This article summarizes frequently asked questions about Azure Site Recovery. For specific scenarios, review these articles:
General
What does Site Recovery do?
Site Recovery contributes to your business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) strategy, by orchestrating and automating replication of Azure VMs between regions, on-premises virtual machines and physical servers to Azure, and on-premises machines to a secondary datacenter. Learn more.
Can I protect a virtual machine that has a Docker disk?
No, Azure Site Recovery doesn't support Docker workloads running on virtual machines. To protect these virtual machines with Site Recovery, exclude the disks that have Docker installed on them.
What does Site Recovery do to ensure data integrity?
There are various measures taken by Site Recovery to ensure data integrity. A secure connection is established between all services by using the HTTPS protocol. This makes sure that any malware or outside entities can't tamper the data. Another measure taken is using checksums. The data transfer between source and target is executed by computing checksums of data between them. This ensures that the transferred data is consistent.
How can I migrate/protect software which requires a persistent MAC address on the virtual machine?
Azure doesn't support persistent MAC addresses and so software with MAC based license models cannot be used for both on-premises to Azure migration or disaster recovery.
Does Azure Site Recovery currently support Ephemeral Disks?
No, Azure Site Recovery currently doesn't support Ephemeral Disks.
What is the Azure Recovery Services agent used for?
Azure Recovery Services agent is used for configuring/registering with Site Recovery services, and for monitoring the health of all the components. This component is one of the basic building blocks of the entire Azure Site Recovery on-premises infrastructure. It helps to replicate your workloads to another Azure region from an on-premises site, and fail over to Azure in a disaster.
Service providers
I'm a service provider. Does Site Recovery work for dedicated and shared infrastructure models?
Yes, Site Recovery supports both dedicated and shared infrastructure models.
For a service provider, is the identity of my tenant shared with the Site Recovery service?
No. Tenant identity remains anonymous. Your tenants don't need access to the Site Recovery portal. Only the service provider administrator interacts with the portal.
Will tenant application data ever go to Azure?
When you're replicating to Azure, application data is sent to Azure storage but not to the Site Recovery service. Data is encrypted in-transit (HTTPS), and remains encrypted in Azure.
Will my tenants receive a bill for any Azure services?
No. Azure's billing relationship is directly with the service provider. Service providers are responsible for generating specific bills for their tenants.
If I'm replicating to Azure, do we always need to run virtual machines in Azure?
No, Data is replicated to Azure storage in your subscription. When you perform a test failover (disaster recovery drill) or an actual failover, Site Recovery automatically creates virtual machines in your subscription.
Do you ensure tenant-level isolation when I replicate to Azure?
Yes.
What platforms do you currently support?
We support Azure Pack, Cloud Platform System, and System Center based (2012 and higher) deployments. Learn more about Azure Pack and Site Recovery integration.
Do you support single Azure Pack and single VMM server deployments?
No, you can replicate Hyper-V virtual machines only to Azure.
Pricing
Where can I find pricing information?
Review Site Recovery pricing details.
How can I calculate approximate charges during the use of Site Recovery?
You can use the pricing calculator to estimate costs while using Site Recovery.
Do I also incur charges for the cache storage account when using Site Recovery?
Yes, there are extra charges for cache storage account usage when replicating virtual machines using Site Recovery. The cache storage account costs remain the same when the replica storage is of type managed disks or unmanaged disks.
I have been an Azure Site Recovery user for over a month. Do I still get the first 31 days free for every protected instance?
Yes. Every protected instance incurs no Azure Site Recovery charges for the first 31 days. For example, if you have been protecting 10 instances for the last six months and you connect an 11th instance to Azure Site Recovery, there are no charges for the 11th instance for the first 31 days. The first 10 instances continue to incur Azure Site Recovery charges since they've been protected for more than 31 days.
During the first 31 days, will I incur any other Azure charges?
Yes, even though Site Recovery is free during the first 31 days of a protected instance, you might incur charges for Azure Storage, storage transactions, and data transfer. A recovered virtual machine might also incur Azure compute charges.
Is there a cost associated to perform disaster recovery drills/test failover?
There isn't any separate cost for disaster recovery drill. There are compute charges after the virtual machine is created after the test failover.
Security
Is replication data sent to the Site Recovery service?
