Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this quickstart, you do the following steps:
Create a Service Bus namespace, using the Azure portal.
Create a Service Bus queue, using the Azure portal.
Write a .NET console application to send a set of messages to the queue.
Write a .NET console application to receive those messages from the queue.
This quickstart provides step-by-step instructions to implement a simple scenario of sending a batch of messages to a Service Bus queue and then receiving them. For an overview of the .NET client library, see Azure Service Bus client library for .NET. For more samples, see Service Bus .NET samples on GitHub.
Prerequisites
If you're new to the service, see Service Bus overview before you do this quickstart.
- Azure subscription. To use Azure services, including Azure Service Bus, you need a subscription. If you don't have an existing Azure account, you can sign up for a trial subscription.
- Visual Studio 2022. The sample application makes use of new features that were introduced in C# 10. You can still use the Service Bus client library with previous C# language versions, but the syntax might vary. To use the latest syntax, we recommend that you install .NET 6.0, or higher and set the language version to
latest. If you're using Visual Studio, versions before Visual Studio 2022 aren't compatible with the tools needed to build C# 10 projects.
Create a namespace in the Azure portal
To begin using Service Bus messaging entities in Azure, create a namespace with a name that is unique across Azure. A namespace provides a scoping container for Service Bus resources, such as queues and topics, in your application.
To create a namespace:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
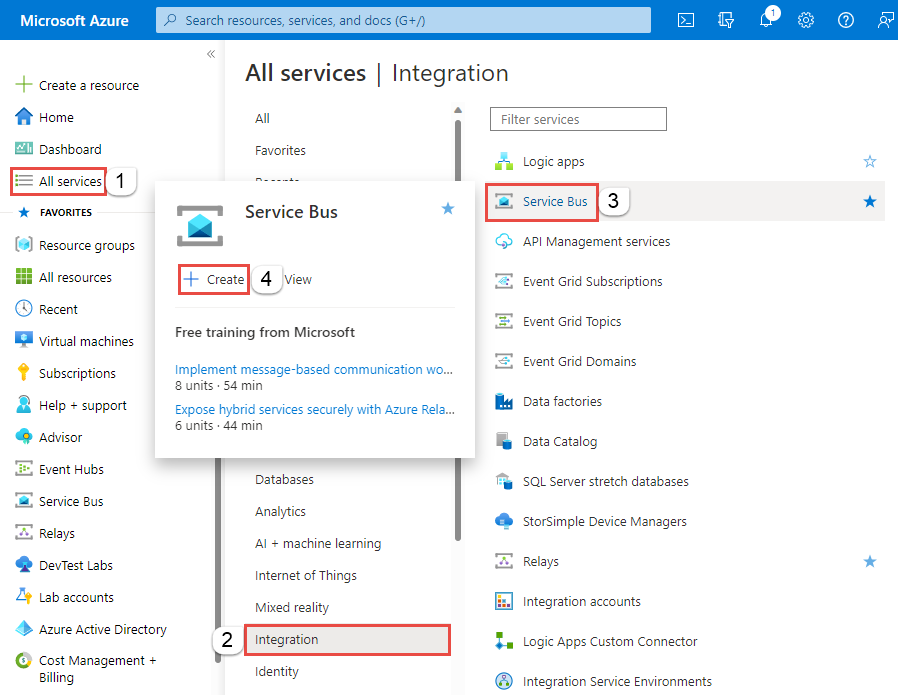
Select the flyout menu from the top left and navigate to the All services page.
On the left navigation bar, select Integration.
Scroll down to Messaging services > Service Bus and select Create.
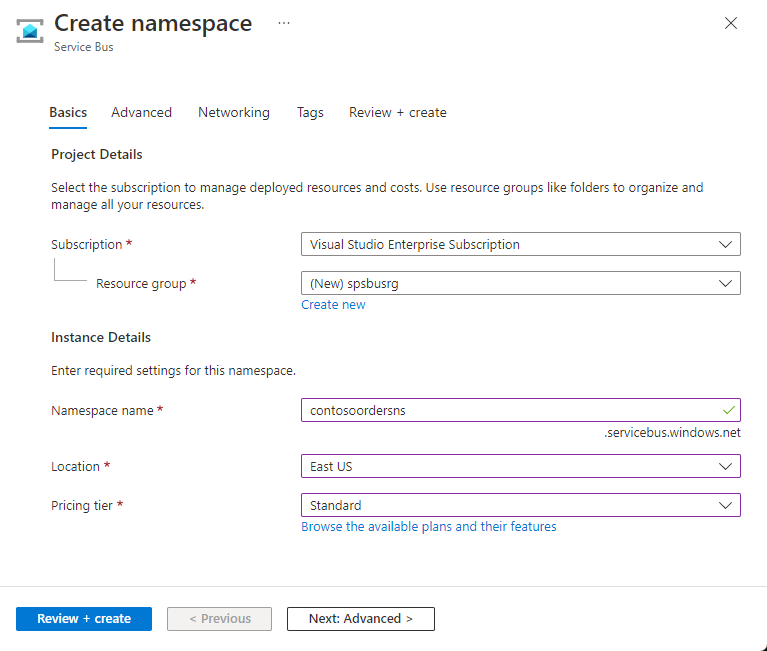
In the Basics tab of the Create namespace page, follow these steps:
For Subscription, choose an Azure subscription in which to create the namespace.
For Resource group, choose an existing resource group, or create a new one.
Enter a Namespace name that meets the following naming conventions:
- The name must be unique across Azure. The system immediately checks to see if the name is available.
- The name length is at least 6 and at most 50 characters.
- The name can contain only letters, numbers, hyphens
-. - The name must start with a letter and end with a letter or number.
- The name doesn't end with
-sbor-mgmt.
For Location, choose the region to host your namespace.
For Pricing tier, select the pricing tier (Basic, Standard, or Premium) for the namespace. For this quickstart, select Standard.
If you select Premium tier, you can enable geo-replication for the namespace. The geo-replication feature ensures that the metadata and data of a namespace are continuously replicated from a primary region to one or more secondary regions.
