Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service (DPS) supports several built-in allocation policies that determine how it assigns devices across one or more IoT hubs. DPS also includes support for custom allocation policies, which let you create and use your own allocation policies when your IoT scenario requires functionality not provided by the built-in policies.
This article helps you understand how to use and manage DPS allocation policies.
Understand allocation policies
Allocation policies determine how DPS assigns devices to an IoT hub. Each DPS instance has a default allocation policy, but an allocation policy set on an enrollment can override the default allocation policy. Only IoT hubs that are linked to the DPS instance can participate in allocation. Whether a linked IoT hub participates in allocation depends on settings on the enrollment that a device provisions through.
DPS supports four allocation policies:
Evenly weighted distribution: devices are provisioned to an IoT hub using a weighted hash. By default, linked IoT hubs have the same allocation weight setting, so they're equally likely to have devices provisioned to them. The allocation weight of an IoT hub can be adjusted to increase or decrease its likelihood of being assigned. Evenly weighted distribution is the default allocation policy for a DPS instance. If you're provisioning devices to only one IoT hub, we recommend using this policy.
Lowest latency: devices are provisioned to the IoT hub with the lowest latency to the device. If multiple IoT hubs would provide the lowest latency, DPS hashes devices across those hubs based on their configured allocation weight.
Static configuration: devices are provisioned to a single IoT hub, which must be specified on the enrollment.
Custom (Use Azure Function): A custom allocation policy gives you more control over how devices are assigned to an IoT hub. This custom allocation is accomplished by using a custom webhook hosted in Azure Functions to assign devices to an IoT hub. DPS calls your webhook providing all relevant information about the device and the enrollment. Your webhook returns the IoT hub and initial device twin (optional) used to provision the device. Custom payloads can also be passed to and from the device. To learn more, see Understand custom allocation policies with Azure IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service. Can't be set as the DPS instance default policy.
Note
The preceding list shows the names of the allocation policies as they appear in the Azure portal. When setting the allocation policy using the DPS REST API, Azure CLI, and DPS service SDKs, they're referred to as follows: hashed, geolatency, static, and custom.
There are two settings on a linked IoT hub that control how it participates in allocation:
Allocation weight: sets the weight that the IoT hub has when participating in allocation policies that involve multiple IoT hubs. It can be a value between one and 1000. The default is one (or null).
With the Evenly weighted distribution allocation policy, IoT hubs with higher allocation weight values have a greater likelihood of being selected compared to those with lower weight values.
With the Lowest latency allocation policy, the allocation weight value affects the probability of an IoT hub being selected when more than one IoT hub satisfies the lowest latency requirement.
With a Custom allocation policy, whether and how the allocation weight value is used depends on the webhook logic.
Apply allocation policy: specifies whether the IoT hub participates in allocation policy. The default is Yes (true). If set to No (false), devices aren't assigned to the IoT hub. The IoT hub can still be selected on an enrollment, but it doesn't participate in allocation. You can use this setting to temporarily or permanently remove an IoT hub from participating in allocation; for example, if it's approaching the allowed number of devices.
To learn more about linking and managing IoT hubs in your DPS instance, see How to link and manage IoT hubs.
When a device provisions through DPS, the service assigns it to an IoT hub according to the following guidelines:
If the enrollment specifies an allocation policy, use that policy; otherwise, use the default allocation policy for the DPS instance.
If the enrollment specifies one or more IoT hubs, apply the allocation policy across those IoT hubs; otherwise, apply the allocation policy across all of the IoT hubs linked to the DPS instance. If the allocation policy is Static configuration, the enrollment must specify an IoT hub.
Important
When you change an allocation policy or the IoT hubs it applies to, the changes only affect subsequent device registrations. Devices already provisioned to an IoT hub isn't affected. If you want your changes to apply retroactively to these devices, you need to reprovision them. To learn more, see How to reprovision devices.
Set the default allocation policy for the DPS instance
The default allocation policy for the DPS instance is used when an allocation policy isn't specified on an enrollment. Only Evenly weighted distribution, Lowest latency, and Static configuration are supported for the default allocation policy. Custom allocation isn't supported. When a DPS instance is created, its default policy is automatically set to Evenly weighted distribution.
Note
If you set Static configuration as the default allocation policy for a DPS instance, a linked IoT hub must be specified in enrollments that rely on the default policy.
Use the Azure portal to the set default allocation policy
To set the default allocation policy for the DPS instance in the Azure portal:
On the left menu of your DPS instance, select Manage allocation policy.
Select the button for the allocation policy you want to set: Lowest latency, Evenly weighted distribution, or Static configuration. (Custom allocation isn't supported for the default allocation policy.)
Select Save.
Use the Azure CLI to set the default allocation policy
Use the az iot dps update Azure CLI command to set the default allocation policy for the DPS instance. You use --set properties.allocationPolicy to specify the policy. For example, the following command sets the allocation policy to Evenly weighted distribution (the default):
az iot dps update --name MyExampleDps --set properties.allocationPolicy=hashed
DPS also supports setting the default allocation policy using the Create or Update DPS resource REST API, Resource Manager templates, and the DPS Management SDKs.
Set allocation policy and IoT hubs for enrollments
Individual enrollments and enrollment groups can specify an allocation policy and the linked IoT hubs that it should apply to. If the enrollment doesn't specify an allocation policy, then the default allocation policy for the DPS instance is used.
In either case, the following conditions apply:
For Evenly weighted distribution, Lowest latency, and Custom allocation policies, the enrollment can specify which linked IoT hubs should be used. If no IoT hubs are selected in the enrollment, then all of the linked IoT hubs in the DPS instance are used.
For Static configuration, the enrollment must specify a single IoT hub from the list of linked IoT hubs.
For both individual enrollments and enrollment groups, you can specify an allocation policy and the linked IoT hubs to apply it to when you create or update an enrollment.
Use the Azure portal to manage enrollment allocation policy and IoT hubs
To set allocation policy and select IoT hubs on an enrollment in the Azure portal:
On the left menu of your DPS instance, select Manage enrollments.
On the Manage enrollments page:
To create a new enrollment, select either the Enrollment groups or Individual enrollments tab, and then select Add enrollment group or Add individual enrollment.
To update an existing enrollment, select it from the list under either the Enrollment Groups or Individual Enrollments tab.
On the Add Enrollment page (on create) or the Enrollment details page (on update), select the IoT hubs tab. On this tab, you can select the allocation policy you want applied to the enrollment and select the IoT hubs that should be used:
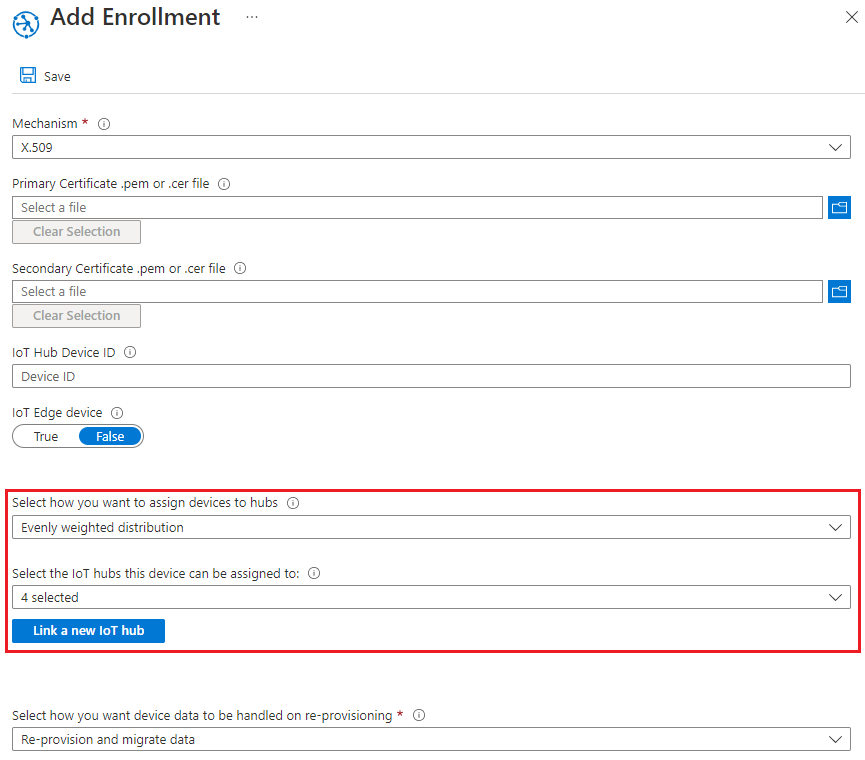
Select the IoT hubs that devices can be assigned to from the drop-down list. If you select the Static configuration allocation policy, you're limited to selecting a single linked IoT hub. For all other allocation policies, all the linked IoT hubs are selected by default, but you can modify this selection using the drop-down. To have the enrollment automatically use linked IoT hubs as they're added to (or deleted from) the DPS instance, unselect all IoT hubs.