No, Site Recovery doesn't intercept replicated data, and doesn't have any information about what's running on your virtual machines or physical servers. Replication data is exchanged between on-premises Hyper-V hosts, VMware hypervisors, or physical servers and Azure storage or your secondary site. Site Recovery has no ability to intercept that data. Only the metadata needed to orchestrate replication and failover is sent to the Site Recovery service.
Site Recovery is ISO 27001:2013, 27018, HIPAA, DPA certified, and is in the process of SOC2 and FedRAMP JAB assessments.
For compliance reasons, even our on-premises metadata must remain within the same geographic region. Can Site Recovery help us?
Yes. When you create a Site Recovery vault in a region, we ensure that all metadata that we need to enable and orchestrate replication and failover remains within that region's geographic boundary.
Does Site Recovery encrypt replication?
For virtual machines and physical servers replicating to Azure, both encryption-in-transit and encryption-at-rest (in Azure) are supported.
Does Azure-to-Azure Site Recovery use TLS 1.2 for all communications across microservices of Azure?
Yes, TLS 1.2 protocol is enforced by default for Azure-to-Azure Site Recovery scenario.
How can I enforce TLS 1.2 on VMware-to-Azure and Physical Server-to-Azure Site Recovery scenarios?
Mobility agents installed on the replicated items communicate to Process Server only on TLS 1.2. However, communication from Configuration Server to Azure and from Process Server to Azure could be on TLS 1.1 or 1.0. Follow the guidance to enforce TLS 1.2 on all Configuration Servers and Process Servers set up by you.
Note
The modernized experience uses TLS 1.2 for all the communication and enforces it by default.
How can I enforce TLS 1.2 on Hyper-V-to-Azure Site Recovery scenarios?
All communication between the microservices of Azure Site Recovery happens on TLS 1.2 protocol. Site Recovery uses security providers configured in the system (OS) and uses the latest available TLS protocol. One needs to explicitly enable the TLS 1.2 in the Registry and then Site Recovery will start using TLS 1.2 for communication with services.
How can I enforce restricted access on my storage accounts which are accessed by Site Recovery service for reading/writing replication data?
You can switch on the managed identity of the recovery services vault by going to the Identity setting. Once the vault gets registered with Microsoft Entra ID, you can go to your storage accounts and give the following role-assignments to the vault:
- Resource Manager based storage accounts (Standard Type):
- Resource Manager based storage accounts (Premium Type):
- Classic storage accounts:
Cache storage account is not supported for managed identity.
Can Azure Site Recovery track source virtual machine changes outside the Source OS?
Azure Site Recovery doesn't track source virtual machine changes outside the Source OS. For example, If you are using Azure to Azure replication and change the size of the source virtual machine, the change in size of source virtual machine isn't replicated to the target virtual machine.
Disaster recovery
What can Site Recovery protect?
- Azure virtual machines: Site Recovery can replicate any workload running on a supported Azure virtual machine.
- Hyper-V virtual machines: Site Recovery can protect any workload running on a Hyper-V virtual machine.
- Physical servers: Site Recovery can protect physical servers running Windows or Linux.
- VMware virtual machines: Site Recovery can protect any workload running in a VMware virtual machine.
What workloads can I protect with Site Recovery?
You can use Site Recovery to protect most workloads running on a supported virtual machine or physical server. Site Recovery provides support for application-aware replication, so that apps can be recovered to an intelligent state. It integrates with Microsoft applications such as SharePoint, Exchange, Dynamics, SQL Server and Active Directory, and works closely with leading vendors, including Oracle, SAP, IBM, and Red Hat. Learn more about workload protection.
Can I manage disaster recovery for my branch offices with Site Recovery?
Yes. When you use Site Recovery to orchestrate replication and failover in your branch offices, you'll get a unified orchestration and view of all your branch office workloads in a central location. You can easily run failovers and administer disaster recovery of all branches from your head office, without visiting the branches.
Is disaster recovery supported for Azure virtual machines?
Yes, Site Recovery supports disaster for Azure virtual machines between Azure regions. Review common questions about Azure virtual machine disaster recovery. If you want to replicate between two Azure regions on the same continent, use our Azure to Azure disaster recovery offering. No need to set up configuration server/process server and ExpressRoute connections.
Is disaster recovery supported for VMware virtual machines?