Important
If you want to use topics and subscriptions, choose either Standard or Premium. Topics and subscriptions aren't supported in the Basic pricing tier.
If you selected the Premium pricing tier, specify the number of messaging units. The premium tier provides resource isolation at the CPU and memory level so that each workload runs in isolation. This resource container is called a messaging unit. A premium namespace has at least one messaging unit. You can select 1, 2, 4, 8 or 16 messaging units for each Service Bus Premium namespace. For more information, see Service Bus premium messaging tier.
Select Review + create at the bottom of the page.
On the Review + create page, review settings, and select Create.
After the deployment of the resource is successful, select Go to resource on the deployment page.
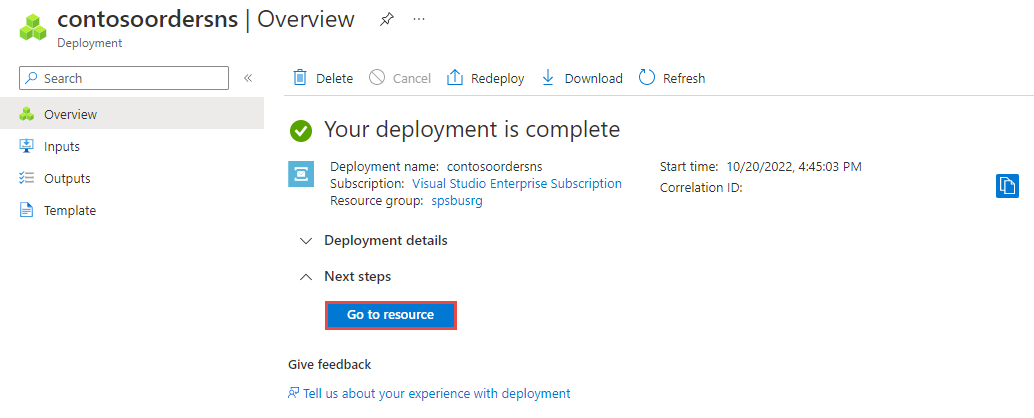
You see the home page for your service bus namespace.
Create a queue in the Azure portal
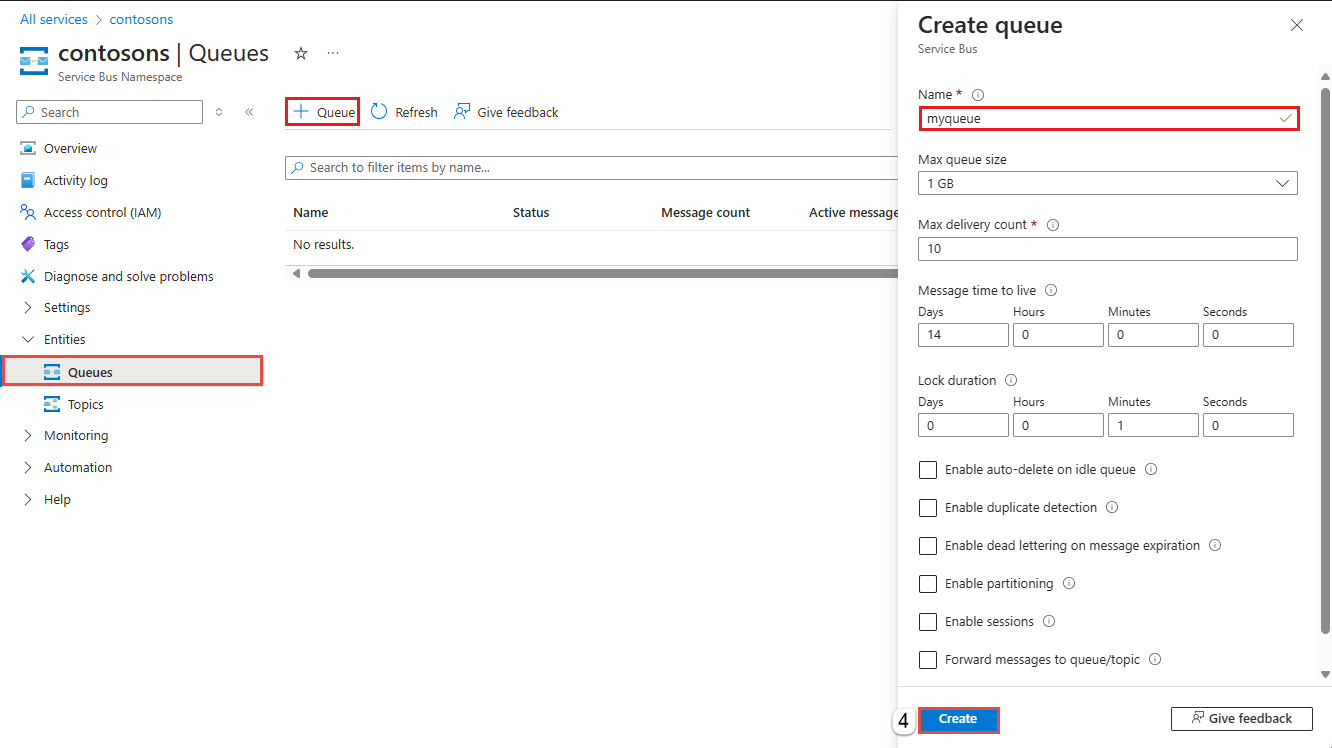
On the Service Bus Namespace page, expand Entities on the navigational menu to the left, and select Queues.
On the Queues page, on the toolbar, select + Queue.
Enter a name for the queue. Leave the other values with their defaults.
Select Create.
Important
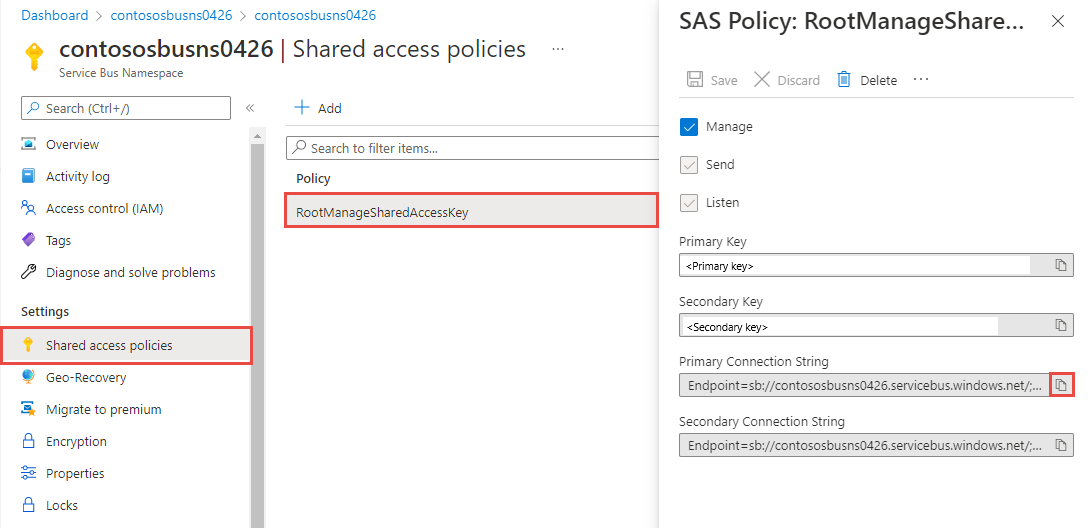
If you're new to Azure, you might find the Connection String option easier to follow. Select the Connection String tab to see instructions on using a connection string in this quickstart. We recommend that you use the Passwordless option in real-world applications and production environments.
Authenticate the app to Azure
This article shows you two ways of connecting to Azure Service Bus: passwordless and connection string.
The first option shows you how to use your security principal in Microsoft Entra ID and role-based access control (RBAC) to connect to a Service Bus namespace. You don't need to worry about having a hard-coded connection string in your code, in a configuration file, or in a secure storage like Azure Key Vault.
The second option shows you how to use a connection string to connect to a Service Bus namespace. If you're new to Azure, you might find the connection string option easier to follow. We recommend using the passwordless option in real-world applications and production environments. For more information, see Service Bus authentication and authorization. To read more about passwordless authentication, see Authenticate .NET apps.
Assign roles to your Microsoft Entra user
When you develop locally, make sure that the user account that connects to Azure Service Bus has the correct permissions. You need the Azure Service Bus Data Owner role in order to send and receive messages. To assign yourself this role, you need the User Access Administrator role, or another role that includes the Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/write action.
You can assign Azure RBAC roles to a user using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell. To learn more the available scopes for role assignments, see Understand scope for Azure RBAC.
The following example assigns the Azure Service Bus Data Owner role to your user account, which provides full access to Azure Service Bus resources. In a real scenario, follow the principle of least privilege to give users only the minimum permissions needed for a more secure production environment.
Azure built-in roles for Azure Service Bus
For Azure Service Bus, the management of namespaces and all related resources through the Azure portal and the Azure resource management API is already protected using the Azure RBAC model. Azure provides the following Azure built-in roles for authorizing access to a Service Bus namespace:
- Azure Service Bus Data Owner: Enables data access to Service Bus namespace and its entities, including queues, topics, subscriptions, and filters. A member of this role can send and receive messages from queues or topics/subscriptions.
- Azure Service Bus Data Sender: Use this role to give the
sendaccess to Service Bus namespace and its entities. - Azure Service Bus Data Receiver: Use this role to give the
receiveaccess to Service Bus namespace and its entities.
If you want to create a custom role, see Rights required for Service Bus operations.
Add Microsoft Entra user to Azure Service Bus Owner role
Add your Microsoft Entra user name to the Azure Service Bus Data Owner role at the Service Bus namespace level. This configuration allows an app that runs in the context of your user account to send messages to a queue or a topic. It can receive messages from a queue or a topic's subscription.
Important
In most cases, it takes a minute or two for the role assignment to propagate in Azure. In rare cases, it might take up to eight minutes. If you receive authentication errors when you first run your code, wait a few moments and try again.
If you don't have the Service Bus Namespace page open in the Azure portal, locate your Service Bus namespace using the main search bar or left navigation.
On the Overview page, select Access control (IAM) from the left-hand menu.
On the Access control (IAM) page, select the Role assignments tab.
Select + Add from the top menu and then Add role assignment.
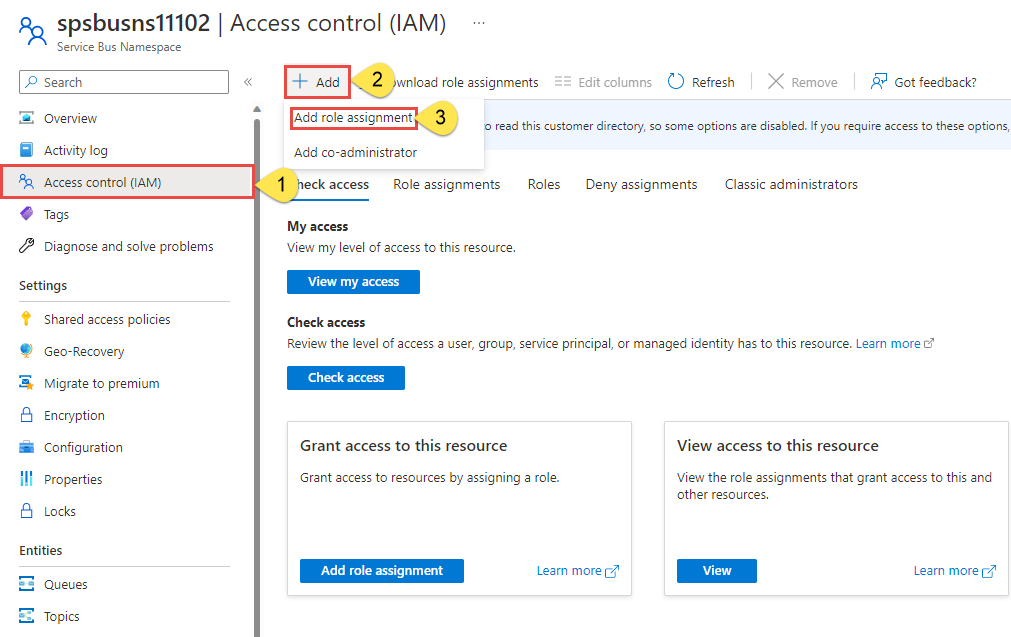
Use the search box to filter the results to the desired role. For this example, search for
Azure Service Bus Data Ownerand select the matching result. Then choose Next.Under Assign access to, select User, group, or service principal, and then choose + Select members.
