Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
This feature is currently in preview and is provided without a service-level agreement. At this time, previews aren't recommended for production workloads. Certain features of this preview aren't supported or might have capability constraints. For more information, see supplemental terms of use for Azure previews.
In this guide, you enable Azure Cosmos DB fleet analytics for your Microsoft Fabric workspace.
In this guide, you enable Azure Cosmos DB fleet analytics for your Azure Data Lake Storage account.
Prerequisites
An existing Azure Cosmos DB fleet
If you don't have an existing a fleet, create a new fleet.
Fleet analytics only supports Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL accounts that are configured with the fleet.
An existing Microsoft Fabric workspace
The workspace must use OneLake as the default storage location.
The workspace must be backed by a licensed or trial Fabric capacity.
Note
It is recommended to create a dedicated Fabric workspace for Fleet Analytics because the service principal associated with the feature requires Contributor access to the entire workspace.
An existing Azure Storage account compatible with Azure Data Lake Storage (Gen2)
- The hierarchical namespace feature must be enabled at account creation.
Enable fleet analytics
First, configure the resources required for fleet analytics.
Sign-in to the Azure portal (https://portal.azure.cn).
Navigate to the existing Azure Cosmos DB fleet.
On the page for the fleet, select Fleet analytics in the Monitoring section of the resource menu.
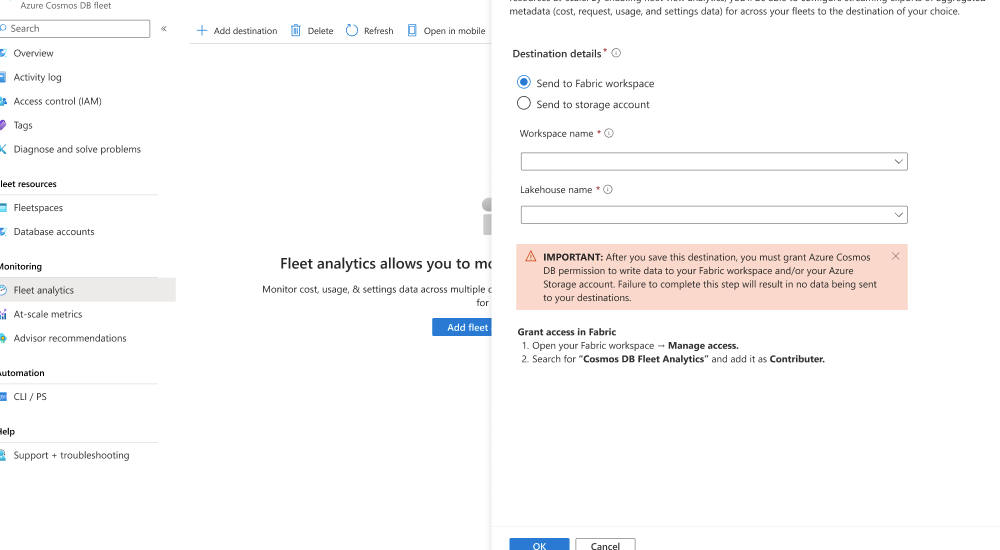
Then, select Add destination.
In the Fleet analytics dialog, select Send to Fabric workspace. Then, select your existing Fabric workspace, select an existing OneLake lakehouse, and then save the destination.
Navigate to your Fabric workspace in the Microsoft Fabric portal.
In the Manage section of your workspace, add the principal for fleet analytics as the Contributor role by searching for the shared Cosmos DB Fleet Analytics service principal.
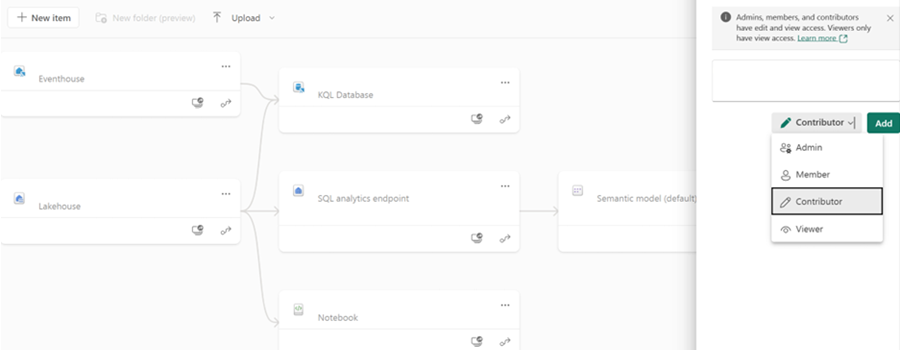
Important
Failure to complete this step results in data not being written to your destination Fabric workspace.
