Using cluster resource propagation (preview)
Azure Kubernetes Fleet Manager (Fleet) resource propagation, based on an open-source cloud-native multi-cluster solution allows for deployment of any Kubernetes objects to fleet member clusters according to specified criteria. Workload orchestration can handle many use cases where an application needs to be deployed across multiple clusters, including the following and more:
- An infrastructure application that needs to be on all clusters in the fleet
- A web application that should be deployed into multiple clusters in different regions for high availability, and should have updates rolled out in a nondisruptive manner
- A batch compute application that should be deployed into clusters with inexpensive spot node pools available
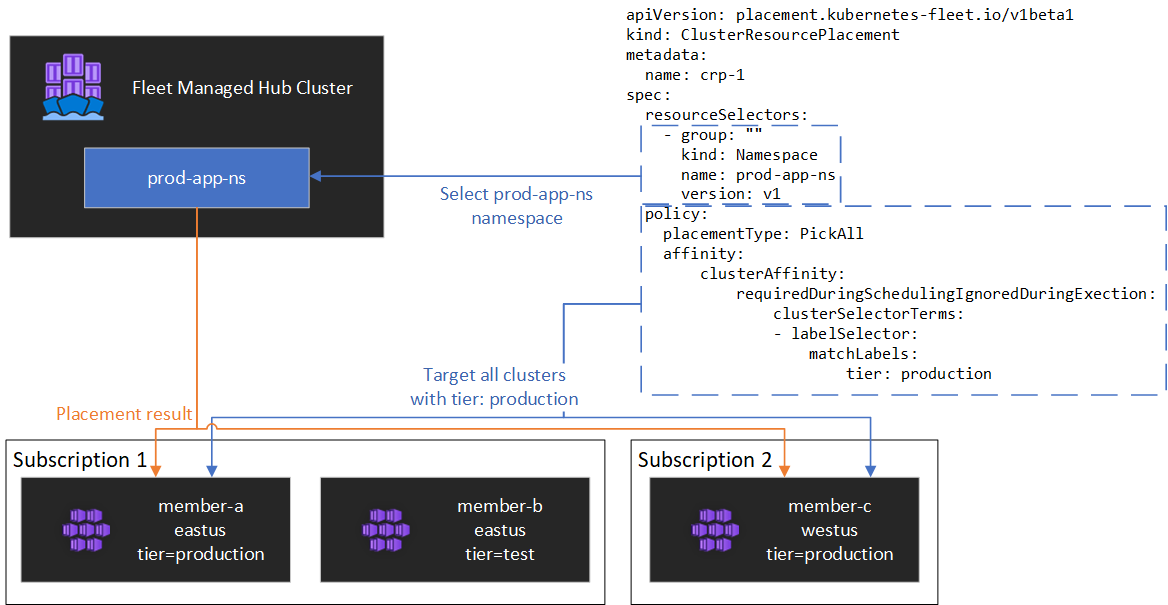
Fleet workload placement can deploy any Kubernetes objects to clusters In order to deploy resources to hub member clusters, the objects must be created in a Fleet hub cluster, and a ClusterResourcePlacement object must be created to indicate how the objects should be placed.
Important
Azure Kubernetes Fleet Manager preview features are available on a self-service, opt-in basis. Previews are provided "as is" and "as available," and they're excluded from the service-level agreements and limited warranty. Azure Kubernetes Fleet Manager previews are partially covered by customer support on a best-effort basis. As such, these features aren't meant for production use.
Prerequisites
- Read the conceptual overview of this feature, which provides an explanation of
MemberClusterandClusterResourcePlacementreferenced in this document. - You must have a Fleet resource with a hub cluster and member clusters. If you don't have this resource, follow Quickstart: Create a Fleet resource and join member clusters.
- Member clusters must be labeled appropriately in the hub cluster to match the desired selection criteria. Example labels could include region, environment, team, availability zones, node availability, or anything else desired.
- You must gain access to the Kubernetes API of the hub cluster by following the steps in Access the Kubernetes API of the Fleet resource.
Resource placement with ClusterResourcePlacement resources
A ClusterResourcePlacement object is used to tell the Fleet scheduler how to place a given set of cluster-scoped objects from the hub cluster into member clusters. Namespace-scoped objects like Deployments, StatefulSets, DaemonSets, ConfigMaps, Secrets, and PersistentVolumeClaims are included when their containing namespace is selected.