In the dialog, search for your Microsoft Entra username (usually your user@domain email address) and then choose Select at the bottom of the dialog.
Select Review + assign to go to the final page, and then Review + assign again to complete the process.
Launch Visual Studio
You can authorize access to the service bus namespace using the following steps:
Launch Visual Studio. If you see the Get started window, select the Continue without code link in the right pane.
Select the Sign in button in the top right of Visual Studio.
Sign-in using the Microsoft Entra account you assigned a role to previously.
Send messages to the queue
This section shows you how to create a .NET console application to send messages to a Service Bus queue.
Note
This quick start provides step-by-step instructions to implement a simple scenario of sending a batch of messages to a Service Bus queue and then receiving them. For more samples on other and advanced scenarios, see Service Bus .NET samples on GitHub.
Create a console application
In Visual Studio, select File -> New -> Project menu.
On the Create a new project dialog box, do the following steps: If you don't see this dialog box, select File on the menu, select New, and then select Project.
Select C# for the programming language.
Select Console for the type of the application.
Select Console App from the results list.
Then, select Next.
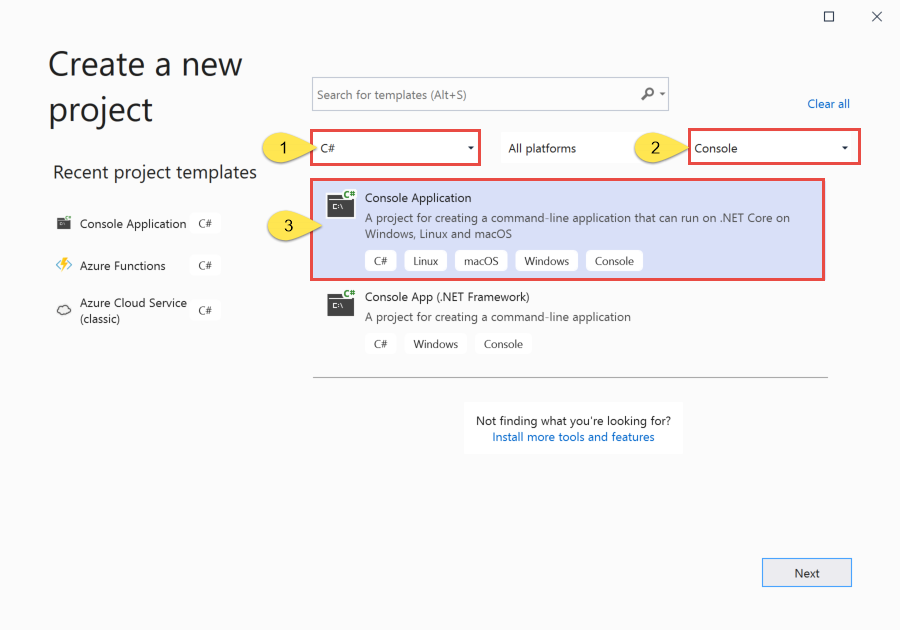
Enter QueueSender for the project name, ServiceBusQueueQuickStart for the solution name, and then select Next.
On the Additional information page, select Create to create the solution and the project.
Add the NuGet packages to the project
Select Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console from the menu.
Run the following command to install the Azure.Messaging.ServiceBus NuGet package.
Install-Package Azure.Messaging.ServiceBusRun the following command to install the Azure.Identity NuGet package.
Install-Package Azure.Identity
Add code to send messages to the queue
Replace the contents of
Program.cswith the following code. The important steps are outlined in the following section, with additional information in the code comments.- Creates a ServiceBusClient object using the
DefaultAzureCredentialobject.DefaultAzureCredentialautomatically discovers and uses the credentials of your Visual Studio sign-in to authenticate to Azure Service Bus. - Invokes the CreateSender method on the ServiceBusClient object to create a ServiceBusSender object for the specific Service Bus queue.
- Creates a ServiceBusMessageBatch object by using the ServiceBusSender.CreateMessageBatchAsync method.
- Add messages to the batch using the ServiceBusMessageBatch.TryAddMessage.
- Sends the batch of messages to the Service Bus queue using the ServiceBusSender.SendMessagesAsync method.
Important
Update placeholder values (
<NAMESPACE-NAME>and<QUEUE-NAME>) in the code snippet with names of your Service Bus namespace and queue.using Azure.Messaging.ServiceBus; using Azure.Identity; // name of your Service Bus queue // the client that owns the connection and can be used to create senders and receivers ServiceBusClient client; // the sender used to publish messages to the queue ServiceBusSender sender; // number of messages to be sent to the queue const int numOfMessages = 3; // The Service Bus client types are safe to cache and use as a singleton for the lifetime // of the application, which is best practice when messages are being published or read // regularly. // // Set the transport type to AmqpWebSockets so that the ServiceBusClient uses the port 443. // If you use the default AmqpTcp, ensure that ports 5671 and 5672 are open. var clientOptions = new ServiceBusClientOptions { TransportType = ServiceBusTransportType.AmqpWebSockets }; //TODO: Replace the "<NAMESPACE-NAME>" and "<QUEUE-NAME>" placeholders. client = new ServiceBusClient( "<NAMESPACE-NAME>.servicebus.chinacloudapi.cn", new DefaultAzureCredential(), clientOptions); sender = client.CreateSender("<QUEUE-NAME>"); // create a batch using ServiceBusMessageBatch messageBatch = await sender.CreateMessageBatchAsync(); for (int i = 1; i <= numOfMessages; i++) { // try adding a message to the batch if (!messageBatch.TryAddMessage(new ServiceBusMessage($"Message {i}"))) { // if it is too large for the batch throw new Exception($"The message {i} is too large to fit in the batch."); } } try { // Use the producer client to send the batch of messages to the Service Bus queue await sender.SendMessagesAsync(messageBatch); Console.WriteLine($"A batch of {numOfMessages} messages has been published to the queue."); } finally { // Calling DisposeAsync on client types is required to ensure that network // resources and other unmanaged objects are properly cleaned up. await sender.DisposeAsync(); await client.DisposeAsync(); } Console.WriteLine("Press any key to end the application"); Console.ReadKey();- Creates a ServiceBusClient object using the
Build the project, and ensure that there are no errors.
