Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: ✅ Azure Data Explorer ✅ Azure Monitor ✅ Microsoft Sentinel
Joining data from multiple tables lets you analyze data across sources and create relationships between data points. In the Kusto Query Language (KQL), use the join and lookup operators to combine data across tables.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
The examples in this tutorial use the StormEvents table, which is publicly available in the help cluster.
Prerequisites
Run the queries in a query environment that has access to the sample data. Use one of the following:
- Microsoft account or Microsoft Entra user identity to sign in to the help cluster
Use the join operator
The Samples database has two related storm event tables: StormEvents and PopulationData. In this section, you join them to analyze data that's not possible with one table alone.
Understand the data
Use the take operator to see what data each table contains.
StormEvents
| take 5
The following table shows only six of the 22 returned columns.
| StartTime | EndTime | EpisodeId | EventId | State | EventType | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007-09-20T21:57:00Z | 2007-09-20T22:05:00Z | 11078 | 60913 | FLORIDA | Tornado | ... |
| 2007-12-20T07:50:00Z | 2007-12-20T07:53:00Z | 12554 | 68796 | MISSISSIPPI | Thunderstorm Wind | ... |
| 2007-12-30T16:00:00Z | 2007-12-30T16:05:00Z | 11749 | 64588 | GEORGIA | Thunderstorm Wind | ... |
| 2007-09-29T08:11:00Z | 2007-09-29T08:11:00Z | 11091 | 61032 | ATLANTIC SOUTH | Waterspout | ... |
| 2007-09-18T20:00:00Z | 2007-09-19T18:00:00Z | 11074 | 60904 | FLORIDA | Heavy Rain | ... |
PopulationData
| take 5
Output
| State | Population |
|---|---|
| ALABAMA | 4918690 |
| ALASKA | 727951 |
| ARIZONA | 7399410 |
| ARKANSAS | 3025880 |
| CALIFORNIA | 39562900 |
Both tables have a State column. StormEvents has many more columns, and PopulationData has one other column with the state's population.
Join the tables
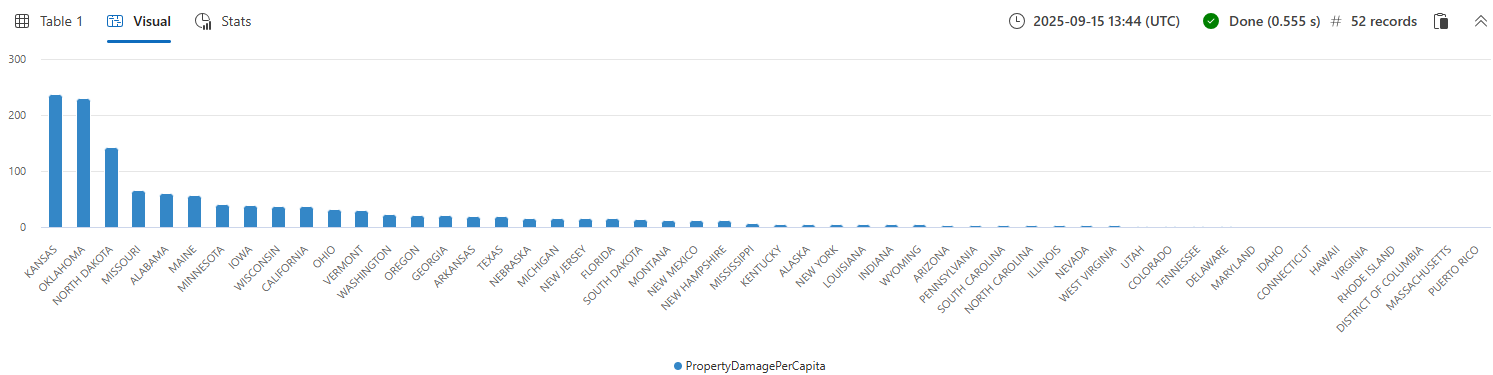
Join PopulationData with StormEvents on State to calculate total property damage per capita by state.
StormEvents
| summarize PropertyDamage = sum(DamageProperty) by State
| join kind=innerunique PopulationData on State
| project State, PropertyDamagePerCapita = PropertyDamage / Population
| sort by PropertyDamagePerCapita
Add | render columnchart to the query to visualize the result.
If the columns have different names (for example, StormEvents has State and PopulationData has StateName), specify the join as:
StormEvents
| join kind=innerunique PopulationData on $left.State == $right.StateName
$left refers to the left (outer) table in the join: StormEvents. $right refers to the right (inner) table: PopulationData.
Tip
Use the join operator for many join types. See the list of join flavors.
Use the lookup operator
The lookup operator optimizes queries that enrich a fact table with data from a dimension table. It extends the fact table with values from the dimension table. By default, the system assumes the left table is the larger fact table and the right table is the smaller dimension table. This default is the opposite of the join operator's assumption.
The help cluster includes a database named ContosoSales with sales data. The following query uses lookup to merge the SalesFact and Products tables to return total sales by product category.
SalesFact
| lookup Products on ProductKey
| summarize TotalSales = count() by ProductCategoryName
| order by TotalSales desc
Output
| ProductCategoryName | TotalSales |
|---|---|
| Games and Toys | 966782 |
| TV and Video | 715024 |
| Cameras and camcorders | 323003 |
| Computers | 313487 |
| Home Appliances | 237508 |
| Audio | 192671 |
| Cell phones | 50342 |
| Music, Movies and Audio Books | 33376 |
Note
The lookup operator supports only two join flavors: leftouter and inner.
Join query-generated tables
Join results from the same table.
Suppose you want a list of states that have both lightning and avalanche events. Use the join operator to merge rows from two queries that return distinct states for each event type on the State column.
StormEvents
| where EventType == "Lightning"
| distinct State
| join kind=inner (
StormEvents
| where EventType == "Avalanche"
| distinct State
)
on State
| project State
Output
| State |
|---|
| OREGON |
| UTAH |
| WYOMING |
| WASHINGTON |
| COLORADO |
| IDAHO |
| NEVADA |
Related content
- Learn about different kinds of join operator.
- Perform cross-database and cross-cluster queries.
- Follow the Create geospatial visualizations tutorial.