(To propagate to the member clusters without any unintended side effects, the ClusterResourcePlacement object supports using ConfigMap to envelope the object.) Multiple methods of selection can be used:
- Group, version, and kind - select and place all resources of the given type
- Group, version, kind, and name - select and place one particular resource of a given type
- Group, version, kind, and labels - select and place all resources of a given type that match the labels supplied
Once resources are selected, multiple types of placement are available:
PickAllplaces the resources into all available member clusters. This policy is useful for placing infrastructure workloads, like cluster monitoring or reporting applications.PickFixedplaces the resources into a specific list of member clusters by name.PickNis the most flexible placement option and allows for selection of clusters based on affinity or topology spread constraints, and is useful when spreading workloads across multiple appropriate clusters to ensure availability is desired.
Using a PickAll placement policy
To deploy a workload across all member clusters in the fleet (optionally matching a set of criteria), a PickAll placement policy can be used. To deploy the test-deployment Namespace and all of the objects in it across all of the clusters labeled with environment: production, create a ClusterResourcePlacement object as follows:
apiVersion: placement.kubernetes-fleet.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterResourcePlacement
metadata:
name: crp-1
spec:
policy:
placementType: PickAll
affinity:
clusterAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
clusterSelectorTerms:
- labelSelector:
matchLabels:
environment: production
resourceSelectors:
- group: ""
kind: Namespace
name: prod-deployment
version: v1
This simple policy takes the test-deployment namespace and all resources contained within it and deploys it to all member clusters in the fleet with the given environment label. If all clusters are desired, remove the affinity term entirely.
Using a PickFixed placement policy
If a workload should be deployed into a known set of member clusters, a PickFixed policy can be used to select the clusters by name. This ClusterResourcePlacement deploys the test-deployment namespace into member clusters cluster1 and cluster2:
apiVersion: placement.kubernetes-fleet.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterResourcePlacement
metadata:
name: crp-2
spec:
policy:
placementType: PickFixed
clusterNames:
- cluster1
- cluster2
resourceSelectors:
- group: ""
kind: Namespace
name: test-deployment
version: v1
Using a PickN placement policy
The PickN placement policy is the most flexible option and allows for placement of resources into a configurable number of clusters based on both affinities and topology spread constraints.
PickN with affinities
Using affinities with PickN functions similarly to using affinities with pod scheduling. Both required and preferred affinities can be set. Required affinities prevent placement to clusters that don't match them; preferred affinities allow for ordering the set of valid clusters when a placement decision is being made.
As an example, the following ClusterResourcePlacement object places a workload into three clusters. Only clusters that have the label critical-allowed: "true" are valid placement targets, with preference given to clusters with the label critical-level: 1:
apiVersion: placement.kubernetes-fleet.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterResourcePlacement
metadata:
name: crp
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- ...
policy:
placementType: PickN
numberOfClusters: 3
affinity:
clusterAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
weight: 20
preference:
- labelSelector:
matchLabels:
critical-level: 1
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
clusterSelectorTerms:
- labelSelector:
matchLabels:
critical-allowed: "true"
PickN with topology spread constraints:
Topology spread constraints can be used to force the division of the cluster placements across topology boundaries to satisfy availability requirements (for example, splitting placements across regions or update rings). Topology spread constraints can also be configured to prevent scheduling if the constraint can't be met (whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule) or schedule as best possible (whenUnsatisfiable: ScheduleAnyway).
This ClusterResourcePlacement object spreads a given set of resources out across multiple regions and attempts to schedule across member clusters with different update days:
apiVersion: placement.kubernetes-fleet.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterResourcePlacement
metadata:
name: crp
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- ...
policy:
placementType: PickN
topologySpreadConstraints:
- maxSkew: 2
topologyKey: region
whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule
- maxSkew: 2
topologyKey: updateDay
whenUnsatisfiable: ScheduleAnyway
For more details on how placement works with topology spread constraints, review the documentation in the open source fleet project on the topic..
Update strategy
Azure Kubernetes Fleet uses a rolling update strategy to control how updates are rolled out across multiple cluster placements. The default settings are in this example:
apiVersion: placement.kubernetes-fleet.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterResourcePlacement
metadata:
name: crp
spec:
resourceSelectors:
- ...
policy:
...
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 25%
maxSurge: 25%
unavailablePeriodSeconds: 60
The scheduler will roll updates to each cluster sequentially, waiting at least unavailablePeriodSeconds between clusters. Rollout status is considered successful if all resources were correctly applied to the cluster. Rollout status checking doesn't cascade to child resources - for example, it doesn't confirm that pods created by a deployment become ready.
For more details on cluster rollout strategy, see the rollout strategy documentation in the open source project.
Placement status
The fleet scheduler updates details and status on placement decisions onto the ClusterResourcePlacement object. This information can be viewed via the kubectl describe crp <name> command. The output includes the following information:
- The conditions that currently apply to the placement, which include if the placement was successfully completed
- A placement status section for each member cluster, which shows the status of deployment to that cluster
This example shows a ClusterResourcePlacement that deployed the test namespace and the test-1 ConfigMap it contained into two member clusters using PickN. The placement was successfully completed and the resources were placed into the aks-member-1 and aks-member-2 clusters.
Name: crp-1
Namespace:
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: placement.kubernetes-fleet.io/v1beta1
Kind: ClusterResourcePlacement
Metadata:
...
Spec:
Policy:
Number Of Clusters: 2
Placement Type: PickN
Resource Selectors:
Group:
Kind: Namespace
Name: test
Version: v1
Revision History Limit: 10
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:14:52Z
Message: found all the clusters needed as specified by the scheduling policy
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: SchedulingPolicyFulfilled
Status: True
Type: ClusterResourcePlacementScheduled
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:23:43Z
Message: All 2 cluster(s) are synchronized to the latest resources on the hub cluster
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: SynchronizeSucceeded
Status: True
Type: ClusterResourcePlacementSynchronized
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:23:43Z
Message: Successfully applied resources to 2 member clusters
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: ApplySucceeded
Status: True
Type: ClusterResourcePlacementApplied
Placement Statuses:
Cluster Name: aks-member-1
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:14:52Z
Message: Successfully scheduled resources for placement in aks-member-1 (affinity score: 0, topology spread score: 0): picked by scheduling policy
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: ScheduleSucceeded
Status: True
Type: ResourceScheduled
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:23:43Z
Message: Successfully Synchronized work(s) for placement
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: WorkSynchronizeSucceeded
Status: True
Type: WorkSynchronized
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:23:43Z
Message: Successfully applied resources
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: ApplySucceeded
Status: True
Type: ResourceApplied
Cluster Name: aks-member-2
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:14:52Z
Message: Successfully scheduled resources for placement in aks-member-2 (affinity score: 0, topology spread score: 0): picked by scheduling policy
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: ScheduleSucceeded
Status: True
Type: ResourceScheduled
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:23:43Z
Message: Successfully Synchronized work(s) for placement
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: WorkSynchronizeSucceeded
Status: True
Type: WorkSynchronized
Last Transition Time: 2023-11-10T08:23:43Z
Message: Successfully applied resources
Observed Generation: 5
Reason: ApplySucceeded
Status: True
Type: ResourceApplied
Selected Resources:
Kind: Namespace
Name: test
Version: v1
Kind: ConfigMap
Name: test-1
Namespace: test
Version: v1
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal PlacementScheduleSuccess 12m (x5 over 3d22h) cluster-resource-placement-controller Successfully scheduled the placement
Normal PlacementSyncSuccess 3m28s (x7 over 3d22h) cluster-resource-placement-controller Successfully synchronized the placement
Normal PlacementRolloutCompleted 3m28s (x7 over 3d22h) cluster-resource-placement-controller Resources have been applied to the selected clusters
Placement changes
The Fleet scheduler prioritizes the stability of existing workload placements, and thus the number of changes that cause a workload to be removed and rescheduled is limited.
- Placement policy changes in the
ClusterResourcePlacementobject can trigger removal and rescheduling of a workload- Scale out operations (increasing
numberOfClusterswith no other changes) will only place workloads on new clusters and won't affect existing placements.
- Scale out operations (increasing
- Cluster changes
- A new cluster becoming eligible may trigger placement if it meets the placement policy - for example, a
PickAllpolicy. - A cluster with a placement is removed from the fleet will attempt to re-place all affected workloads without affecting their other placements.
- A new cluster becoming eligible may trigger placement if it meets the placement policy - for example, a
Resource-only changes (updating the resources or updating the ResourceSelector in the ClusterResourcePlacement object) will be rolled out gradually in existing placements but will not trigger rescheduling of the workload.
Access the Kubernetes API of the Fleet resource cluster
If the Azure Kubernetes Fleet Manager resource was created with the hub cluster enabled, then it can be used to centrally control scenarios like Kubernetes object propagation. To access the Kubernetes API of the Fleet resource cluster, follow the steps in the Access the Kubernetes API of the Fleet resource cluster with Azure Kubernetes Fleet Manager article.
Next steps
- Review the
ClusterResourcePlacementdocumentation and more in the open-source fleet repository for more examples - Review the API specifications for all fleet custom resources.
- Review more information about the fleet scheduler and how placement decisions are made.
- Review our troubleshooting guide to help resolve common issues related to the Fleet APIs.