Optionally, you can select the Link a new IoT hub button to link a new IoT hub to the DPS instance and make it available in the list of IoT hubs that can be selected. For details about linking an IoT hub, see Add a linked IoT Hub.
Select the allocation policy you want to apply to the enrollment. The default allocation policy for the DPS instance is selected by default. For custom allocation, you also need to specify a custom allocation policy webhook in Azure Functions. For more information, see Tutorial: Use custom allocation policies with Device Provisioning Service (DPS).
Set any other properties needed for the enrollment and then save your settings.
Use the Azure CLI to manage enrollment allocation policy and IoT hubs
Use the az iot dps enrollment create, az iot dps enrollment update, az iot dps enrollment-group create, az iot dps enrollment-group update Azure CLI commands to create or update individual enrollments or enrollment groups.
For example, the following command creates a symmetric key enrollment group that defaults to using the default allocation policy set on the DPS instance and all the IoT hubs linked to the DPS instance:
az iot dps enrollment-group create --dps-name MyExampleDps --enrollment-id MyEnrollmentGroup
The following command updates the same enrollment group to use the Lowest latency allocation policy with IoT hubs named MyExampleHub and MyExampleHub-2:
az iot dps enrollment-group update --dps-name MyExampleDps --enrollment-id MyEnrollmentGroup --allocation-policy geolatency --iot-hubs "MyExampleHub.azure-devices.cn MyExampleHub-2.azure-devices.cn"
DPS also supports setting allocation policy and selected IoT hubs on the enrollment using the Create or Update individual enrollment and Create or Update enrollment group REST APIs, and the DPS service SDKs.
Allocation behavior
Note the following behavior when using allocation policies with IoT hub:
With the Azure CLI, the REST API, and the DPS service SDKs, you can create enrollments with no allocation policy. In this case, DPS uses the default policy for the DPS instance when a device provisions through the enrollment. Changing the default policy setting on the DPS instance changes how devices are provisioned through the enrollment.
With the Azure portal, the allocation policy setting for the enrollment is prepopulated with the default allocation policy. You can keep this setting or change it to another policy, but, when you save the enrollment, the allocation policy is set on the enrollment. Subsequent changes to the service default allocation policy don't change how devices are provisioned through the enrollment.
For the Equally weighted distribution, Lowest latency and Custom allocation policies you can configure the enrollment to use all the IoT hubs linked to the DPS instance:
With the Azure CLI and the DPS service SDKs, create the enrollment without specifying any IoT hubs.
With the Azure portal, the enrollment is prepopulated with all the IoT hubs linked to the DPS instance selected; unselect all the IoT hubs before you save the enrollment.
If no IoT hubs are selected on the enrollment, then whenever a new IoT hub is linked to the DPS instance, it participates in allocation; and vice-versa for an IoT hub that is removed from the DPS instance.
If IoT hubs are specified on an enrollment, the IoT hubs setting on the enrollment must be manually or programmatically updated for a newly linked IoT hub to be added or a deleted IoT hub to be removed from allocation.
Changing the allocation policy or IoT hubs used for an enrollment only affects subsequent registrations through that enrollment. If you want the changes to affect prior registrations, you need to reprovision all previously registered devices.
Limitations
There are some limitations when working with allocation policies and private endpoints. For more information, see Private endpoint limitations.
Next steps
To learn more about linking and managing linked IoT hubs, see How to link and manage IoT hubs.
To learn more about custom allocation policies, see Understand custom allocation policies with Azure IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service.
For an end-to-end example using the lowest latency allocation policy, see Tutorial: Provision for geo latency.
For an end-to-end example using a custom allocation policy, see Tutorial: Use custom allocation policies with Device Provisioning Service (DPS).