Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Managed feature store lets you independently develop and productionize features. You provide a feature set specification, and the system handles serving, securing, and monitoring the features. This approach eliminates the underlying feature engineering pipeline setup and management overhead.
The feature store integrates across the machine learning lifecycle, enabling you to experiment and ship models faster, increase model reliability, and reduce operational costs.
For more information about top-level entities in feature store, including feature set specifications, see Understanding top-level entities in managed feature store.
What are features?
A feature is input data for your model. In enterprise data-driven use cases, a feature often transforms historical data through simple aggregates, window aggregates, row-level transforms, and similar operations. For example, consider a customer churn machine learning model. The model inputs might include customer interaction data like 7day_transactions_sum (number of transactions in the past seven days) or 7day_complaints_sum (number of complaints in the past seven days). Both aggregate functions compute values from the previous seven days of data.
Problems solved by feature store
To better understand managed feature store, first understand the problems that a feature store solves:
Search and reuse features - Search and reuse features that your team creates to avoid redundant work and deliver consistent predictions.
Create features with transformations - Create new features with transformation capabilities to address feature engineering requirements in an agile, dynamic way.
Operationalize feature engineering pipelines - The system operationalizes and manages the feature engineering pipelines required for transformation and materialization, freeing your team from operational aspects.
Maintain online/offline consistency - Use the same feature pipeline for both training data generation and inference to provide online/offline consistency and avoid training/serving skew.
Share managed feature store
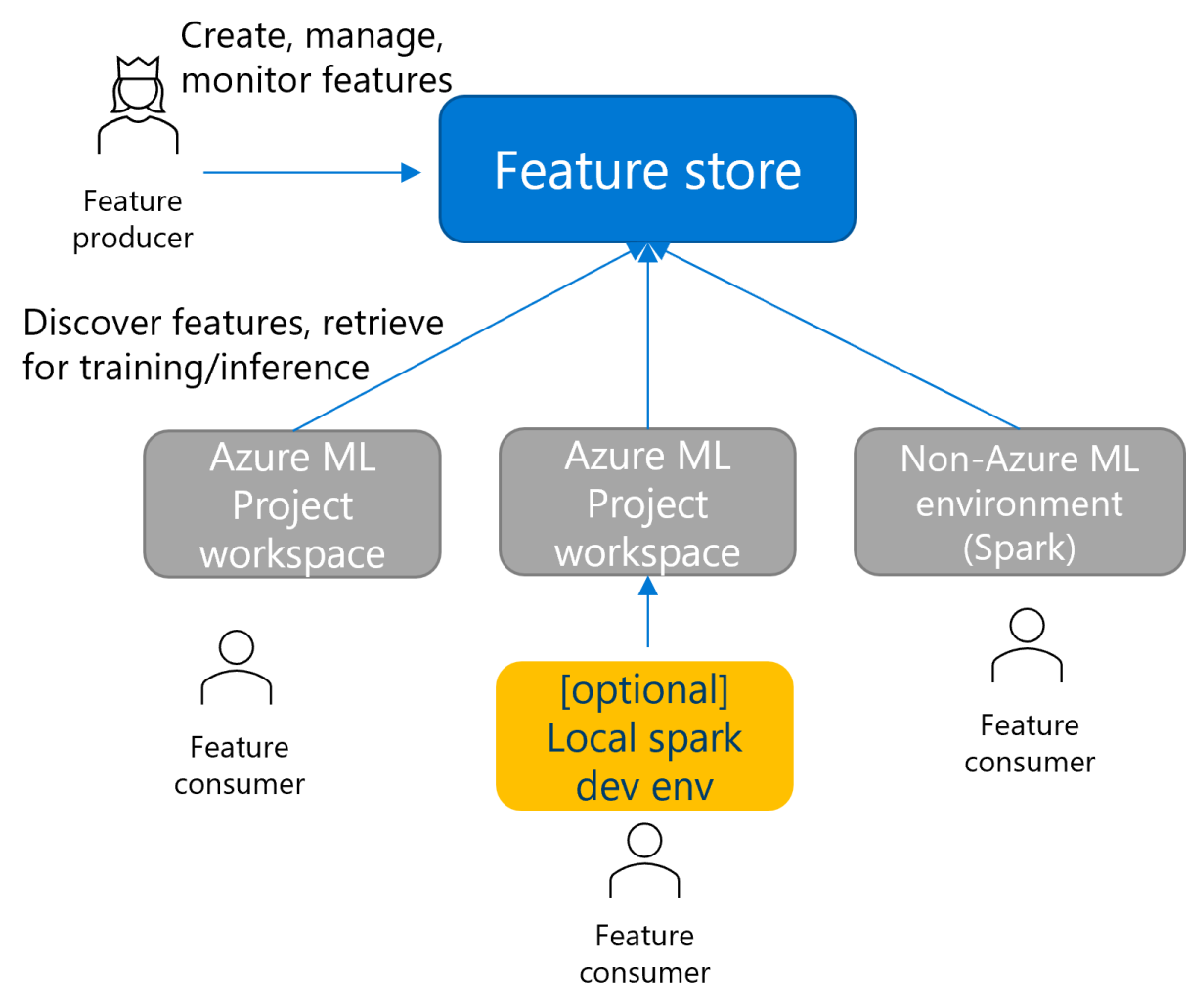
Feature store is a workspace type that multiple project workspaces can use. You can consume features from Spark-based environments other than Azure Machine Learning, such as Azure Databricks. You can also perform local development and testing of features.