Run the program and wait for the confirmation message.
A batch of 3 messages has been published to the queueImportant
In most cases, it takes a minute or two for the role assignment to propagate in Azure. In rare cases, it might take up to eight minutes. If you receive authentication errors when you first run your code, wait a few moments and try again.
In the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Navigate to your Service Bus namespace.
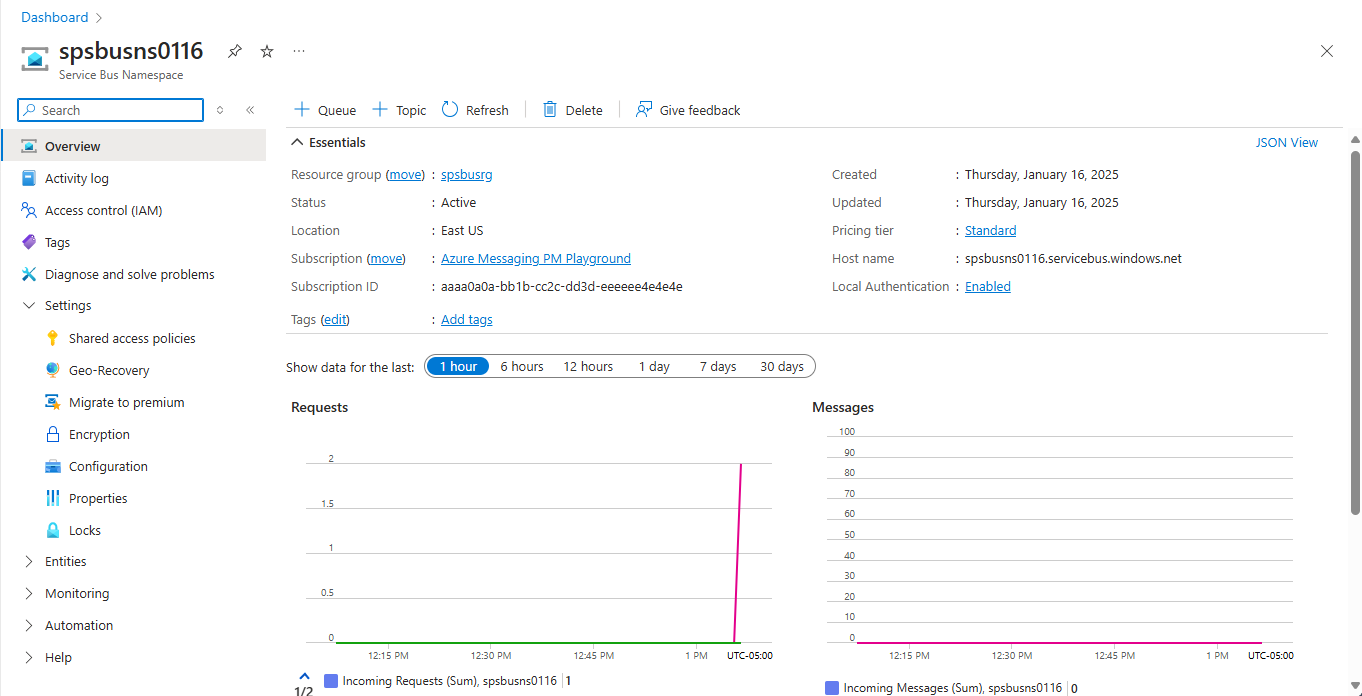
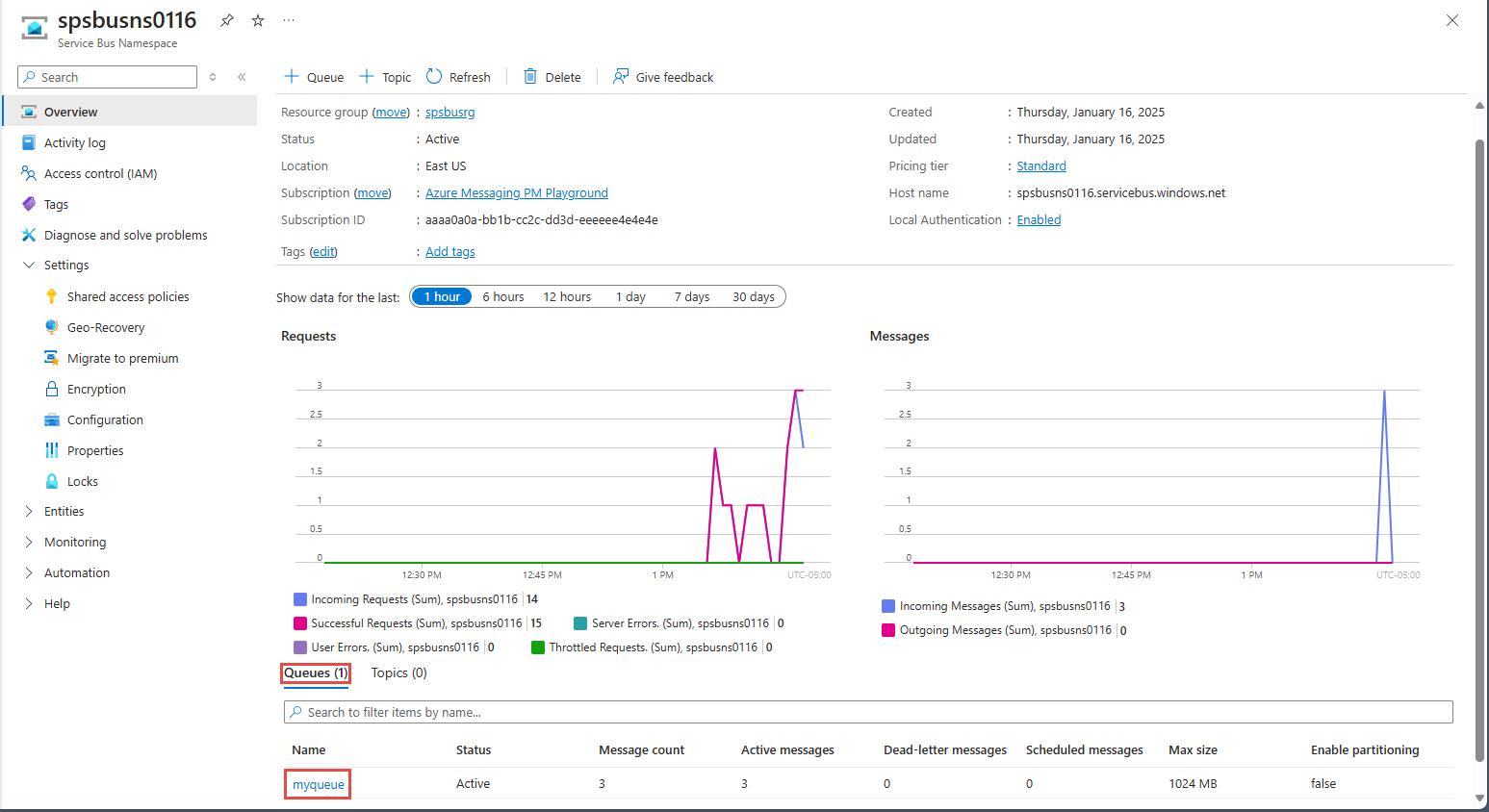
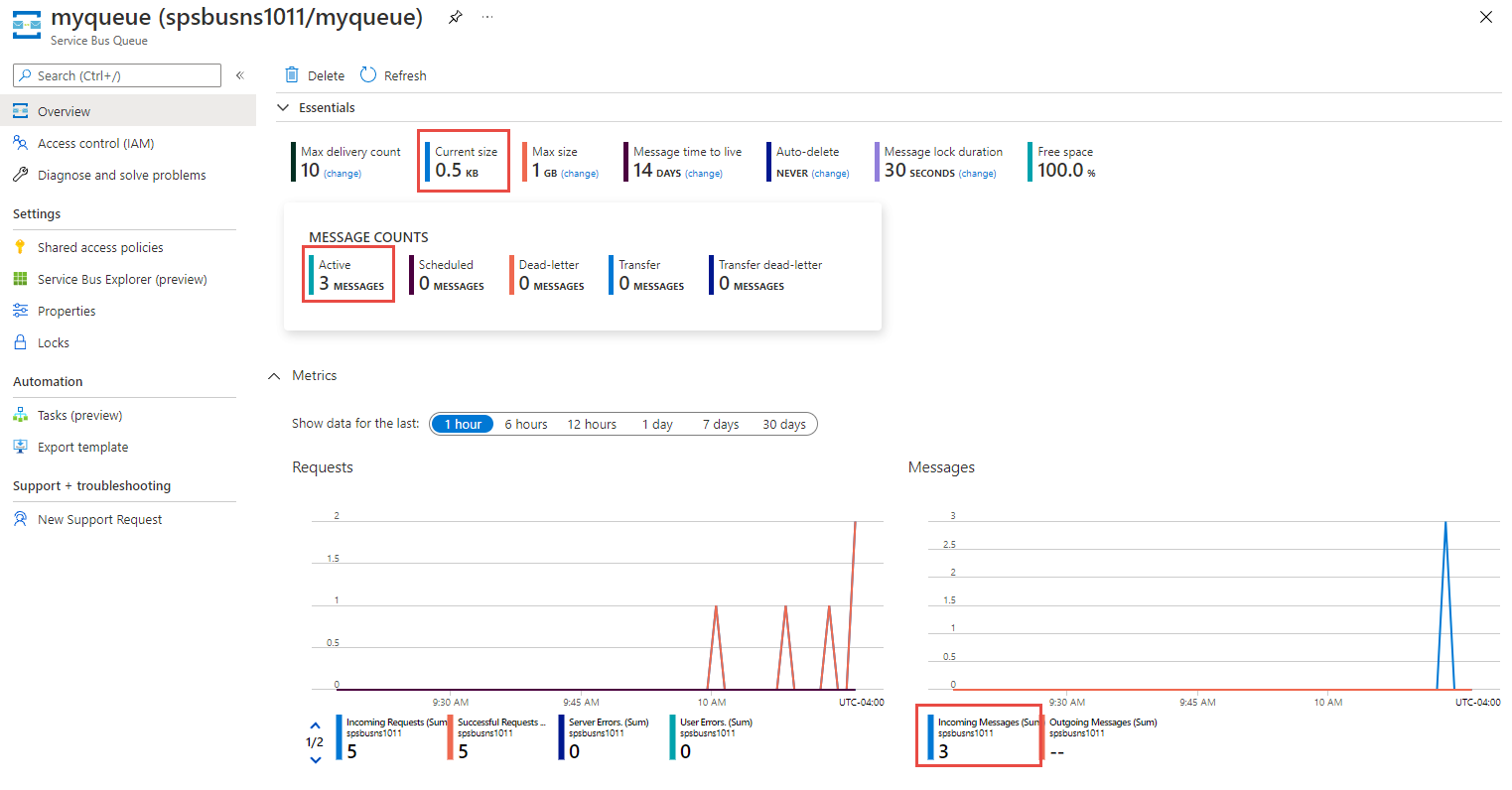
On the Overview page, select the queue in the bottom-middle pane.
Notice the values in the Settings section.
Notice the following values:
- The Active message count value for the queue is now 3. Each time you run this sender app without retrieving the messages, this value increases by 3.
- The current size of the queue increments each time the app adds messages to the queue.
- In the Messages chart in the bottom Metrics section, you can see that there are three incoming messages for the queue.
Receive messages from the queue
In this section, you create a .NET console application that receives messages from the queue.
