Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
An Azure container registry stores and manages private Docker container images, similar to the way Docker Hub stores public Docker images. It can also host repositories for Helm charts (preview), a packaging format to deploy applications to Kubernetes. You can use webhooks to trigger events when certain actions take place in one of your registry repositories. Webhooks can respond to events at the registry level, or they can be scoped down to a specific repository tag. With a geo-replicated registry, you configure each webhook to respond to events in a specific regional replica.
The endpoint for a webhook must be publicly accessible from the registry. You can configure registry webhook requests to authenticate to a secured endpoint.
For details on webhook requests, see Azure Container Registry webhook schema reference.
Prerequisites
- Azure container registry - Create a container registry in your Azure subscription. For example, use the Azure portal or the Azure CLI. The Azure Container Registry service tiers have different webhooks quotas.
- Docker CLI - To set up your local computer as a Docker host and access the Docker CLI commands, install Docker Engine.
Create webhook - Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to the container registry in which you want to create a webhook.
Under Services, select Webhooks.
Select Add in the webhook toolbar.
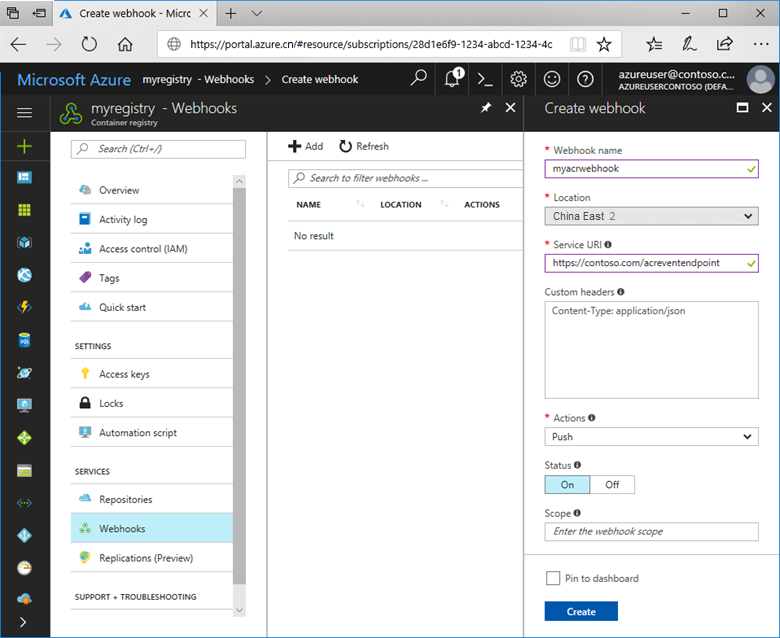
Complete the Create webhook form with the following information:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Webhook name | The name you want to give to the webhook. It may contain only letters and numbers, and must be 5-50 characters in length. |
| Location | For a geo-replicated registry, specify the Azure region of the registry replica. |
| Service URI | The URI where the webhook should send POST notifications. |
| Custom headers | Headers you want to pass along with the POST request. They should be in "key: value" format. |
| Trigger actions | Actions that trigger the webhook. Actions include image push, image delete, Helm chart push, Helm chart delete, and image quarantine. You can choose one or more actions to trigger the webhook. |
| Status | The status for the webhook after it's created. It's enabled by default. |
| Scope | The scope at which the webhook works. If not specified, the scope is for all events in the registry. It can be specified for a repository or a tag by using the format "repository:tag", or "repository:*" for all tags under a repository. |
Example webhook form:
Create webhook - Azure CLI
To create a webhook using the Azure CLI, use the az acr webhook create command. The following command creates a webhook for all image delete events in the registry mycontainerregistry:
az acr webhook create --registry mycontainerregistry --name myacrwebhook01 --actions delete --uri http://webhookuri.com
Test webhook
Azure portal
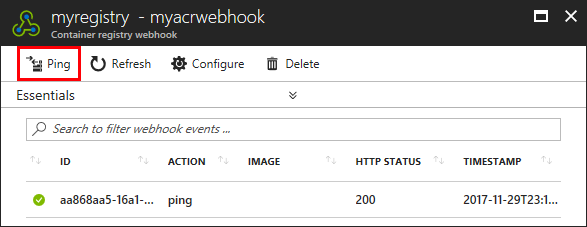
Prior to using the webhook, you can test it with the Ping button. Ping sends a generic POST request to the specified endpoint and logs the response. Using the ping feature can help you verify you've correctly configured the webhook.
Select the webhook you want to test.
In the top toolbar, select Ping.
Check the endpoint's response in the HTTP STATUS column.
Azure CLI
To test an ACR webhook with the Azure CLI, use the az acr webhook ping command.
az acr webhook ping --registry mycontainerregistry --name myacrwebhook01
To see the results, use the az acr webhook list-events command.
az acr webhook list-events --registry mycontainerregistry08 --name myacrwebhook01
Delete webhook
Azure portal
Each webhook can be deleted by selecting the webhook and then the Delete button in the Azure portal.
Azure CLI
az acr webhook delete --registry mycontainerregistry --name myacrwebhook01
Next steps
Webhook schema reference
For details on the format and properties of the JSON event payloads emitted by Azure Container Registry, see the webhook schema reference: