Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server, the error log is available to users to configure and access. Error logs in MySQL gather diagnostic messages during server startup and shutdown, and while the server is running, information that can help proactive troubleshooting. For more information about the MySQL error log, see the Error log section in the MySQL documentation.
Under Preview phase, error logs are available under Server logs only, error logs can't be emitted to Azure Diagnostic logs.
In Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server, enabling the error log under Server logs in the Azure portal records details in multiple files named using the syntax mysql-error-servername-timestamp.log. In the file name, the timestamp (in GMT/UTC) associated with when the file was generated is appended, identifying the specific time that that log entries were recorded. For more information, see Server logs retention.
Enable error logs (Preview)
Users can access and configure the error logs in Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server via the Server logs feature, which can be enabled using the Azure portal or List and download Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server logs by using the Azure CLI.
After the feature is enabled, your MySQL flexible server starts capturing events and writes them to a series of files saved as activity occurs.
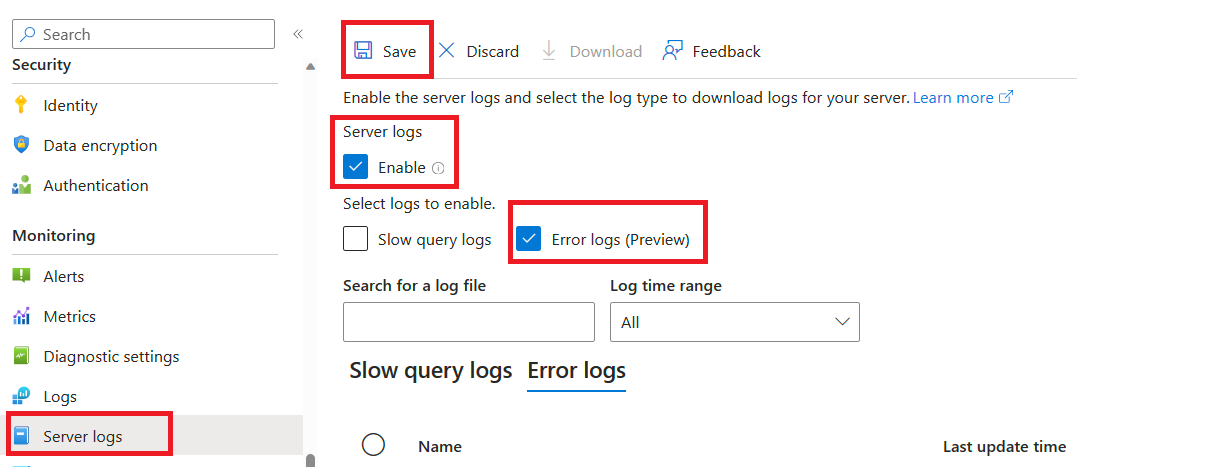
To enable Error logs, perform the following steps.
In the Azure portal, navigate to your flexible server, and then, under Monitoring, select Server logs.
Under Server logs, select the Enable check box, which enables the server logs features
Under Select logs to enable, select the Error logs check box.
Select Save to proceed with deployment.
You can also enable Error logs on your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server by enabling the server parameter named "error_server_log_file" via the Server parameters pane or via the Configure server parameters in Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server using the Azure CLI.
Ensure that the Server logs feature is activated by selecting the Enable checkbox in the Server logs pane. Alternatively, set the server parameter "log_output" to FILE to enable server logs. Failure to perform either of these actions result in FILE logging not being enabled for your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server .
Access error logs
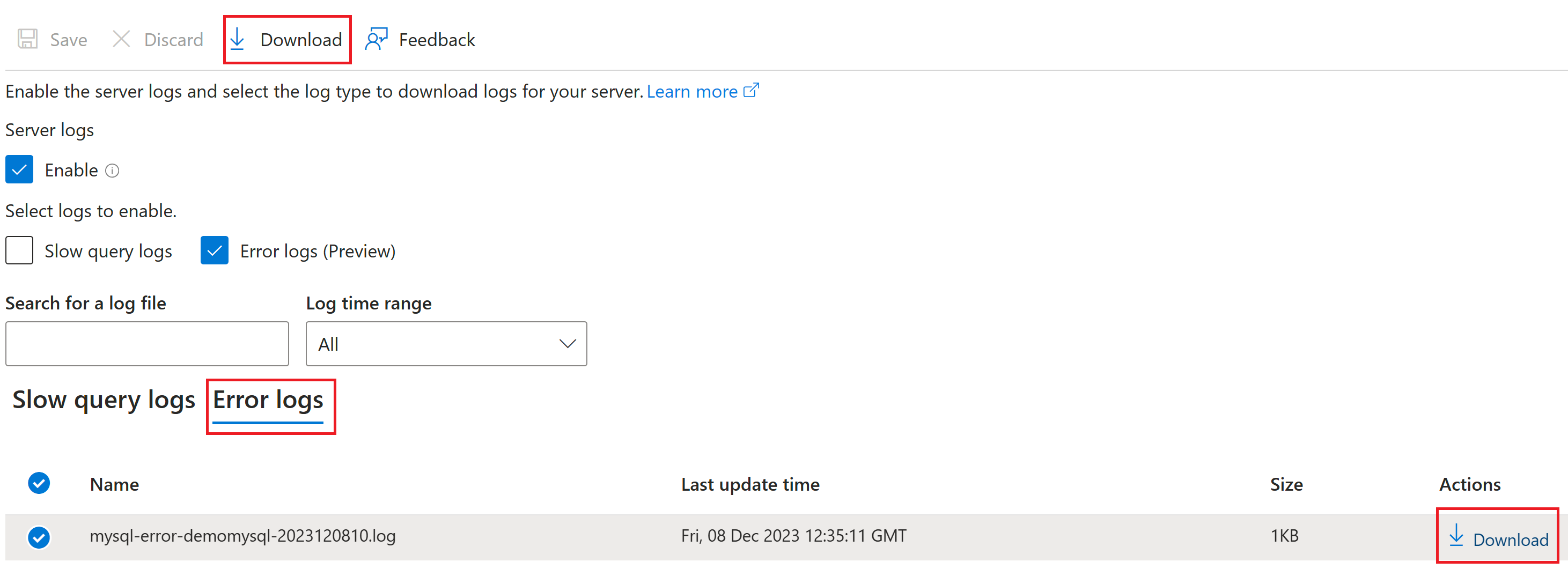
You can download the error logs for further analysis of your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server. To download the logs, in the Azure portal, navigate to the Server logs section, and then select the Error logs tab, as shown.
Under Name, select the log file you want to download, and then, under Action, select Download.
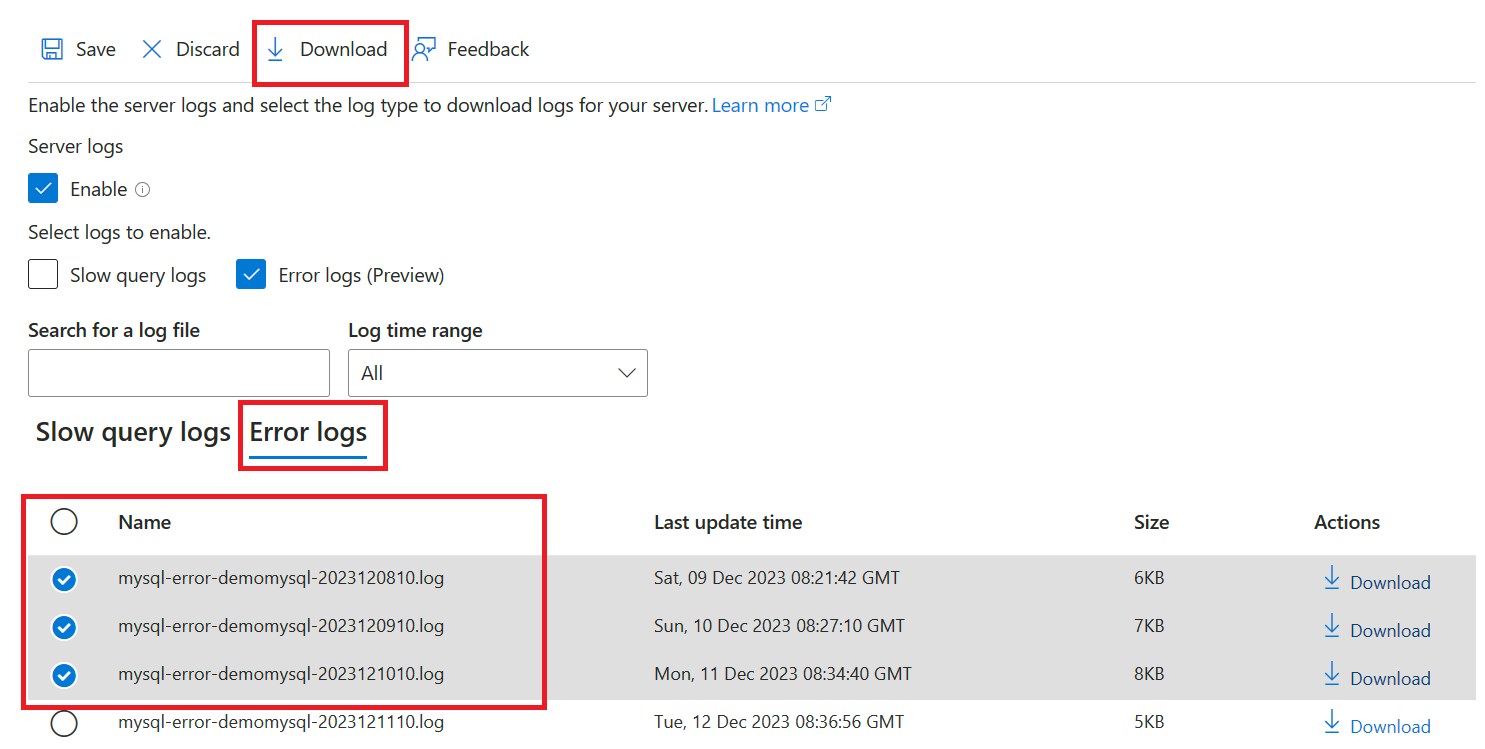
To download multiple log files at one time, under Name, select the files you want to download, select Download.
Access error logs using Azure CLI
You can list the server logs from your flexible server by using the following command.
az mysql flexible-server server-logs list --resource-group <myresourcegroup> --server-name <server_name> --out table
To download the mentioned server logs to your current directory, use the following command:
az mysql flexible-server server-logs download --resource-group <myresourcegroup> --server-name <server_name> --name <mysql-error-<server_name>-<timestamp>.log>
For more information, see how to download the server logs files via the Azure portal or via the Azure CLI.
Error logs under server logs retention
When logging is enabled for an Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server, logs are available up to seven days from their creation. If the total size of the available logs exceeds 7 GB, then the oldest files are deleted until space is available. The 7-GB storage limit for server logs is available free of cost and can't be extended. Logs are rotated every 24 hours or 500 MB, whichever comes first.
Importantly, you can download the logs before rotation, ensuring they have access to valuable server logs at any point within the retention period.
For more detailed information on log rotation schedules and storage limits for various log types, refer to the documentation on Server log retention.
