Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
With Azure Container Apps resiliency, you can proactively prevent, detect, and recover from service request failures by using simple resiliency policies. In this article, you learn how to configure Azure Container Apps resiliency policies when initiating requests by using Azure Container Apps service discovery.
Note
Currently, you can't apply resiliency policies to requests made by using the Dapr Service Invocation API.
Each request to a container app enforces policies. You can tailor policies to the container app that accepts requests with configurations like:
- The number of retries
- Retry and timeout duration
- Retry matches
- Circuit breaker consecutive errors, and others
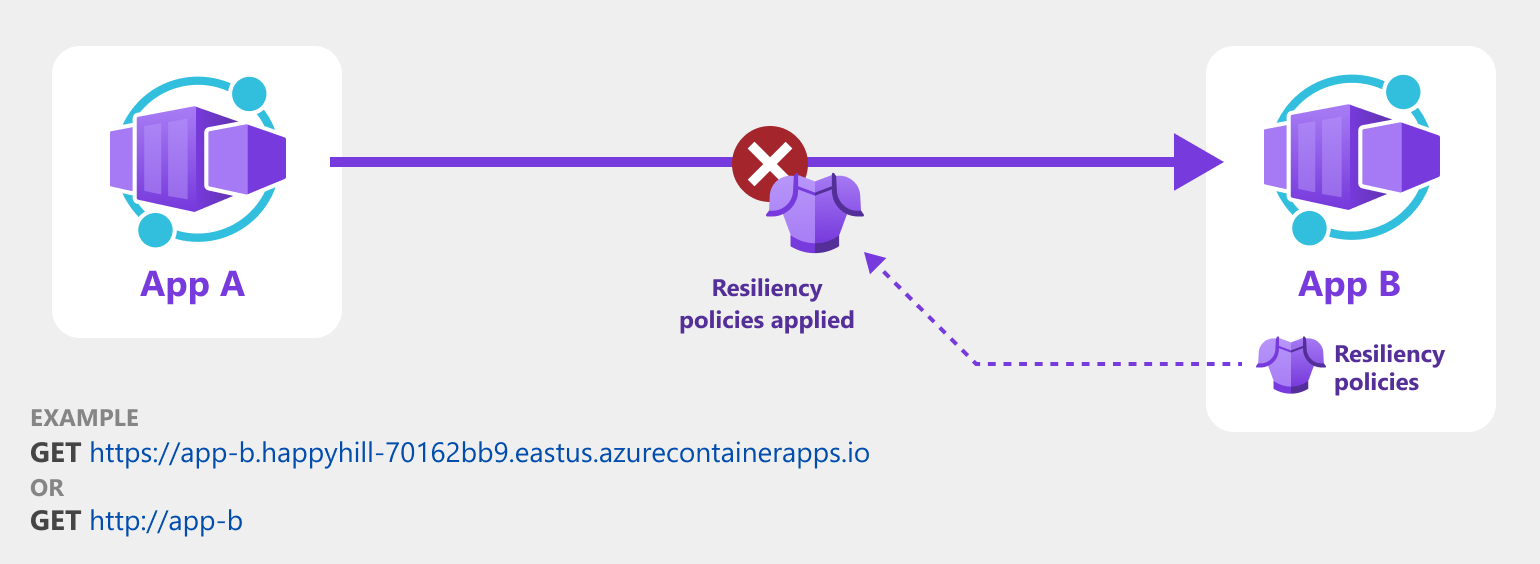
The following screenshot shows how an application uses a retry policy to attempt to recover from failed requests.
Supported resiliency policies
Configure resiliency policies
Whether you configure resiliency policies by using Bicep, the CLI, or the Azure portal, you can only apply one policy per container app.
When you apply a policy to a container app, the rules apply to all requests made to that container app, not to requests made from that container app. For example, a retry policy is applied to a container app named App B. All inbound requests made to App B automatically retry on failure. However, outbound requests sent by App B aren't guaranteed to retry in failure.
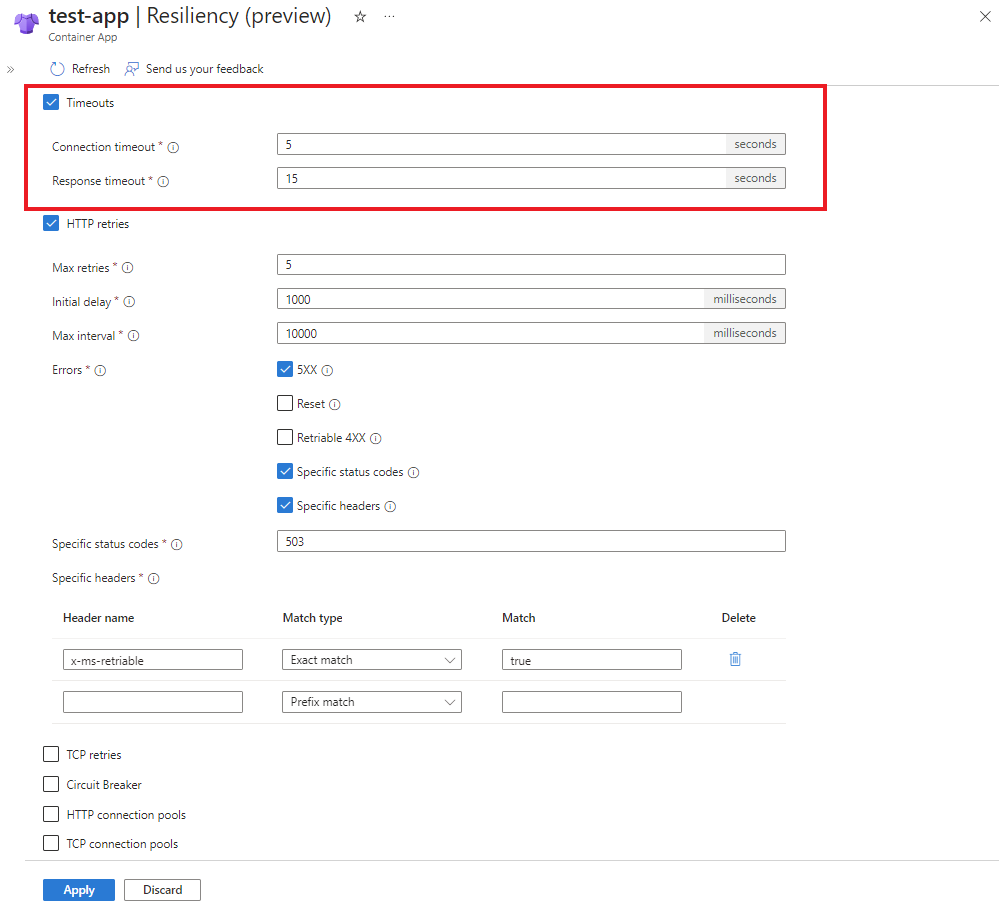
The following resiliency example demonstrates all of the available configurations.
resource myPolicyDoc 'Microsoft.App/containerApps/resiliencyPolicies@2023-11-02-preview' = {
name: 'my-app-resiliency-policies'
parent: '${appName}'
properties: {
timeoutPolicy: {
responseTimeoutInSeconds: 15
connectionTimeoutInSeconds: 5
}
httpRetryPolicy: {
maxRetries: 5
retryBackOff: {
initialDelayInMilliseconds: 1000
maxIntervalInMilliseconds: 10000
}
matches: {
headers: [
{
header: 'x-ms-retriable'
match: {
exactMatch: 'true'
}
}
]
httpStatusCodes: [
502
503
]
errors: [
'retriable-status-codes'
'5xx'
'reset'
'connect-failure'
'retriable-4xx'
]
}
}
tcpRetryPolicy: {
maxConnectAttempts: 3
}
circuitBreakerPolicy: {
consecutiveErrors: 5
intervalInSeconds: 10
maxEjectionPercent: 50
}
tcpConnectionPool: {
maxConnections: 100
}
httpConnectionPool: {
http1MaxPendingRequests: 1024
http2MaxRequests: 1024
}
}
}
Policy specifications
Timeouts
Timeouts early-terminate long-running operations. The timeout policy includes the following properties.
