Dynamic scaling (per region and per partition autoscale)
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
MongoDB
Cassandra
Gremlin
Table
Azure Cosmos DB autoscale by default scales workloads based on the most active region and partition. For nonuniform workloads that have different workload patterns across regions and partitions, this scaling can cause unnecessary scale-ups. With this improvement to autoscale, also known as "dynamic scaling," the per region and per partition autoscale feature now allows your workloads’ regions and partitions to scale independently based on usage.
Dynamic scaling is recommended for autoscale workloads that are nonuniform across regions and partitions. This feature allows you to save cost if you often experience hot partitions and/or have multiple regions. When enabled, dynamic scaling applies to all autoscale resources in the account.
Use cases
- Database workloads that have a highly trafficked primary region and a secondary passive region for disaster recovery.
- With dynamic scaling, achieving high availability with multiple regions is more cost effective. The secondary region independently and automatically scales down while idle. The secondary region also automatically scales up as it becomes active and while handling write replication traffic from the primary region.
- Multi-region database workloads.
- These workloads often observe uneven distribution of requests across regions due to natural traffic growth and dips throughout the day. For example, a database might be active during business hours across multiple-regionally distributed time zones.
Example
For example, if we have a collection with 1000 RU/s and 2 partitions, each partition can go up to 500 RU/s. For one hour of activity, the utilization would look like this:
| Region | Partition | Throughput | Utilization | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Write | P1 | <= 500 RU/s | 100% | 500 RU/s consisting of 50 RU/s used for write operations and 450 RU/s for read operations. |
| Write | P2 | <= 200 RU/s | 40% | 200 RU/s consisting of all read operations. |
| Read | P1 | <= 150 RU/s | 30% | 150 RU/s consisting of 50 RU/s used for writes replicated from the write region. 100 RU/s are used for read operations in this region. |
| Read | P2 | <= 50 RU/s | 10% |
Because all partitions are scaled uniformly based on the hottest partition, both the write and read regions are scaled to 1000 RU/s, making the total RU/s as much as 2000 RU/s.
With dynamic scaling, you can optimize your throughput. The total consumption would be 900 RU/s as each partition or region's throughput is scaled independently and measured per hour using the same scenario.
Monitoring dynamic autoscale
You can use the following metrics to monitor dynamic autoscale:
| Metric Name | Definition | Metric Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Autoscaled RU | Shows the dynamically scaled provisioned throughput at each partition and region level only for dynamic autoscale enabled accounts. | Use this metric to see how partitions in each region scale independently based on their usage. Use Azure Monitor metrics - Autoscaled RU to analyze how the new autoscaling is applied across partitions and regions. Filter to your desired database account and container, then filter or split by the Physical PartitionID metric. This metric shows all partitions across their various regions. |
| Provisioned Throughput | Shows the aggregated highest RU/s scaled to across the hour, and represents the total RU/s scaled to for the hour. | You can use the Provisioned Throughput metric to see the RU/s you're billed for in each hour. With dynamic autoscale, you're billed for the aggregated highest RU/s scaled to in each hour at each partition and region level. |
| Normalized RU Consumption | This metric represents the ratio of consumed RU/s to provisioned RU/s at each partition and region level. | Use this metric to determine if the autoscale maximum throughput is under or over-provisioned. If the metric value is consistently 100% and your application is seeing rate-limiting (429 error code), then you might need more RU/s. In contrast, if this metric value is low and there's no rate-limiting, then there might be room to optimize and scale-down the RU/s. Learn how to interpret and debug code 429 rate limiting errors. The Normalized RU Consumption metric reflects the RU/s consumed in secondary region due to write replication traffic from the primary, in addition to any read traffic on the secondary. |
Get started
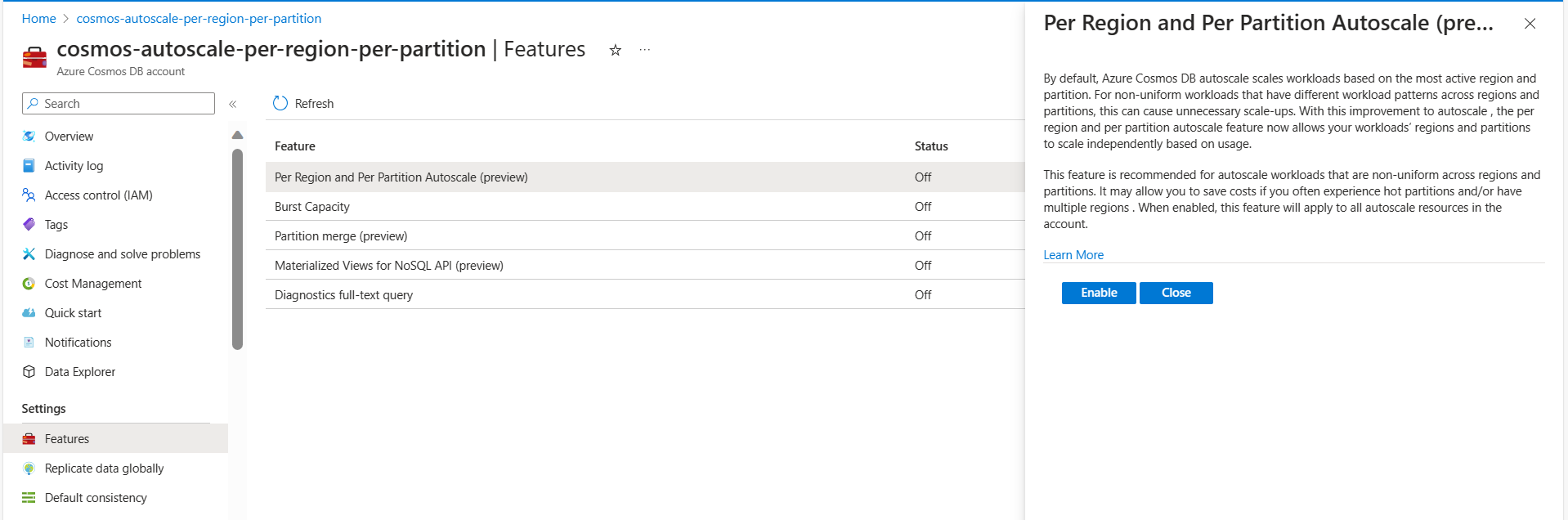
Dynamic scaling is enabled by default for all Azure Cosmos DB accounts created after September 25, 2024. Customers who wish to enable this feature for their older accounts can do so programmatically through Azure PowerShell/CLI/Rest API or from the features pane of Azure portal as shown:
Navigate to your Azure Cosmos DB account in the Azure portal.
Navigate to the Features page.
Locate and enable the Dynamic Scaling (Per Region and Per Partition Autoscale) feature.
Important
The feature is enabled at the account level, so all autoscale containers and shared throughput databases within the account will automatically have this capability applied. Enabling this feature does not affect resources in the account that are using manual throughput. Manual resources will need to be changed to autoscale to take advantage of dynamic scaling. Enabling this feature has zero downtime or performance impact. This feature is not applicable for serverless accounts.