Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
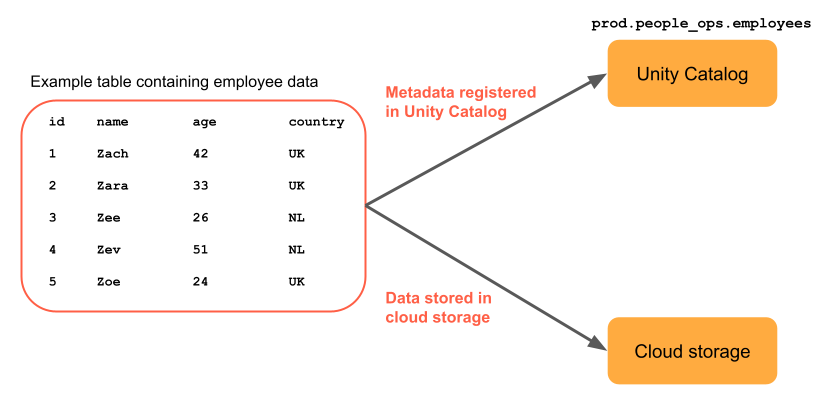
An Azure Databricks table resides in a schema and contains rows of data. The default table type created in Azure Databricks is a Unity Catalog managed table.
The following example shows a managed table named prod.people_ops_employees that contains data about five employees. As a managed table, the data files are stored in Unity Catalog's managed storage location in cloud storage.
Storage formats
Table types in Azure Databricks define how data is owned and accessed. Separately, the storage format defines how the data is physically structured and tracked on disk.
Azure Databricks supports two primary open table storage formats:
- Delta Lake is the default storage format for managed and external tables in Azure Databricks. Delta is also supported for foreign tables.
- Apache Iceberg is supported on managed and foreign tables in Azure Databricks. This format is useful when you're integrating with the Iceberg ecosystem.
These formats add a transactional storage layer that tracks metadata and enables Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability (ACID) compliance, time travel, and other features.
Table types
Azure Databricks offers three primary table types, each designed for different data management scenarios and ownership models. Your choice of table type determines how Azure Databricks manages the underlying data files and metadata.
The primary differentiator for table types in Azure Databricks is the owning catalog, as described in the following table:
| Table type | Managing catalog | Read/write support | Performance optimization | Storage cost optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Managed | Unity Catalog | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Temporary | None (session-scoped managed table) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| External | None (files only) | Yes | Manual only | Manual only |
| Foreign | An external system or catalog service | Read only | No | No |
Managed tables
Managed tables manage underlying data files alongside the metastore registration. Databricks recommends that you use managed tables whenever you create a new table. Unity Catalog managed tables are the default when you create tables in Azure Databricks. See Managed tables.
External tables
External tables, sometimes called unmanaged tables, reference data stored outside of Azure Databricks in an external storage system, such as cloud object storage. They decouple the management of underlying data files from metastore registration. Unity Catalog supports external tables in several formats, including Delta Lake. Unity Catalog external tables can store data files using common formats readable by external systems. See External tables.
Foreign tables
Foreign tables represent data stored in external systems connected to Azure Databricks through Lakehouse Federation. Foreign tables are read-only on Azure Databricks. See Foreign tables.
Temporary tables
Temporary tables are session-scoped tables that store data for the duration of an Azure Databricks session. They're useful for materializing intermediate results without creating permanent tables in your catalog. Azure Databricks automatically drops temporary tables when the session ends, and you don't need catalog or schema privileges to create them. See v.
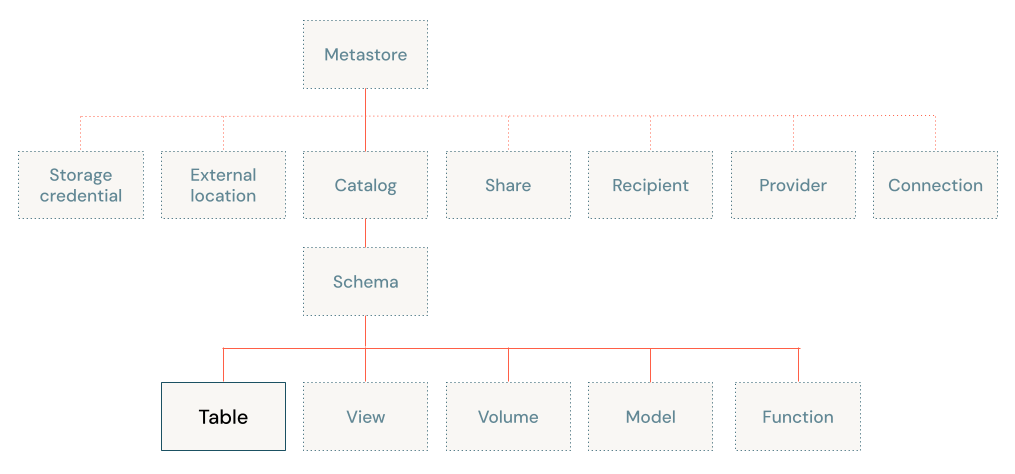
Tables in Unity Catalog
In Unity Catalog, tables sit at the third level of the three-level namespace (catalog.schema.table), as shown in the following diagram:
Basic table permissions
Most table operations require USE CATALOG and USE SCHEMA permissions on the catalog and schema containing a table.
The following table summarizes the additional permissions needed for common table operations in Unity Catalog:
| Operation | Permissions |
|---|---|
| Create a table | CREATE TABLE on the containing schema |
| Query a table | SELECT on the table |
| Update, delete, merge, or insert data to a table | SELECT and MODIFY on the table |
| Drop a table | MANAGE on the table |
| Replace a table | MANAGE on the table, CREATE TABLE on the containing schema |
For SQL syntax reference for these operations, see:
For more information about Unity Catalog permissions, see Manage privileges in Unity Catalog.