Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
These features and Azure Databricks platform improvements were released in July 2018.
Note
The release date and content listed below only corresponds to actual deployment of the Azure Public Cloud in most case.
It provide the evolution history of Azure Databricks service on Azure Public Cloud for your reference that may not be consistent with the actual deployment on Azure operated by 21Vianet.
Libraries API supports Python wheel files
July 31-August 7, 2018: Version 2.77
You can now install wheel libraries using the Libraries API. When you install a wheel library on a cluster running Databricks Runtime 4.2 or above,
all of the dependencies specified in the library setup.py file are included. When you install a wheel library on a cluster running Databricks Runtime 4.1 or below, the file is added to the PYTHONPATH variable, without installing the dependencies.
IPython notebook export
July 31-August 7, 2018: Version 2.77
When you export an Azure Databricks notebook to the IPython notebook format, results are now included in the export.
Azure Key Vault-backed secret scopes
July 19-24, 2018: Version 2.76
Secrets now support scopes backed by an Azure Key Vault. Once you create the scope, you can access all the secrets in the corresponding Key Vault from that scope. For details, see Manage secret scopes.
Note
The Azure Key Vault-backed secret scope is a read-only interface to the Key Vault. To manage secrets in Azure Key Vault you must use the Azure Set Secret REST API or Azure portal UI.
Trial Premium workspaces
July 20-24, 2018: Version 2.76
Azure Databricks now offers trial Premium workspaces. During a 14-day trial you have access to free Azure Databricks DBUs. For further information, see Create a workspace.
Cluster mode and High Concurrency clusters
July 19-24, 2018: Version 2.76
When creating a cluster, the Cluster Type option has been renamed to Cluster Mode. The Serverless Pool option has been replaced by High Concurrency cluster mode. High Concurrency clusters are tuned to provide efficient resource utilization, isolation, security, and the best performance when shared by multiple concurrently active users. A High Concurrency cluster supports only SQL, Python, and R languages. High Concurrency clusters provide all the benefits of serverless pools while also allowing flexibility in Spark and resource configuration. For further information, see High Concurrency clusters.
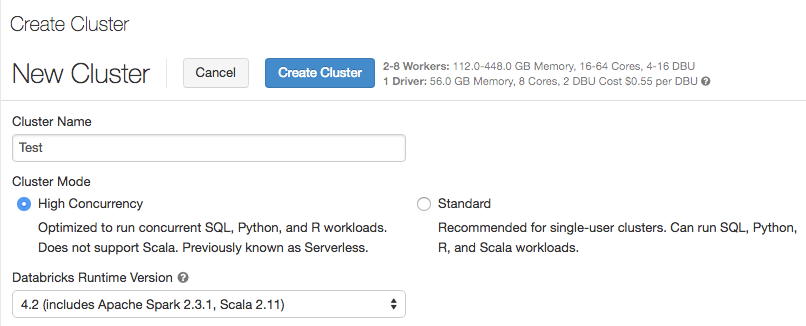
Table access control
July 19-24, 2018: Version 2.76
The Table Access Control checkbox is available only for High Concurrency clusters.

Unavailable cluster node types grayed out
July 3-10, 2018: Version 2.75
Cluster node types that are not available for your subscription and region are now grayed out, and you cannot select them when you create a cluster.
R Markdown support
July 3-10, 2018: Version 2.75
Azure Databricks R notebooks can be exported to R Markdown format, and R Markdown documents can be imported as Azure Databricks notebooks.
Home page redesign, with ability to drop files to import data
July 3-10, 2018: Version 2.75
The new home page adds a cleaner, simpler interface, with links to an improved Getting Started tutorial and the ability to drag and drop files to import data. See Explore and create tables in DBFS.
Widget default behavior
July 3-10, 2018: Version 2.75
The default execution behavior when a new value is selected for a widget is now to Do Nothing. You must update the widget settings if you want to rerun a complete notebook or only value-related commands when you change a widget value. See Configure widget settings.
Table creation UI
July 3-10, 2018: Version 2.75
When you create a table in the UI, you now select Add Data from the Data page.
![]()
See Explore and create tables in DBFS.
Multi-line JSON data import
July 3-10, 2018: Version 2.75
You can now import multi-line JSON data files when you are creating tables. Previously, JSON data files had to be flattened to one line. See Explore and create tables in DBFS.