Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this quickstart, you will learn how to provision a Windows development machine as a device to an IoT hub using Node.js. This device will use a symmetric key and an individual enrollment to authenticate with a Device Provisioning Service (DPS) instance in order to be assigned to an IoT hub. Sample code from the Azure IoT SDK for Node.js will be used to provision the device.
Although this article demonstrates provisioning with an individual enrollment, you can also use enrollment groups. There are some differences when using enrollment groups. For example, you must use a derived device key with a unique registration ID for the device. Provision devices with symmetric keys provides an enrollment group example. For more information on enrollment groups, see Group Enrollments for Symmetric Key Attestation.
If you're unfamiliar with the process of auto-provisioning, review the provisioning overview.
Also, make sure you've completed the steps in Set up IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service with the Azure portal before continuing with this quickstart. This quickstart requires you to have already created your Device Provisioning Service instance.
This article is oriented toward a Windows-based workstation. However, you can perform the procedures on Linux. For a Linux example, see Provision for multitenancy.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a trial account before you begin.
Prerequisites
- Familiar with provisioning concepts.
- Completion of Set up IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service with the Azure portal.
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Trial Subscription.
- Node.js v4.0+.
- Git.
Create a device enrollment
Sign in to the Azure portal, select the All resources button on the left-hand menu and open your Device Provisioning service (DPS) instance.
Select the Manage enrollments tab, and then select the Add individual enrollment button at the top.
In the Add Enrollment panel, enter the following information, and press the Save button.
Mechanism: Select Symmetric Key as the identity attestation Mechanism.
Auto-generate keys: Check this box.
Registration ID: Enter a registration ID to identify the enrollment. Use only lowercase alphanumeric and dash ('-') characters. For example, symm-key-nodejs-device-01.
IoT Hub Device ID: Enter a device identifier. For example, nodejs-device-01.
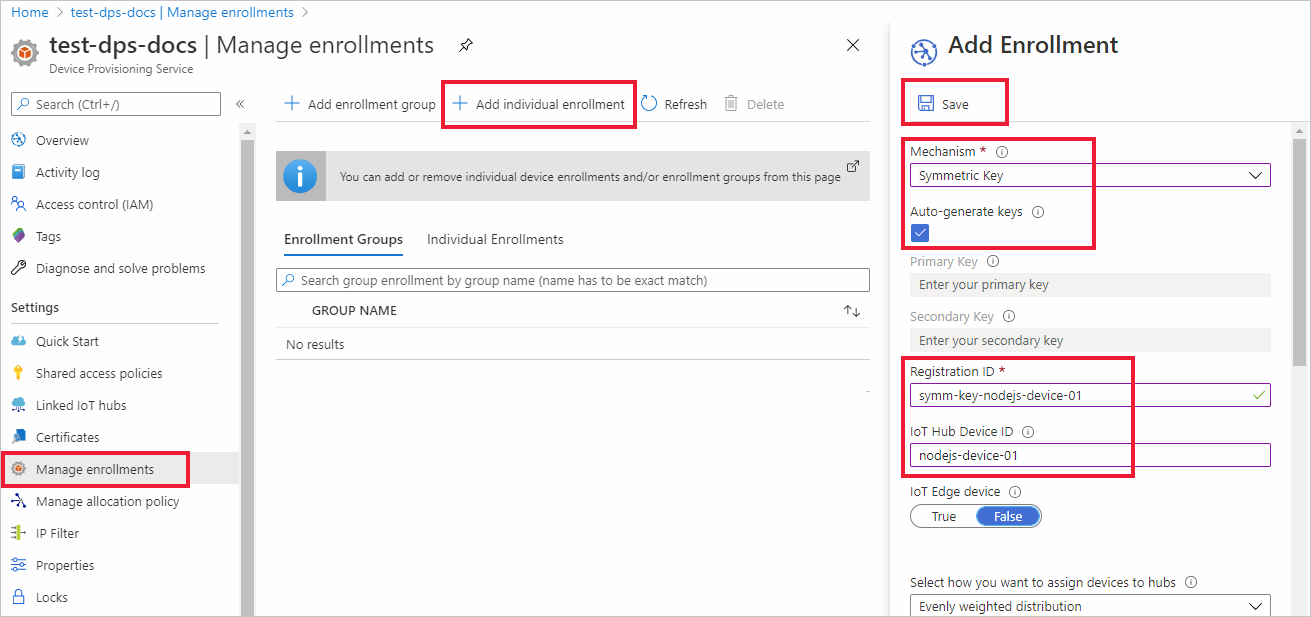
Once you have saved your enrollment, the Primary Key and Secondary Key will be generated and added to the enrollment entry. Your symmetric key device enrollment appears as symm-key-nodejs-device-01 under the Registration ID column in the Individual Enrollments tab.