Save your changes.
Sign-in to the Azure portal (https://portal.azure.cn).
Navigate to the existing Azure Cosmos DB fleet.
On the page for the fleet, select Fleet analytics in the Monitoring section of the resource menu.
Then, select Add destination.
In the Fleet analytics dialog, select Send to storage account. Then, select your existing Azure Storage account, select an existing container, and then save the destination.

Navigate to your Azure Storage account. Then, navigate to the Access Control (IAM) page.
Select the Add role assignment menu option.
On the Add role assignment page, select the Storage Blob Contributor role to grant permissions to contribute blobs to the existing account.
Now, use the + Select members option. In the dialog, search for and select the shared Cosmos DB Fleet Analytics service principal.
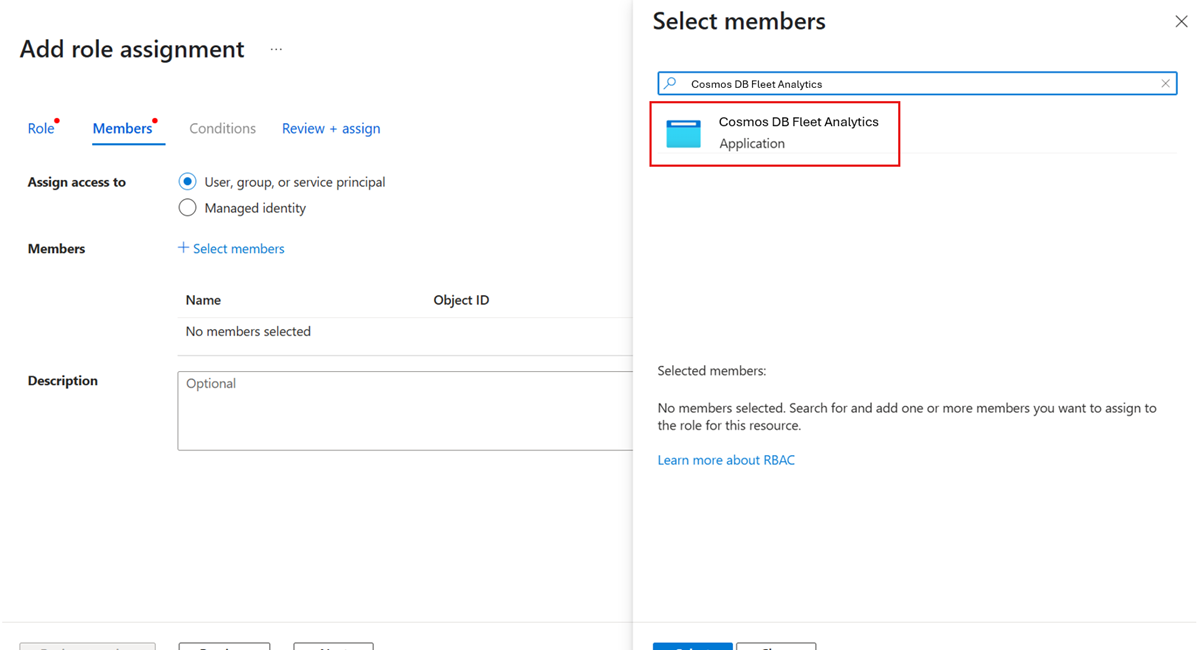
Important
Failure to complete this step results in data not being written to your destination Azure Storage account.
Review + assign your role assignment.
Query and visualize data
In a star schema design, retrieving detailed information typically requires joining fact tables with their related dimension tables, following standard best practices. This section walks through the steps to query and visualize data using Microsoft Fabric.
Open your Fabric workspace.
Navigate to your existing OneLake resource.

In the SQL endpoint explorer, select any table and run a
SELECT TOP 100query to quickly observe the data. This query can be found in the context menu.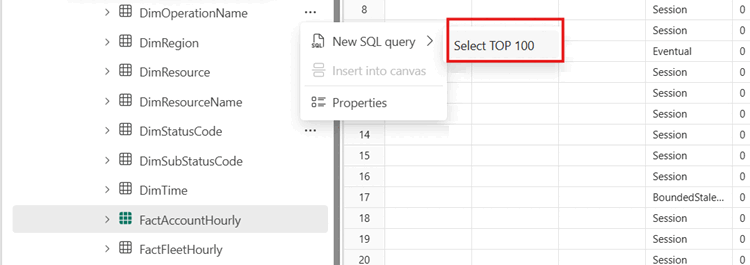
Tip
Alternatively, run the following query to view Account-level details:
SELECT TOP (100) [Timestamp], [ResourceId], [FleetId], [DefaultConsistencyLevel], [IsSynapseLinkEnabled], [IsFreeTierEnabled], [IsBurstEnabled], [BackupMode], [BackupStrategy], [BackupRedundancy], [BackupIntervalInMinutes], [BackupRetentionIntervalInHours], [TotalRUPerSecLimit], [APISettings], [AccountKeySettings], [LastDateAnyAccountKeyRotated] FROM [FactAccountHourly]Observe the results of the query. Notice that you only have a reference to the
ResourceIdfield. Using just the results of this query, you can't determine the exact database or container for individual rows.Run this sample query joining both the
DimResourceandFactRequestHourlytables to find your top 100 most active accounts by transactions.SELECT TOP 100 DR.[SubscriptionId], DR.[AccountName], DR.[ResourceGroup], SUM(FRH.[TotalRequestCount]) AS sum_total_requests FROM [FactRequestHourly] FRH JOIN [DimResource] DR ON FRH.[ResourceId] = DR.[ResourceId] WHERE FRH.[Timestamp] >= DATEADD(DAY, -7, GETDATE()) -- Filter for the last 7 days AND ResourceName IN ('Document', 'StoredProcedure') -- Filter for Dataplane Operations GROUP BY DR.[AccountName], DR.[SubscriptionId], DR.[ResourceGroup] ORDER BY sum_total_requests DESC; -- Order by total requests in descending orderRun this query to find the top 100 largest accounts by storage.
SELECT TOP 100 DR.[SubscriptionId], DR.[AccountName], MAX(FRH.[MaxDataStorageInKB] / (1024.0 * 1024.0)) AS DataUsageInGB, MAX(FRH.[MaxIndexStorageInKB] / (1024.0 * 1024.0)) AS IndexUsageInGB, MAX( FRH.[MaxDataStorageInKB] / (1024.0 * 1024.0) + FRH.[MaxIndexStorageInKB] / (1024.0 * 1024.0) ) AS StorageInGB FROM [FactResourceUsageHourly] FRH JOIN [DimResource] DR ON FRH.[ResourceId] = DR.[ResourceId] WHERE FRH.[Timestamp] >= DATEADD(DAY, -1, GETDATE()) -- Filter for the last 1 day GROUP BY DR.[AccountName], DR.[SubscriptionId] ORDER BY StorageInGB DESC; -- Order by total storage usageNow, create a view on the data by opening the context menu and selecting Save as view. Give the view a unique name and then select Ok.