Note
This quickstart provides step-by-step instructions to implement a scenario of sending a batch of messages to a Service Bus queue and then receiving them. For more samples on other and advanced scenarios, see Service Bus .NET samples on GitHub.
Create a project for the receiver
- In the Solution Explorer window, right-click the ServiceBusQueueQuickStart solution, point to Add, and select New Project.
- Select Console application, and select Next.
- Enter QueueReceiver for the Project name, and select Create.
- In the Solution Explorer window, right-click QueueReceiver, and select Set as a Startup Project.
Add the NuGet packages to the project
Select Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console from the menu.
Select QueueReceiver for Default project.
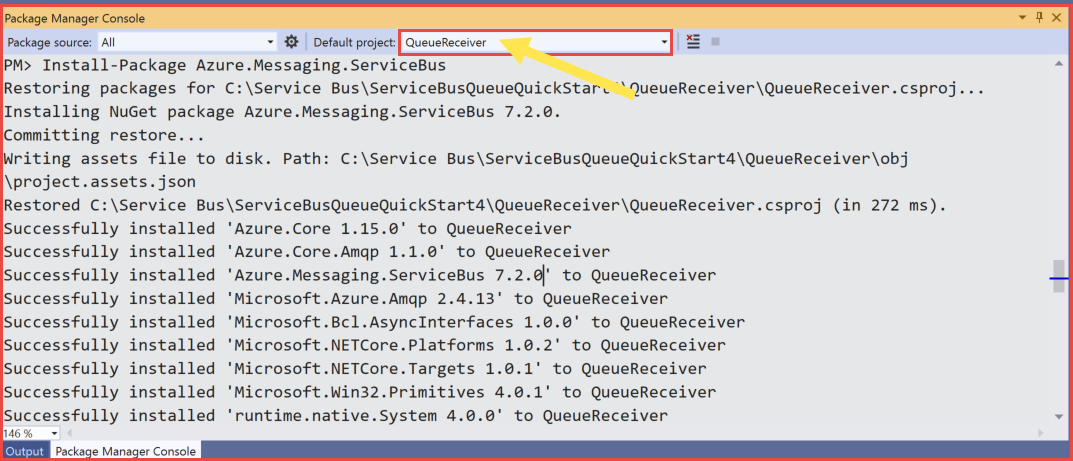
Run the following command to install the Azure.Messaging.ServiceBus NuGet package.
Install-Package Azure.Messaging.ServiceBusRun the following command to install the Azure.Identity NuGet package.
Install-Package Azure.Identity
Add the code to receive messages from the queue
In this section, you add code to retrieve messages from the queue.
Within the
Programclass, add the following code:using System.Threading.Tasks; using Azure.Identity; using Azure.Messaging.ServiceBus; // the client that owns the connection and can be used to create senders and receivers ServiceBusClient client; // the processor that reads and processes messages from the queue ServiceBusProcessor processor;Append the following methods to the end of the
Programclass.// handle received messages async Task MessageHandler(ProcessMessageEventArgs args) { string body = args.Message.Body.ToString(); Console.WriteLine($"Received: {body}"); // complete the message. message is deleted from the queue. await args.CompleteMessageAsync(args.Message); } // handle any errors when receiving messages Task ErrorHandler(ProcessErrorEventArgs args) { Console.WriteLine(args.Exception.ToString()); return Task.CompletedTask; }Append the following code to the end of the
Programclass. The important steps are outlined in the following section, with additional information in the code comments.- Creates a ServiceBusClient object using the
DefaultAzureCredentialobject.DefaultAzureCredentialautomatically discovers and uses the credentials of your Visual Studio sign in to authenticate to Azure Service Bus. - Invokes the CreateProcessor method on the
ServiceBusClientobject to create a ServiceBusProcessor object for the specified Service Bus queue. - Specifies handlers for the ProcessMessageAsync and ProcessErrorAsync events of the ServiceBusProcessor object.
- Starts processing messages by invoking the StartProcessingAsync on the
ServiceBusProcessorobject. - When user presses a key to end the processing, invokes the StopProcessingAsync on the
ServiceBusProcessorobject.
Important
Update placeholder values (
<NAMESPACE-NAME>and<QUEUE-NAME>) in the code snippet with names of your Service Bus namespace and queue.// The Service Bus client types are safe to cache and use as a singleton for the lifetime // of the application, which is best practice when messages are being published or read // regularly. // // Set the transport type to AmqpWebSockets so that the ServiceBusClient uses port 443. // If you use the default AmqpTcp, make sure that ports 5671 and 5672 are open. // TODO: Replace the <NAMESPACE-NAME> placeholder var clientOptions = new ServiceBusClientOptions() { TransportType = ServiceBusTransportType.AmqpWebSockets }; client = new ServiceBusClient( "<NAMESPACE-NAME>.servicebus.chinacloudapi.cn", new DefaultAzureCredential(), clientOptions); // create a processor that we can use to process the messages // TODO: Replace the <QUEUE-NAME> placeholder processor = client.CreateProcessor("<QUEUE-NAME>", new ServiceBusProcessorOptions()); try { // add handler to process messages processor.ProcessMessageAsync += MessageHandler; // add handler to process any errors processor.ProcessErrorAsync += ErrorHandler; // start processing await processor.StartProcessingAsync(); Console.WriteLine("Wait for a minute and then press any key to end the processing"); Console.ReadKey(); // stop processing Console.WriteLine("\nStopping the receiver..."); await processor.StopProcessingAsync(); Console.WriteLine("Stopped receiving messages"); } finally { // Calling DisposeAsync on client types is required to ensure that network // resources and other unmanaged objects are properly cleaned up. await processor.DisposeAsync(); await client.DisposeAsync(); }- Creates a ServiceBusClient object using the
The completed
Programclass should match the following code:using System.Threading.Tasks; using Azure.Messaging.ServiceBus; using Azure.Identity; // the client that owns the connection and can be used to create senders and receivers ServiceBusClient client; // the processor that reads and processes messages from the queue ServiceBusProcessor processor; // The Service Bus client types are safe to cache and use as a singleton for the lifetime // of the application, which is best practice when messages are being published or read // regularly. // // Set the transport type to AmqpWebSockets so that the ServiceBusClient uses port 443. // If you use the default AmqpTcp, make sure that ports 5671 and 5672 are open. // TODO: Replace the <NAMESPACE-NAME> and <QUEUE-NAME> placeholders var clientOptions = new ServiceBusClientOptions() { TransportType = ServiceBusTransportType.AmqpWebSockets }; client = new ServiceBusClient("<NAMESPACE-NAME>.servicebus.chinacloudapi.cn", new DefaultAzureCredential(), clientOptions); // create a processor that we can use to process the messages // TODO: Replace the <QUEUE-NAME> placeholder processor = client.CreateProcessor("<QUEUE-NAME>", new ServiceBusProcessorOptions()); try { // add handler to process messages processor.ProcessMessageAsync += MessageHandler; // add handler to process any errors processor.ProcessErrorAsync += ErrorHandler; // start processing await processor.StartProcessingAsync(); Console.WriteLine("Wait for a minute and then press any key to end the processing"); Console.ReadKey(); // stop processing Console.WriteLine("\nStopping the receiver..."); await processor.StopProcessingAsync(); Console.WriteLine("Stopped receiving messages"); } finally { // Calling DisposeAsync on client types is required to ensure that network // resources and other unmanaged objects are properly cleaned up. await processor.DisposeAsync(); await client.DisposeAsync(); } // handle received messages async Task MessageHandler(ProcessMessageEventArgs args) { string body = args.Message.Body.ToString(); Console.WriteLine($"Received: {body}"); // complete the message. message is deleted from the queue. await args.CompleteMessageAsync(args.Message); } // handle any errors when receiving messages Task ErrorHandler(ProcessErrorEventArgs args) { Console.WriteLine(args.Exception.ToString()); return Task.CompletedTask; }Build the project, and ensure that there are no errors.
