Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
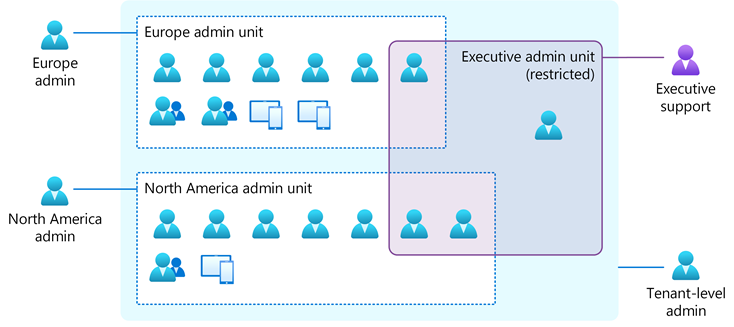
Organizations have resources that need strict security, like the CEO's user account. Currently, a Helpdesk Administrator can potentially gain access to a CEO's account by resetting its password, and a tenant-level Groups Administrator can add users to security groups with financial data access on SharePoint.
Restricted management administrative units allow you to protect specific objects in your tenant from modification by anyone other than a specific set of people that you designate. This allows you to meet security or compliance requirements without having to remove tenant-level role assignments from your administrators.
Why use restricted management administrative units?
Here are some reasons why you might use restricted management administrative units to help manage access in your tenant.
Protect your executive accounts and their devices
You want to protect your C-level executive accounts and their devices from Helpdesk Administrators who would otherwise be able to reset their passwords or access BitLocker recovery keys. You can add your C-level user accounts to a restricted management administrative unit and enable a specific trusted set of administrators who can reset their passwords and access BitLocker recovery keys when needed.
Implement compliance control to only local administrators
You want to implement a compliance control to ensure that certain resources can only be managed by administrators in a specific country/region. You can add those resources in a restricted management administrative unit and assign local administrators to manage those objects. Even Global Administrators won't be allowed to modify the objects unless they assign themselves explicitly to a role scoped to the restricted management administrative unit (which is an auditable event).
Restrict management of sensitive security groups to specific administrators
You're using security groups to control access to sensitive applications in your organization, and you don't want to allow your tenant-scoped administrators who can modify groups to be able to control who can access the applications. You can add those security groups to a restricted management administrative unit and then be sure that only the specific administrators you assign can manage them.
Example scenario
The following diagram shows an example executive restricted management administrative unit (shown in the purple box) with objects that can only be modified by executive support. Tenant-level administrators and local administrators cannot modify the objects in the Executive administrative unit.
Note
Placing objects in a restricted management administrative unit severely restricts who can make changes to the objects. This restriction can cause existing workflows to break.
What objects can be members?
Here are the objects that can be members of restricted management administrative units.
| Microsoft Entra object type | Administrative unit | Restricted management administrative unit |
|---|---|---|
| Users | Yes | Yes |
| Devices | Yes | Yes |
| Groups (Security) | Yes | Yes |
| Groups (Microsoft 365) | Yes | No |
| Groups (Mail enabled security) | Yes | No |
| Groups (Distribution) | Yes | No |
What types of operations are blocked?
For administrators not explicitly assigned at the restricted management administrative unit scope, operations that directly modify the Microsoft Entra properties of objects in restricted management administrative units are blocked, whereas operations on related objects in Microsoft 365 services aren't affected.
| Operation type | Blocked | Allowed |
|---|---|---|
| Read standard properties like user principal name, user photo | ✅ | |
| Modify any Microsoft Entra properties of the user, group, or device | ❌ | |
| Delete the user, group, or device | ❌ | |
| Update password for a user | ❌ | |
| Modify owners or members of the group in the restricted management administrative unit | ❌ | |
| Add users, groups, or devices in a restricted management administrative unit to groups in Microsoft Entra ID | ✅ | |
| Modify email and mailbox settings in Exchange for the user in the restricted management administrative unit | ✅ | |
| Apply policies to a device in a restricted management administrative unit using Intune | ✅ | |
| Add or remove a group as a site owner in SharePoint | ✅ | |
| Assign licenses and update the usage location of users in a restricted management administrative unit | ✅ |
Who can modify objects?