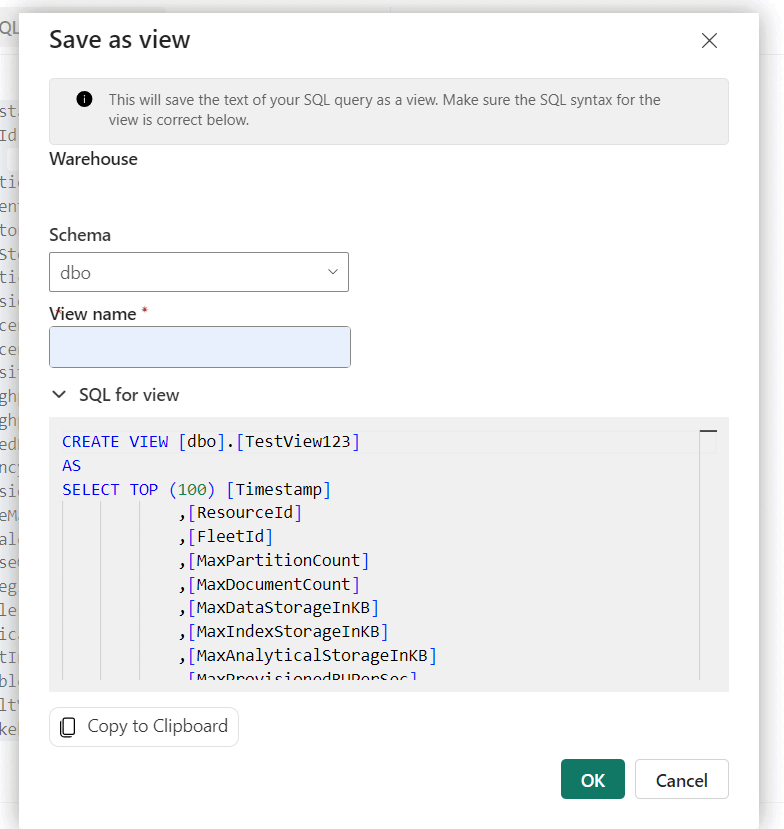
Tip
Alternatively, create a view directly using this query:
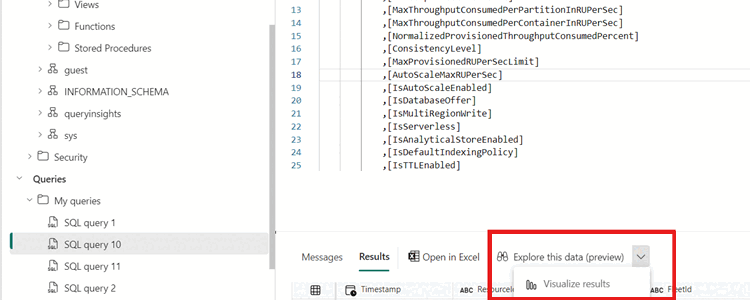
CREATE VIEW [MostActiveCustomers] AS SELECT a.ResourceId AS UsageResourceId, a.Timestamp, a.MeterId, a.FleetId, a.ConsumedUnits, b.ResourceId AS ResourceDetailId FROM FactMeterUsageHourly a INNER JOIN DimResource b ON a.ResourceId = b.ResourceIdNavigate to the newly created view within the Views folder of your endpoint.

Navigate to the view you recently created (or a query) and then select Explorer this data (preview) and then select Visualize results.
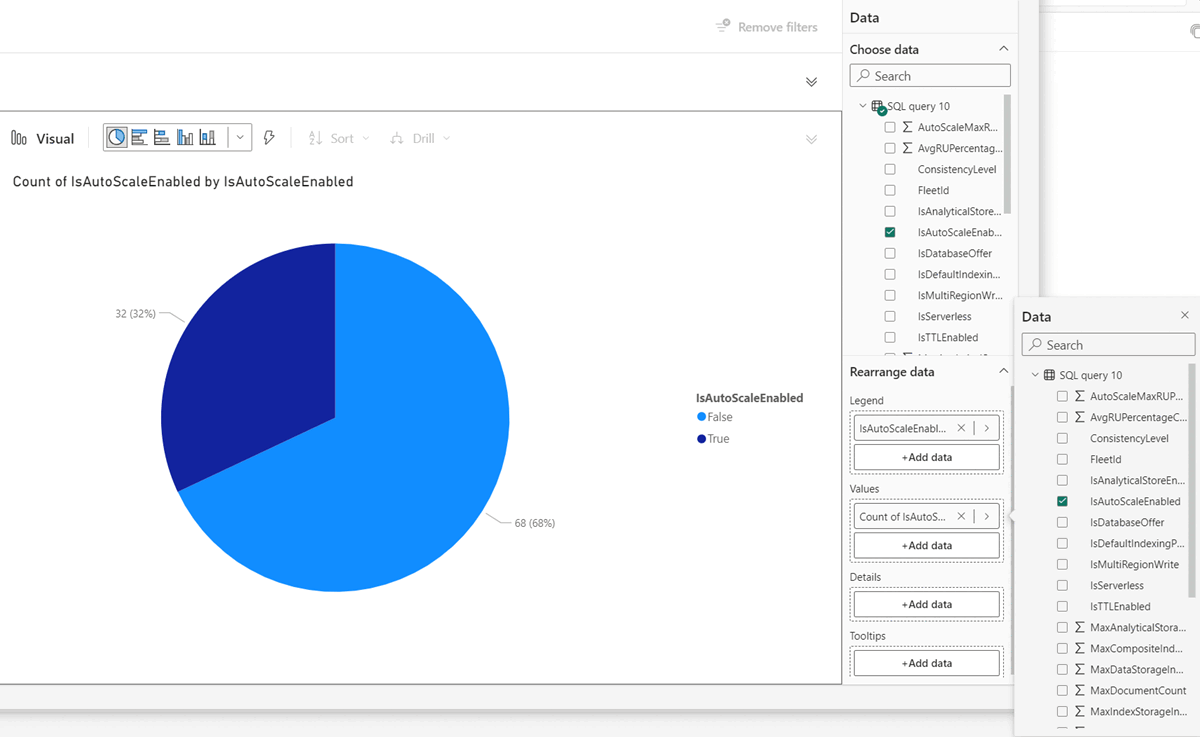
On the Power BI landing page, create relevant visuals for your scenario. For example, you can show the percentage of your Azure Cosmos DB workload with the autoscale feature enabled.