Feature store overview
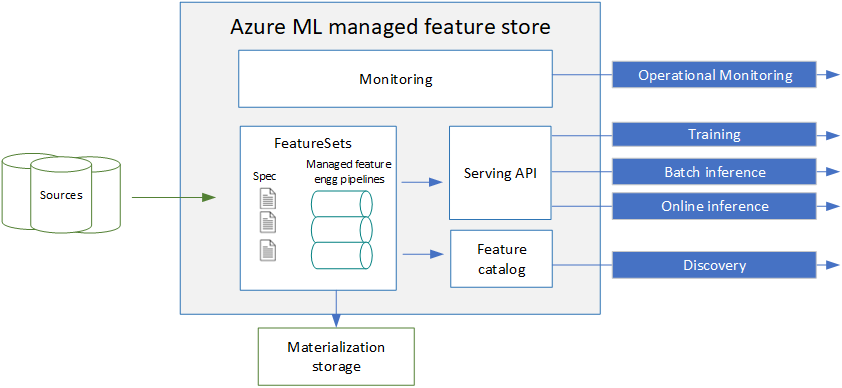
For a managed feature store, you provide a feature set specification, and the system handles serving, securing, and monitoring your features. A feature set specification contains feature definitions and optional transformation logic. You can also declaratively provide materialization settings to materialize to an offline store (ADLS Gen2). The system generates and manages the underlying feature materialization pipelines. Use the feature catalog to search, share, and reuse features. With the serving API, you can look up features to generate data for training and inference. The serving API can pull data directly from the source or from an offline materialization store for training or batch inference. The system also provides capabilities for monitoring feature materialization jobs.
Benefits of using Azure Machine Learning managed feature store
- Increases agility in shipping the model (prototyping to operationalization)
- Discover and reuse features instead of creating features from scratch
- Faster experimentation with local development and testing of new features with transformation support and use of feature retrieval spec as a connective tissue in the MLOps flow
- Declarative materialization and backfill
- Prebuilt constructs: feature retrieval component and feature retrieval spec
- Improves reliability of ML models
- Consistent feature definition across business units and organizations
- Feature sets are versioned and immutable: Newer model versions can use newer feature versions without disrupting older model versions
- Monitor feature set materialization
- Materialization avoids training/serving skew
- Feature retrieval supports point-in-time temporal joins (also known as time travel) to avoid data leakage
- Reduces cost
- Reuse features created by others in the organization
- Materialization and monitoring are system managed to reduce engineering cost
Discover and manage features
Managed feature store provides these capabilities for feature discovery and management:
- Search and reuse features - You can search and reuse features across feature stores.
- Versioning support - Feature sets are versioned and immutable, which allows you to independently manage the feature set lifecycle. You can deploy new model versions with different feature versions, and avoid disruption of the older model version.
- View cost at feature store level - The primary cost associated with feature store usage involves managed Spark materialization jobs. You can see this cost at the feature store level.
- Feature set usage - You can see the list of registered models using the feature sets.
Feature transformation
Feature transformation involves dataset feature modification to improve model performance. Transformation code, defined in a feature spec, handles feature transformation. For faster experimentation, transformation code performs calculations on source data, and allows for local development and testing of transformations.
Managed feature store provides these feature transformation capabilities:
- Support for custom transformations - You can write a Spark transformer to develop features with custom transformations, such as window-based aggregates.
- Support for precomputed features - You can bring precomputed features into feature store, and serve them without writing code.
- Local development and testing - With a Spark environment, you can fully develop and test feature sets locally.
Feature materialization
Materialization computes feature values for a given feature window and persists those values in a materialization store. Feature data can then be retrieved more quickly and reliably for training and inference purposes.
- Managed feature materialization pipeline - Declaratively specify the materialization schedule, and the system handles the scheduling, precomputation, and materialization of the values into the materialization store.
- Backfill support - Perform on-demand materialization of feature sets for a given feature window.
- Managed Spark support for materialization - Azure Machine Learning managed Spark (in serverless compute instances) runs the materialization jobs, eliminating the need to set up and manage Spark infrastructure.
Note
Both offline store (ADLS Gen2) and online store (Redis) materialization are currently supported.
Feature retrieval
Azure Machine Learning includes a built-in component that handles offline feature retrieval, allowing you to use features in the training and batch inference steps of an Azure Machine Learning pipeline job.
Managed feature store provides these feature retrieval capabilities:
- Declarative training data generation - With the built-in feature retrieval component, generate training data in your pipelines without writing code
- Declarative batch inference data generation - With the same built-in feature retrieval component, generate batch inference data
- Programmatic feature retrieval - Use Python SDK
get_offline_features()to generate training and inference data
Monitoring
Managed feature store provides the following monitoring capabilities:
- Status of materialization jobs - View the status of materialization jobs using the UI, CLI, or SDK
- Notification on materialization jobs - Set up email notifications for different statuses of the materialization jobs
Security
Managed feature store provides these security capabilities:
- RBAC - Role-based access control for feature store, feature set, and entities
- Query across feature stores - Create multiple feature stores with different access permissions for users, while allowing querying (for example, generate training data) across multiple feature stores