Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article provides step-by-step guidance to validate and diagnose connectivity for your Azure Private Link setup.
With Azure Private Link, you can access Azure platform as a service (PaaS) services and Azure hosted customer or partner services over a private endpoint in your virtual network. Traffic between your virtual network and the service traverses over the Microsoft Azure backbone network, which eliminates exposure from the public internet. You can also create your own private link service in your virtual network and deliver it privately to your customers.
You can enable your service that runs behind the Standard tier of Azure Load Balancer for Private Link access. Consumers of your service can create a private endpoint inside their virtual network and map it to this service to access it privately.
Here are the connectivity scenarios that are available with Private Link:
Virtual network from the same region
Regionally peered virtual networks
Globally peered virtual networks
Customer on-premises over VPN or Azure ExpressRoute circuits
Deployment troubleshooting
For more information on troubleshooting when you're unable to select the source IP address from the subnet of your choice for your private link service, see Disabling network policies on the private link service.
Diagnose connectivity problems
If you experience connectivity problems with your private link setup, review these steps to make sure all the usual configurations are as expected.
Review Private Link configuration by browsing the resource.
a. Go to Private Link Center.
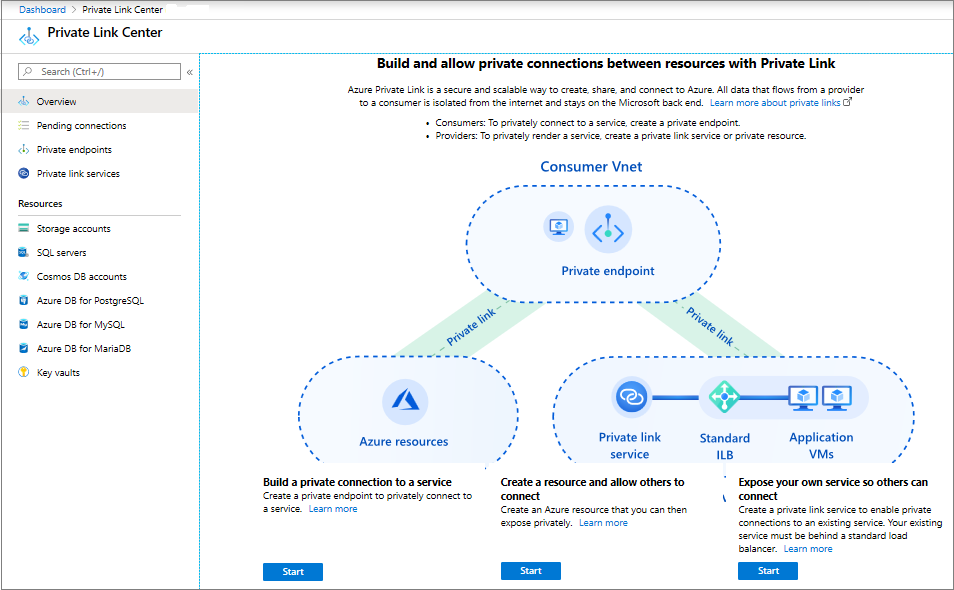
b. On the left pane, select Private link services.
c. Filter and select the private link service that you want to diagnose.
d. Review the private endpoint connections.
Make sure that the private endpoint that you're seeking connectivity from is listed with an Approved connection state.
If the state is Pending, select it and approve it.
Select the private endpoint you're connecting from by clicking on its name. Ensure the connection status is Approved.
After both sides are approved, try the connectivity again.
e. Review Alias on the Overview tab and Resource ID on the Properties tab.
- Ensure that the Alias and Resource ID details match the ones you're using to create a private endpoint for this service.
f. Review Visibility information on the Overview tab. Select See more in the overview pane to see the details.
- Make sure that your subscription falls under the Visibility scope.
g. Review Load balancer information on the Overview tab.
View the load balancer by selecting the load balancer link in the Overview pane.
Confirm the load balancer settings are configured as per your requirements.
Review Frontend IP configuration.
Review Backend pools.
Review Load balancing rules.
Confirm load balancer is working as per the previous settings.
Choose a virtual machine located in a subnet different from the one where the load balancer back-end pool resides.
Access the load balancer front end from the previous virtual machine.
If the connection reaches the back-end pool according to the load-balancing rules, then your load balancer is functioning correctly.
If the connection doesn't reach the back-end pool, then you need to troubleshoot the load balancer configuration.
Use Azure Monitor to review load balancer metrics and verify if data is flowing through the load balancer.
Use Azure Monitor to see if data is flowing.
a. On the private link service resource, select Metrics.
Select Bytes In or Bytes Out.
See if data is flowing when you attempt to connect to the private link service. Expect a delay of approximately 10 minutes.
Use Azure Monitor - Networks for insights and to see a resource view of the resources by going to:
Azure Monitor
Networks
Private Link services
Resource view
Contact the Azure Support team if your problem is still unresolved and a connectivity problem still exists.