properties: {
timeoutPolicy: {
responseTimeoutInSeconds: 15
connectionTimeoutInSeconds: 5
}
}
| Metadata | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
responseTimeoutInSeconds |
Yes | Timeout waiting for a response from the container app. | 15 |
connectionTimeoutInSeconds |
Yes | Timeout to establish a connection to the container app. | 5 |
Retries
Define a tcpRetryPolicy or an httpRetryPolicy strategy for failed operations. The retry policy includes the following configurations.
httpRetryPolicy
properties: {
httpRetryPolicy: {
maxRetries: 5
retryBackOff: {
initialDelayInMilliseconds: 1000
maxIntervalInMilliseconds: 10000
}
matches: {
headers: [
{
header: 'x-ms-retriable'
match: {
exactMatch: 'true'
}
}
]
httpStatusCodes: [
502
503
]
errors: [
'retriable-headers'
'retriable-status-codes'
]
}
}
}
| Metadata | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
maxRetries |
Yes | Maximum retries to execute for a failed HTTP request. | 5 |
retryBackOff |
Yes | Monitor the requests and shut off all traffic to the impacted service when timeout and retry criteria are met. | N/A |
retryBackOff.initialDelayInMilliseconds |
Yes | Delay between first error and first retry. | 1000 |
retryBackOff.maxIntervalInMilliseconds |
Yes | Maximum delay between retries. | 10000 |
matches |
Yes | Set match values to limit when the app should attempt a retry. | headers, httpStatusCodes, errors |
matches.headers |
Y* | Retry when the error response includes a specific header. *Headers are only required properties if you specify the retriable-headers error property. Learn more about available header matches. |
X-Content-Type |
matches.httpStatusCodes |
Y* | Retry when the response returns a specific status code. *Status codes are only required properties if you specify the retriable-status-codes error property. |
502, 503 |
matches.errors |
Yes | Only retries when the app returns a specific error. Learn more about available errors. | connect-failure, reset |
Header matches
If you specify the retriable-headers error, you can use the following header match properties to retry when the response includes a specific header.
matches: {
headers: [
{
header: 'x-ms-retriable'
match: {
exactMatch: 'true'
}
}
]
}
| Metadata | Description |
|---|---|
prefixMatch |
Retries are performed based on the prefix of the header value. |
exactMatch |
Retries are performed based on an exact match of the header value. |
suffixMatch |
Retries are performed based on the suffix of the header value. |
regexMatch |
Retries are performed based on a regular expression rule where the header value must match the regex pattern. |
Errors
You can perform retries on any of the following errors:
matches: {
errors: [
'retriable-headers'
'retriable-status-codes'
'5xx'
'reset'
'connect-failure'
'retriable-4xx'
]
}
| Metadata | Description |
|---|---|
retriable-headers |
HTTP response headers that trigger a retry. A retry is performed if any of the header-matches match the response headers. Required if you'd like to retry on any matching headers. |
retriable-status-codes |
HTTP status codes that should trigger retries. Required if you'd like to retry on any matching status codes. |
5xx |
Retry if server responds with any 5xx response codes. |
reset |
Retry if the server doesn't respond. |
connect-failure |
Retry if a request failed due to a faulty connection with the container app. |
retriable-4xx |
Retry if the container app responds with a 400-series response code, like 409. |
tcpRetryPolicy
properties: {
tcpRetryPolicy: {
maxConnectAttempts: 3
}
}
| Metadata | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
maxConnectAttempts |
Yes | Set the maximum connection attempts (maxConnectionAttempts) to retry on failed connections. |
3 |
Circuit breakers
Circuit breaker policies specify whether a container app replica is temporarily removed from the load balancing pool, based on triggers like the number of consecutive errors.
properties: {
circuitBreakerPolicy: {
consecutiveErrors: 5
intervalInSeconds: 10
maxEjectionPercent: 50
}
}
| Metadata | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
consecutiveErrors |
Yes | Number of consecutive errors before a container app replica is temporarily removed from load balancing. | 5 |
intervalInSeconds |
Yes | The amount of time given to determine if a replica is removed or restored from the load balance pool. | 10 |
maxEjectionPercent |
Yes | Maximum percent of failing container app replicas to eject from load balancing. Removes at least one host regardless of the value. | 50 |
Connection pools
Azure Container Apps connection pooling maintains a pool of established and reusable connections to container apps. This connection pool reduces the overhead of creating and tearing down individual connections for each request.
Connection pools let you specify the maximum number of requests or connections allowed for a service. These limits control the total number of concurrent connections for each service. When this limit is reached, new connections aren't established to that service until existing connections are released or closed. This process of managing connections prevents resources from being overwhelmed by requests and maintains efficient connection management.
httpConnectionPool
properties: {
httpConnectionPool: {
http1MaxPendingRequests: 1024
http2MaxRequests: 1024
}
}
| Metadata | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
http1MaxPendingRequests |
Yes | Used for http1 requests. Maximum number of open connections to a container app. |
1024 |
http2MaxRequests |
Yes | Used for http2 requests. Maximum number of concurrent requests to a container app. |
1024 |
tcpConnectionPool
properties: {
tcpConnectionPool: {
maxConnections: 100
}
}
| Metadata | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
maxConnections |
Yes | Maximum number of concurrent connections to a container app. | 100 |
Resiliency observability
You can perform resiliency observability through your container app's metrics and system logs.
Resiliency logs
From the Monitoring section of your container app, select Logs.
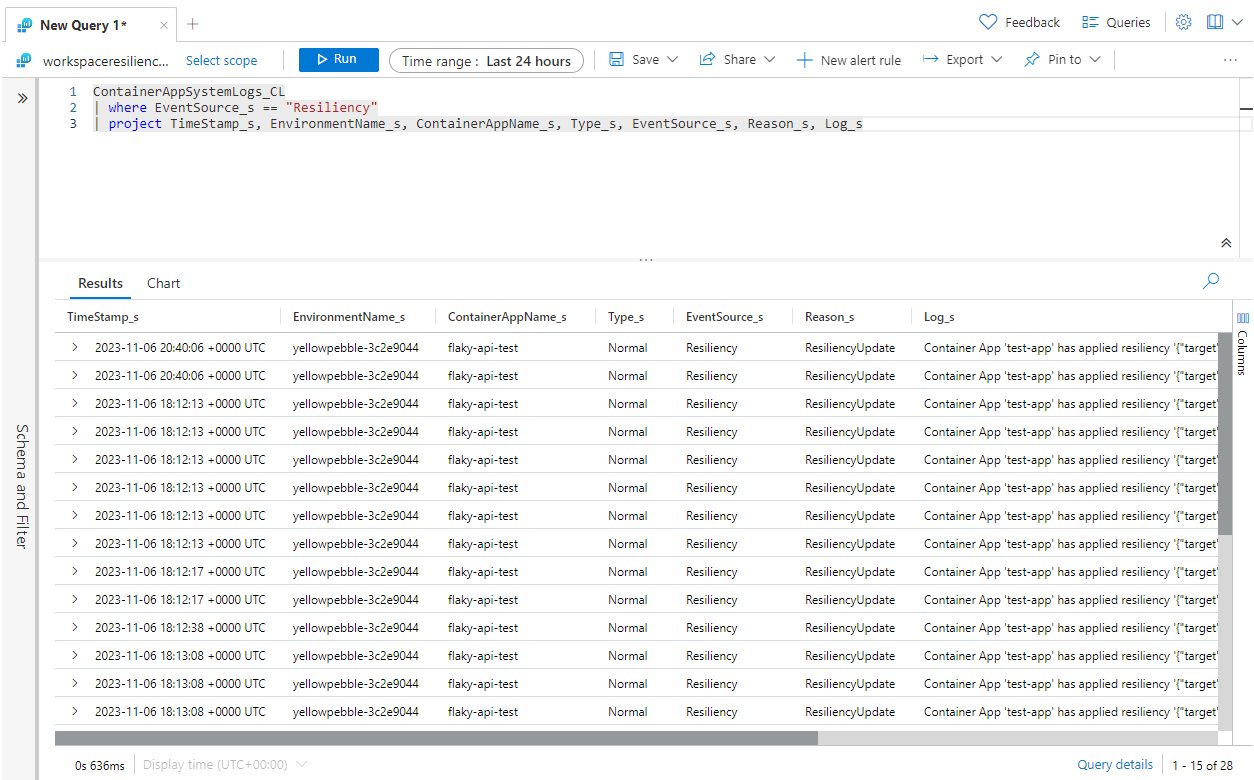
In the Logs pane, write and run a query to find resiliency events in your container app system logs. For example, run a query similar to the following query to search for resiliency events and show their:
- Time stamp
- Environment name
- Container app name
- Resiliency type and reason
- Log messages
ContainerAppSystemLogs_CL
| where EventSource_s == "Resiliency"
| project TimeStamp_s, EnvironmentName_s, ContainerAppName_s, Type_s, EventSource_s, Reason_s, Log_s
Select Run to run the query and view results.
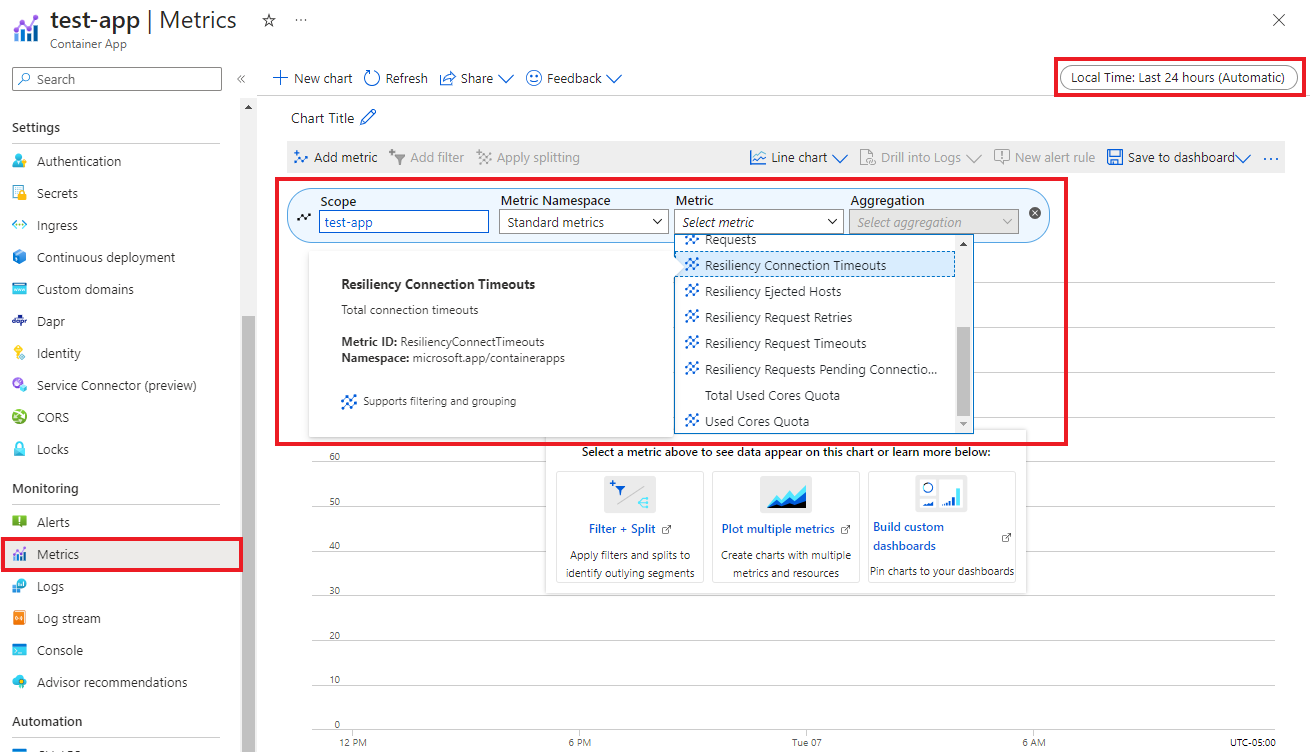
Resiliency metrics
From the Monitoring menu of your container app, select Metrics. In the Metrics pane, select the following filters:
- The scope to the name of your container app.