This section walks through the steps to create and query a table or DataFrame loaded from data stored in Azure Storage (ADLS) or Azure Databricks. This section uses a Notebook connected to Apache Spark with Python and SQL cells.
First, define the Azure Storage account configuration targeting the
# Define storage configuration container_name = "<azure-storage-container-name>" account_name = "<azure-storage-account-name>" base_url = f"abfss://{container_name}@{account_name}.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn" source_path = f"{base_url}/FactResourceUsageHourly"Create the data as a table. Reload and refresh data from an external source (Azure Storage - ADLS) by dropping and recreating the
fleet_datatable.table_name = "fleet_data" # Drop the table if it exists spark.sql(f"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {table_name}") # Create the table spark.sql(f""" CREATE TABLE {table_name} USING delta LOCATION '{source_path}' """)Query and render the results from the
fleet_datatable.# Query and display the table df = spark.sql(f"SELECT * FROM {table_name}") display(df)Define the full list of extra tables to be created for processing fleet analytics data.
# Table names and folder paths (assumed to match) tables = [ "DimResource", "DimMeter", "FactResourceUsageHourly", "FactAccountHourly", "FactRequestHourly", "FactMeterUsageHourly" ] # Drop and recreate each table for table in tables: spark.sql(f"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {table}") spark.sql(f""" CREATE TABLE {table} USING delta LOCATION '{base_url}/{table}' """)Run a query using any of those tables. For example, this query finds your top 100 most active accounts by transactions.
SELECT DR.SubscriptionId, DR.AccountName, DR.ResourceGroup, SUM(FRH.TotalRequestCount) AS sum_total_requests FROM FactRequestHourly FRH JOIN DimResource DR ON FRH.ResourceId = DR.ResourceId WHERE FRH.Timestamp >= DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), 7) -- Filter for the last 7 days AND FRH.ResourceName IN ('Document', 'StoredProcedure') -- Filter for Dataplane Operations GROUP BY DR.AccountName, DR.SubscriptionId, DR.ResourceGroup ORDER BY sum_total_requests DESC LIMIT 100; -- Limit to top 100 resultsRun this query to find the top 100 largest accounts by storage.
SELECT DR.SubscriptionId, DR.AccountName, MAX(FRH.MaxDataStorageInKB / (1024.0 * 1024.0)) AS DataUsageInGB, MAX(FRH.MaxIndexStorageInKB / (1024.0 * 1024.0)) AS IndexUsageInGB, MAX( FRH.MaxDataStorageInKB / (1024.0 * 1024.0) + FRH.MaxIndexStorageInKB / (1024.0 * 1024.0) ) AS StorageInGB FROM FactResourceUsageHourly FRH JOIN DimResource DR ON FRH.ResourceId = DR.ResourceId WHERE FRH.Timestamp >= DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), 1) -- Filter for the last 1 day GROUP BY DR.AccountName, DR.SubscriptionId ORDER BY StorageInGB DESC LIMIT 100; -- Limit to top 100 results