Only administrators with an explicit assignment at the scope of a restricted management administrative unit can change the Microsoft Entra properties of objects in the restricted management administrative unit.
| Role | Scope | Blocked | Allowed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Administrator | Tenant | ❌ | |
| Privileged Role Administrator | Tenant | ❌ | |
| Groups Administrator, User Administrator, or other roles | Resource | ❌ | |
| Owners of groups or devices added to restricted management administrative units | ❌ | ||
| Built-in or custom role | Tenant | ❌ | |
| Roles that can be assigned with administrative unit scope | Restricted management administrative unit | ✅ | |
| Roles that can be assigned with administrative unit scope | Another restricted management administrative unit of which the object is a member | ✅ | |
| Roles that can be assigned with administrative unit scope | Another regular administrative unit of which the object is a member | ❌ |
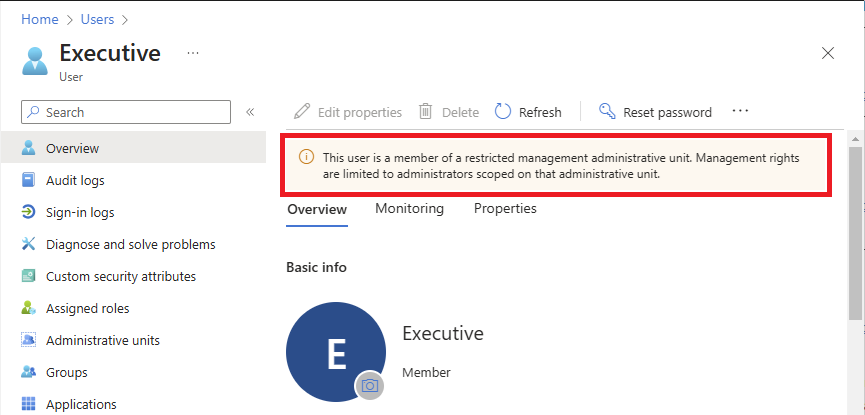
If an administrator with tenant scope attempts to modify an object in a restricted management administrative unit, they will see messages similar to the following:
This user is a member of a restricted management administrative unit. Management rights are limited to administrators scoped on that administrative unit.
Who can manage restricted management administrative units?
The following roles at tenant scope cannot modify objects in restricted management administrative units, but they can manage the restricted management administrative units themselves.
| Role | Scope | Modify objects in restricted management administrative units | Manage restricted management administrative units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Administrator | Tenant | No | Yes |
| Privileged Role Administrator | Tenant | No | Yes |
This management includes the following tasks:
- Create or delete restricted management administrative units
- Add or remove members from a restricted management administrative units
- Assign roles or remove role assignments with restricted management administrative unit scope
- Assign roles to themselves with restricted management administrative units scope
If an administrator with restricted management administrative unit scope changes jobs or leaves the organization, to regain access, a Global Administrator or Privileged Role Administrator can assign another administrator or themselves to the restricted management administrative unit.
Audit logs
To help you track when changes are made to restricted management administrative units, these activities are recorded in the Microsoft Entra audit logs.
| Activity | Category | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Add administrative unit | AdministrativeUnit | IsMemberManagementRestricted = true |
| Add member to restricted management administrative unit | AdministrativeUnit | |
| Remove member from restricted management administrative unit | AdministrativeUnit | |
| Add member to role scoped over Restricted Management Administrative Unit | RoleManagement | |
| Remove member from role scoped over Restricted Management Administrative Unit | RoleManagement |
Limitations
Here are some of the limits and constraints for restricted management administrative units.
- The restricted management setting must be applied during administrative unit creation and can't be changed once the administrative unit is created.
- Groups and users in a restricted management administrative unit can't be managed with Microsoft Entra ID Governance features such as Privileged Identity Management, Entitlement management and Access reviews.
- When a group is configured to have public membership (by setting the visibility property to
Public), users can join the group by using self-service group membership. This configuration is not the default setting, and it is not recommended to configure groups in restricted management administrative units to allow for public membership. This is a temporary limitation and will be removed. - Role-assignable groups, when added to a restricted management administrative unit, can't have their membership modified. Group owners aren't allowed to manage groups in restricted management administrative units and only Global Administrators and Privileged Role Administrators (neither of which can be assigned at administrative unit scope) can modify membership.
- Certain actions might not be possible when an object is in a restricted management administrative unit, if the required role isn't one of the roles that can be assigned at administrative unit scope. For example, a Global Administrator in a restricted management administrative unit can't have their password reset by any other administrator in the system, because there's no administrator role that can be assigned at the administrative unit scope that can reset the password of a Global Administrator. In such scenarios, the Global Administrator would need to be removed from the restricted management administrative unit first, and then have their password reset by another Global Administrator or Privileged Role Administrator.
- When deleting a restricted management administrative unit, it can take up to 30 minutes to remove all protections from the former members.
- A maximum of 100 restricted management administrative units in a tenant.
Programmability
Applications can't modify objects in restricted management administrative units by default. To grant an application access to manage objects in a restricted management administrative unit, you must assign a Microsoft Entra role to the application at the scope of the restricted management administrative unit. If you assign Microsoft Graph application permissions to the application, those permissions won't apply because it's restricted.
License requirements
Restricted management administrative units require a Microsoft Entra ID P1 license for each administrative unit administrator, and Microsoft Entra ID Free licenses for administrative unit members. To find the right license for your requirements, see Comparing generally available features of the Free and Premium editions.