Handle of Personal Identifiable Information (PII) and Sensitive Data
In Azure MySQL Flexible Server, we prioritize the security of your data. As such, any Personal Identifiable Information (PII) or sensitive data such as hostnames, IP addresses, usernames, and database names in error logs are hashed out due to security reasons. This means that while you can gain insights into the operational status and potential issues of your server from the error logs, specific details that could compromise the security of your server are not directly accessible. However, if you need more detailed information on errors, such as "Access Denied" errors where the username would typically be printed, you can find this information in the audit logs of Azure MySQL Flexible Server. The audit logs provide a more granular view of the activities and transactions on your server, allowing you to troubleshoot and resolve issues more effectively.
For more information on how to access and interpret the audit logs, please refer to the official documentation.
Frequently asked questions
Question: My error logs contain the note as shown, what does this mean?
[Note] [Server] Access denied for user ''@'xx.xx.xx.X' (using password: NO).
Answer: This note indicates that an attempt to connect to your MySQL server was unsuccessful due to incorrect or missing authentication details. Specifically, the username provided is empty(''@'xx.xx.xx.X') and no password was entered (using password: NO). This note could indicate an unauthorized attempt to access your database. If your server is publicly accessible, it remains exposed to the internet and can be a target for unauthorized access attempts. To enhance the security of your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server , disable public access or limit access using firewall rules..