- The Standard metrics metrics namespace.
- The resiliency metrics from the drop-down menu.
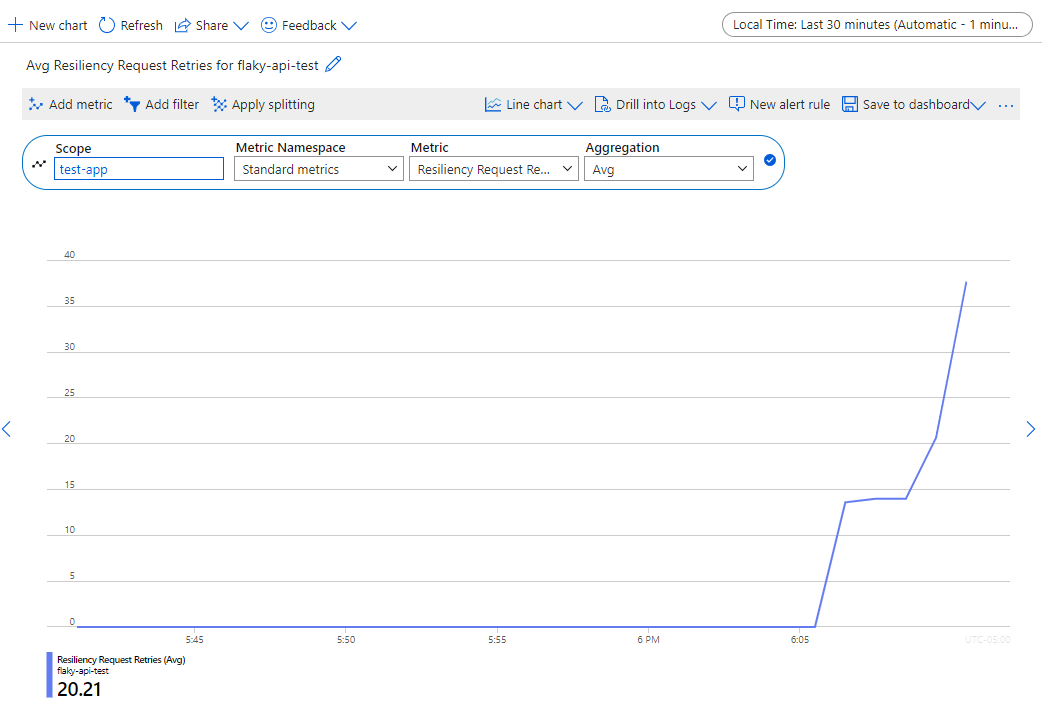
- How you'd like the data aggregated in the results (by average, by maximum, and so on).
- The time duration (for example, last 30 minutes, or last 24 hours).
For example, if you set the Resiliency Request Retries metric in the test-app scope with Average aggregation to search within a 30-minute timeframe, the results look like the following: