloudAdmin", $password)
$shareCred = Get-Credential
$session = New-PSSession -ComputerName $ipAddress -ConfigurationName PrivilegedEndpoint -Credential $cred -SessionOption (New-PSSessionOption -Culture en-US -UICulture en-US)
$fromDate = (Get-Date).AddHours(-8)
$toDate = (Get-Date).AddHours(-2) # Provide the time that includes the period for your issue
Invoke-Command -Session $session {
Invoke-AzureStackOnDemandLog -Generate -FilterByRole "<on-demand role name>" # Provide the supported on-demand role name e.g. OEM, NC, SLB, Gateway
Get-AzureStackLog -OutputSharePath "<external share address>" -OutputShareCredential $using:shareCred -FilterByRole Storage -FromDate $using:fromDate -ToDate $using:toDate
}
if ($session) {
Remove-PSSession -Session $session
}
How diagnostic log collection using the PEP works
Azure Stack Hub diagnostics tools help make log collection easy and efficient. The following diagram shows how the diagnostics tools work:
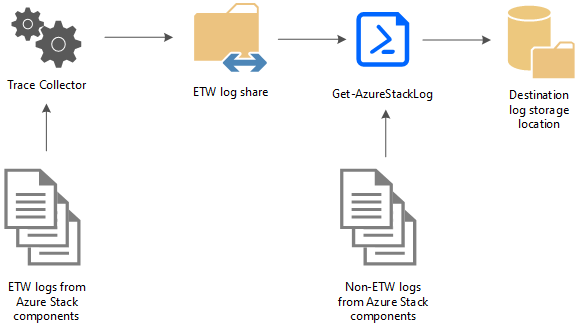
Trace Collector
The Trace Collector is enabled by default and runs continuously in the background to collect all Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) logs from Azure Stack Hub component services. ETW logs are stored in a common local share with a five-day age limit. Once this limit is reached, the oldest files are deleted as new ones are created. The default maximum size allowed for each file is 200 MB. A size check happens every 2 minutes, and if the current file is >= 200 MB, it's saved and a new file generates. There's also an 8 GB limit on the total file size generated per event session.
Get-AzureStackLog
The PowerShell cmdlet Get-AzureStackLog can be used to collect logs from all the components in an Azure Stack Hub environment. It saves them in zip files in a user-defined location. If the Azure Stack Hub technical support team needs your logs to help troubleshoot an issue, they may ask you to run Get-AzureStackLog.
Caution
These log files may contain personally identifiable information (PII). Take this into account before you publicly post any log files.
The following are some example log types that are collected:
- Azure Stack Hub deployment logs
- Windows event logs
- Panther logs
- Cluster logs
- Storage diagnostic logs
- ETW logs
These files are collected and saved in a share by Trace Collector. Get-AzureStackLog can then be used to collect them when necessary.