Yes, Site Recovery supports disaster recovery of on-premises VMware virtual machines. Review common questions for disaster recovery of VMware virtual machines.
Is disaster recovery supported for Hyper-V virtual machines?
Yes, Site Recovery supports disaster recovery of on-premises Hyper-V virtual machines. Review common questions for disaster recovery of Hyper-V virtual machines.
Is disaster recovery supported for physical servers?
Yes, Site Recovery supports disaster recovery of on-premises physical servers running Windows and Linux to Azure. Learn about requirements for disaster recovery to Azure. The physical servers run as virtual machines in Azure after failover. Failback from Azure to an on-premises physical server isn't currently supported. You can only fail back to a VMware virtual machine.
Can I move the Recovery Services vault across subscriptions?
No, Azure Site Recovery doesn't support move of Recovery Services vault that has protected virtual machines hosted in it.
Replication
Can I replicate over a site-to-site VPN to Azure?
Azure Site Recovery replicates data to an Azure storage account or managed disks, over a public endpoint. However, replication can be performed over Site-to-Site VPN as well. Site-to-Site VPN connectivity allows organizations to connect existing networks to Azure, or Azure networks to each other. Site-to-Site VPN occurs over IPsec tunneling over the internet, using existing on-premises edge network equipment and network appliances in Azure, either native features like Azure Virtual Private Network (VPN) Gateway or third party options such as Check Point CloudGuard, Palo Alto NextGen Firewall.
- Private connectivity over the public Internet to Microsoft Edge
- Recovery Service Vaults configured for security with Private Endpoints
- Replication over customer private Virtual Network connection
- Easy transition to "Future State"
- No SLA and potentially higher latency
- Requires an on-premises VPN device availability
Can I use Riverbed SteelHeads for replication?
Our partner, Riverbed, provides detailed guidance on working with Azure Site Recovery. Review their solution guide.
Can I use ExpressRoute to replicate virtual machines to Azure?
Yes, ExpressRoute can be used to replicate on-premises virtual machines to Azure.
- Azure Site Recovery replicates data to an Azure Storage over a public endpoint. You need to set up Azure peering to use ExpressRoute for Site Recovery replication.
- Replication is supported over private peering only when private endpoints are enabled for the vault.
- If you're protecting VMware machines or physical machines, ensure that the Networking Requirements for Configuration Server are also met. Connectivity to specific URLs is required by Configuration Server for orchestration of Site Recovery replication. ExpressRoute cannot be used for this connectivity.
- After the virtual machines have been failed over to an Azure virtual network, you can access them using the private peering setup with the Azure virtual network.
If I replicate to Azure, what kind of storage account or managed disk do I need?
Using storage accounts as target storage isn't supported by Azure Site Recovery. It is recommended to rather use managed disks as the target storage for your machines. Managed disks only support LRS type for data resiliency.
How often can I replicate data?
- Hyper-V: Hyper-V virtual machines can be replicated every 30 seconds (except for premium storage) or five minutes.
- Azure virtual machines, VMware virtual machines, physical servers: A replication frequency isn't relevant here. Replication is continuous.
Can I extend replication from existing recovery site to another tertiary site?
Extended or chained replication isn't supported. Request this feature in feedback forum.
Can I do an offline replication the first time I replicate to Azure?
This isn't supported. Request this feature in the feedback forum.
Can I exclude specific disks from replication?
This is supported when you're replicating VMware virtual machines and Hyper-V virtual machines to Azure, using the Azure portal.
Can I replicate virtual machines with dynamic disks?
Dynamic disks are supported when replicating Hyper-V virtual machines, and when replicating VMware virtual machines and physical machines to Azure. The operating system disk must be a basic disk.
Can I throttle bandwidth allotted for replication traffic?
Yes. You can read more about throttling bandwidth in these articles:
Can I enable replication with app-consistency in Linux servers?
Yes. Azure Site Recovery for Linux Operation System supports application custom scripts for app-consistency. The custom script with pre and post-options is used by the Azure Site Recovery Mobility Agent during app-consistency. Following are the steps to enable it.
Sign in as root into the machine.