Run the receiver application. You should see the received messages. Press any key to stop the receiver and the application.
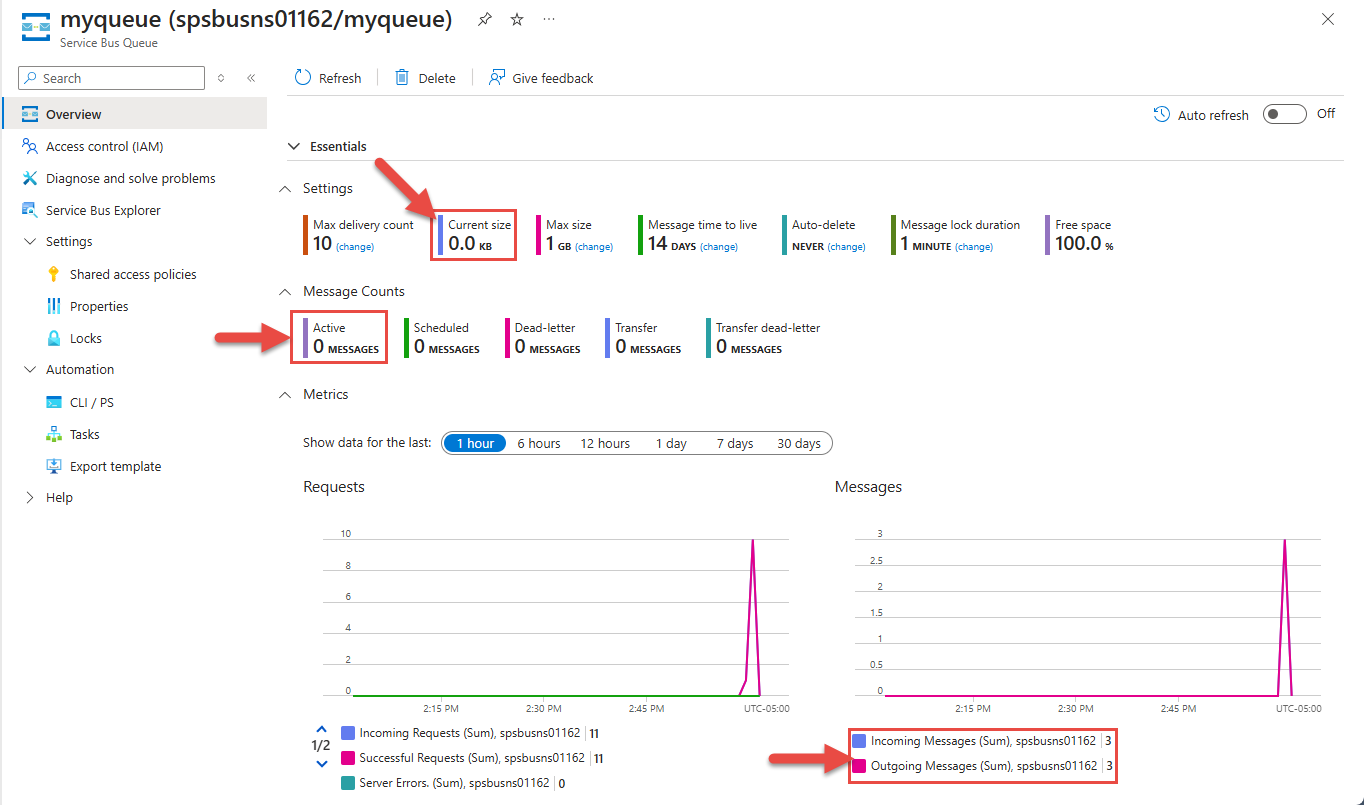
Wait for a minute and then press any key to end the processing Received: Message 1 Received: Message 2 Received: Message 3 Stopping the receiver... Stopped receiving messagesCheck the portal again. Wait for a few minutes and refresh the page if you don't see
0for Active messages.
Additional information
See the following documentation and samples:
- Azure Service Bus client library for .NET - Readme
- Samples on GitHub
- .NET API reference
- Abstract away infrastructure concerns with higher-level frameworks like NServiceBus
Clean up resources
Navigate to your Service Bus namespace in the Azure portal, and select Delete on the Azure portal to delete the namespace and the queue in it.
Related content
See Get started with Azure Service Bus topics and subscriptions (.NET).