Open the enrollment and copy the value of your generated Primary Key. You will use this key value and the Registration ID later when you add environment variables for use with the device provisioning sample code.
Prepare the Node.js environment
Open a Git CMD or Git Bash command-line environment. Clone the Azure IoT SDK for Node.js GitHub repository using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/Azure/azure-iot-sdk-node.git --recursive
Prepare the device provisioning code
In this section, you will add the following four environment variables that will be used as parameters for the device provisioning sample code to provision your symmetric key device.
PROVISIONING_HOSTPROVISIONING_IDSCOPEPROVISIONING_REGISTRATION_IDPROVISIONING_SYMMETRIC_KEY
The provisioning code will contact the DPS instance based on these variables in order to authenticate your device. The device will then be assigned to an IoT hub already linked to the DPS instance based on the individual enrollment configuration. Once provisioned, the sample code will send some test telemetry to the IoT hub.
In the Azure portal, on your Device Provisioning Service menu, select Overview and copy your Service Endpoint and ID Scope. You will use these values for the
PROVISIONING_HOSTandPROVISIONING_IDSCOPEenvironment variables.
Open a command prompt for executing Node.js commands, and navigate to the following provisioning/device/samples directory.
cd azure-iot-sdk-node/provisioning/device/samplesIn the provisioning/device/samples folder, open register_symkey.js and review the code.
Notice the sample code sets a custom payload...
provisioningClient.setProvisioningPayload({a: 'b'});This code is not needed with this quick start. This code is an example of setting a custom payload if you wanted to use a custom allocation function to assign your device to an IoT Hub. For more information, see Tutorial: Use custom allocation policies.
The
provisioningClient.register()method attempts the registration of your device.No changes will be necessary to the sample code to register your device.
In your command prompt, add the environment variables for the provisioning host, ID Scope, registration ID, and primary symmetric key you copied from the individual enrollment in the previous section.
The following commands are examples to show command syntax. Make sure to use your correct values.
set PROVISIONING_HOST=test-dps-docs.azure-devices-provisioning.cnset PROVISIONING_IDSCOPE=0ne00000A0Aset PROVISIONING_REGISTRATION_ID=symm-key-nodejs-device-01set PROVISIONING_SYMMETRIC_KEY=sbDDeEzRuEuGKag+kQKV+T1QGakRtHpsERLP0yPjwR93TrpEgEh/Y07CXstfha6dhIPWvdD1nRxK5T0KGKA+nQ==Build and run the sample code using the following commands.
npm installnode register_symkey.jsThe expected output should look similar to the following that shows the linked IoT hub that the device was assigned to based on the individual enrollment settings. A "Hello World" string is sent to the hub as a test message:
D:\Docs\test\azure-iot-sdk-node\provisioning\device\samples>node register_symkey.js registration succeeded assigned hub=docs-test-iot-hub.azure-devices.cn deviceId=nodejs-device-01 payload=undefined Client connected send status: MessageEnqueuedIn the Azure portal, navigate to the IoT hub linked to your provisioning service and open the IoT devices blade. After successfully provisioning the symmetric key device to the hub, the device ID is shown with STATUS as enabled. You might need to press the Refresh button at the top if you already opened the blade prior to running the device sample code.

Note
If you changed the initial device twin state from the default value in the enrollment entry for your device, it can pull the desired twin state from the hub and act accordingly. For more information, see Understand and use device twins in IoT Hub.
Clean up resources
If you plan to continue working on and exploring the device client sample, do not clean up the resources created in this quickstart. If you do not plan to continue, use the following steps to delete all resources created by this quickstart.
- From the left-hand menu in the Azure portal, select All resources and then select your Device Provisioning service. Open Manage Enrollments for your service, and then select the Individual Enrollments tab. Select the check box next to the REGISTRATION ID of the device you enrolled in this quickstart, and press the Delete button at the top of the pane.
- From the left-hand menu in the Azure portal, select All resources and then select your IoT hub. Open IoT devices for your hub, select the check box next to the DEVICE ID of the device you registered in this quickstart, and then press the Delete button at the top of the pane.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you provisioned a Windows-based symmetric key device to your IoT hub using the IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service. To learn how to provision X.509 certificate devices using Node.js, continue with the quickstart below for X.509 devices.