Change directory to Azure Site Recovery Mobility Agent install location. Default is "/usr/local/ASR"
# cd /usr/local/ASRChange directory to "VX/scripts" under install location
# cd VX/scriptsCreate a bash shell script named "customscript.sh" with execute permissions for root user.
a. The script should support "--pre" and "--post" (Note the double dashes) command-line options
b. When the script is called with pre-option, it should freeze the application input/output and when called with post-option, it should thaw the application input/output.
c. A sample template -# cat customscript.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -ne 1 ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 [--pre | --post]"
exit 1
elif [ "$1" == "--pre" ]; then
echo "Freezing app IO" ##command to freeze the application
exit 0
elif [ "$1" == "--post" ]; then
echo "Thawed app IO" ##command to unfreeze the application
exit 0
fi
- Add the freeze and unfreeze input/output commands in pre and post-steps for the applications requiring app-consistency. You can choose to add another script specifying those and invoke it from "customscript.sh" with pre and post-options.
Note
The Site Recovery agent version should be 9.24 or above to support custom scripts.
Replication policy
What is a replication policy?
A replication policy defines the settings for the retention history of recovery points. The policy also defines the frequency of app-consistent snapshots. By default, Azure Site Recovery creates a new replication policy with default settings of:
- One day for the retention history of recovery points.
- No app-consistent snapshots.
What is a crash-consistent recovery point?
A crash-consistent recovery point has the on-disk data as if you pulled the power cord from the server during the snapshot. The crash-consistent recovery point doesn't include anything that was in memory when the snapshot was taken.
Today, most applications can recover well from crash-consistent snapshots. A crash-consistent recovery point is enough for no-database operating systems and applications like file servers, DHCP servers, and print servers.
What is the frequency of crash-consistent recovery point generation?
Site Recovery creates a crash-consistent recovery point every 5 minutes.
What is an application-consistent recovery point?
Application-consistent recovery points are created from application-consistent snapshots. Application-consistent recovery points capture the same data as crash-consistent snapshots while also capturing data in memory and all transactions in process.
Because of their extra content, application-consistent snapshots are the most involved and take the longest. We recommend application-consistent recovery points for database operating systems and applications such as SQL Server.
Note
Creation of application-consistent recovery points fails on Windows machine, if it has more than 64 volumes.
What is the impact of application-consistent recovery points on application performance?
Application-consistent recovery points capture all the data in memory and in process. Because recovery points capture that data, they require framework like Volume Shadow Copy Service on Windows to quiesce the application. If the capturing process is frequent, it can affect performance when the workload is already busy. We don't recommend that you use low frequency for app-consistent recovery points for non-database workloads. Even for database workload, 1 hour is enough.
What is the minimum frequency of application-consistent recovery point generation?
Site Recovery can create an application-consistent recovery point with a minimum frequency of 1 hour.
How are recovery points generated and saved?
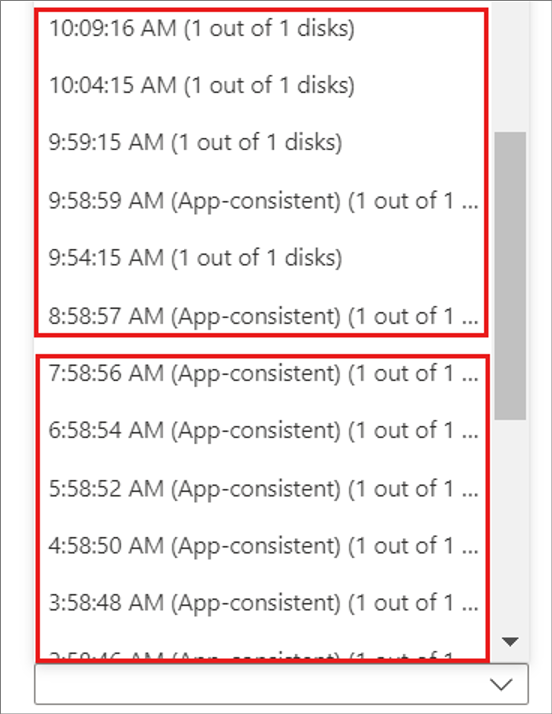
To understand how Site Recovery generates recovery points, let's see an example of a replication policy. This replication policy has a recovery point with a 1-day retention window and an app-consistent frequency snapshot of 1 hour.
Site Recovery creates a crash-consistent recovery point every 5 minutes. You can't change this frequency. For the most recent 2 hours, you can choose from 24 crash-consistent points and 2 app-consistent points. As time progresses, Site Recovery prunes all the recovery points beyond the last 2 hours and saves only one recovery point per hour for up to 24 hours of the day.
The following screenshot illustrates the example. In the screenshot:
Within the past 2 hours, there are recovery points with a frequency of 5 minutes.
Beyond the past 2 hours, Site Recovery keeps only one recovery point per hour.
How far back can I recover?
The oldest recovery point that you can use is 15 days with Managed disk and three days with Unmanaged disk.
I have a replication policy of one day. What will happen if a problem prevents Site Recovery from generating recovery points for more than one day? Will my previous recovery points be lost?
No, Site Recovery keeps all your previous recovery points. Depending on the recovery points' retention window, Site Recovery replaces the oldest point only if it generates new points. Because of the problem, Site Recovery can't generate any new recovery points. Until there are new recovery points, all the old points remain after you reach the window of retention.
After replication is enabled on a virtual machine, how do I change the replication policy?
Go to Site Recovery Vault > Site Recovery Infrastructure > Replication policies. Select the policy that you want to edit, and save the changes. Any change applies to all the existing replications too.
Are all the recovery points a complete copy of the virtual machine or a differential?
The first recovery point that's generated has the complete copy. Any successive recovery points have delta changes.
Does increasing the retention period of recovery points increase the storage cost?
Yes, if you increase the retention period from one day to three days, Site Recovery saves the recovery points for an extra two days. The added time will incur storage charges since there will be 12 additional recovery points that need to be saved with increase in retention period from one day to three days. For example, a single recovery point might have delta changes of 10 GB with a per-GB cost of $0.16 per month. Additional charges would be $1.60 × 12 per month.
Failover
If I'm failing over to Azure, how do I access the Azure virtual machines after failover?
You can access the Azure virtual machines over a secure Internet connection, over a site-to-site VPN, or over Azure ExpressRoute. You need to prepare a number of things in order to connect. Learn more.
If I fail over to Azure how does Azure make sure my data is resilient?
Azure is designed for resilience. Site Recovery is already engineered for failover to a secondary Azure datacenter, in accordance with the Azure SLA. If this happens, we make sure your metadata and vaults remain within the same geographic region that you chose for your vault.
If I'm replicating between two datacenters what happens if my primary datacenter experiences an unexpected outage?
You can trigger an unplanned failover from the secondary site. Site Recovery doesn't need connectivity from the primary site to perform the failover.
Is failover automatic?
Failover isn't automatic. You initiate failovers with single click in the portal, or you can use Site Recovery PowerShell to trigger a failover. Failing back is a simple action in the Site Recovery portal.
To automate you could use on-premises Orchestrator or Operations Manager to detect a virtual machine failure, and then trigger the failover using the SDK.
If my on-premises host isn't responding or crashed, can I fail back to a different host?
Yes, you can use the alternate location recovery to failback to a different host from Azure.
What is the difference between Complete Migration, Commit and Disable Replication?
Once a machine from source location has been failed over to the target location then there are three options available for you to choose from. All three serve different purposes -
- Complete Migration means that you won't go back to the source location anymore. You migrated over to the target region and now you're done. Clicking on Complete Migration triggers Commit and then Disable Replication, internally.
- Commit means that this isn't the end of your replication process. The replication item along with all the configuration will remain, and you can hit Re-protect at a later point in time to enable the replication of your machines back to the source region.
- Disable Replication will disable the replication and remove all the related configuration. It won’t affect the already existing machine in the target region.
Automation
Can I automate Site Recovery scenarios with an SDK?
Yes. You can automate Site Recovery workflows using the REST API, PowerShell, or the Azure SDK. Currently supported scenarios for deploying Site Recovery using PowerShell:
Does the retirement of the AzureRM module affect how Site Recovery automatic updates work with an automation account?
No, the retirement of the AzureRM module doesn't affect how Site Recovery automatic updates work. No changes are needed for the internal runbook, and the REST API used in place, continues to function as intended with the automation account.
Component/provider upgrade
Where can I find the release notes/update rollups of Site Recovery upgrades
Learn about new updates, and get rollup information.
Next steps
- Read the Site Recovery overview