dcount_hll()
Calculates the distinct count from results generated by hll or hll_merge.
Read about the underlying algorithm (HyperLogLog) and estimation accuracy.
Syntax
dcount_hll(hll)
Learn more about syntax conventions.
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| hll | string |
✔️ | An expression generated by hll or hll-merge to be used to find the distinct count. |
Returns
Returns the distinct count of each value in hll.
Example
The following example shows the distinct count hll merged results.
StormEvents
| summarize hllRes = hll(DamageProperty) by bin(StartTime,10m)
| summarize hllMerged = hll_merge(hllRes)
| project dcount_hll(hllMerged)
Output
| dcount_hll_hllMerged |
|---|
| 315 |
Estimation accuracy
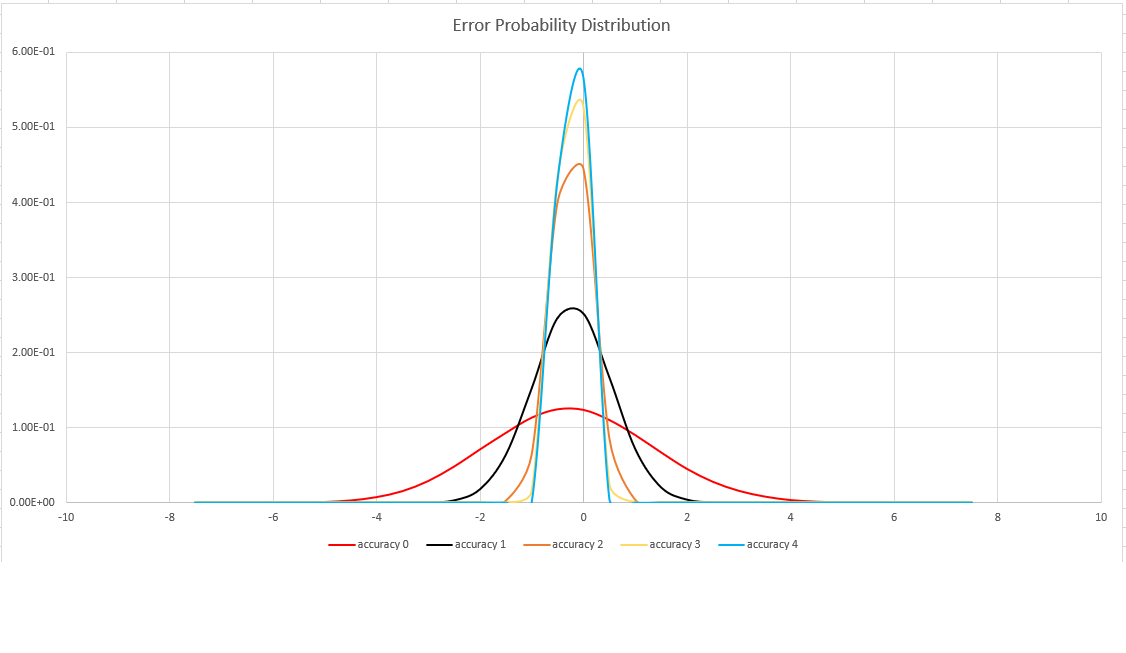
This function uses a variant of the HyperLogLog (HLL) algorithm, which does a stochastic estimation of set cardinality. The algorithm provides a "knob" that can be used to balance accuracy and execution time per memory size:
| Accuracy | Error (%) | Entry count |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.6 | 212 |
| 1 | 0.8 | 214 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 216 |
| 3 | 0.28 | 217 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 218 |
Note
The "entry count" column is the number of 1-byte counters in the HLL implementation.
The algorithm includes some provisions for doing a perfect count (zero error), if the set cardinality is small enough:
- When the accuracy level is
1, 1000 values are returned - When the accuracy level is
2, 8000 values are returned
The error bound is probabilistic, not a theoretical bound. The value is the standard deviation of error distribution (the sigma), and 99.7% of the estimations will have a relative error of under 3 x sigma.
The following image shows the probability distribution function of the relative estimation error, in percentages, for all supported accuracy settings: