Use TLS/SSL certificates in your application in Azure Spring Apps
Note
The Basic, Standard, and Enterprise plans will be deprecated starting from mid-March, 2025, with a 3 year retirement period. We recommend transitioning to Azure Container Apps. For more information, see the Azure Spring Apps retirement announcement.
The Standard consumption and dedicated plan will be deprecated starting September 30, 2024, with a complete shutdown after six months. We recommend transitioning to Azure Container Apps.
This article shows you how to use public certificates in Azure Spring Apps for your application. Your app might act as a client and access an external service that requires certificate authentication, or it might need to perform cryptographic tasks.
When you let Azure Spring Apps manage your TLS/SSL certificates, you can maintain the certificates and your application code separately to safeguard your sensitive data. Your app code can access the public certificates you add to your Azure Spring Apps instance.
Prerequisites
- An application deployed to Azure Spring Apps. See Quickstart: Deploy your first application in Azure Spring Apps, or use an existing app.
- Either a certificate file with .crt, .cer, .pem, or .der extension, or a deployed instance of Azure Key Vault with a private certificate.
Import a certificate
You can choose to import your certificate into your Azure Spring Apps instance from either Key Vault or use a local certificate file.
Import a certificate from Key Vault
You need to grant Azure Spring Apps access to your key vault before you import your certificate.
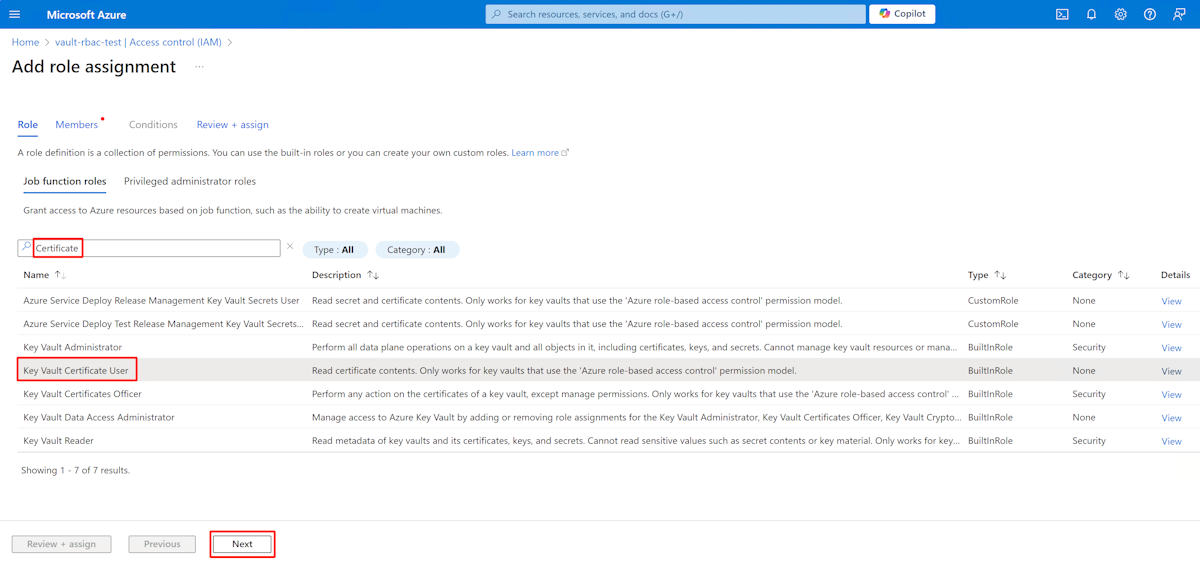
Azure Key Vault offers two authorization systems: Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC), which operates on Azure's control and data planes, and the access policy model, which operates on the data plane alone.
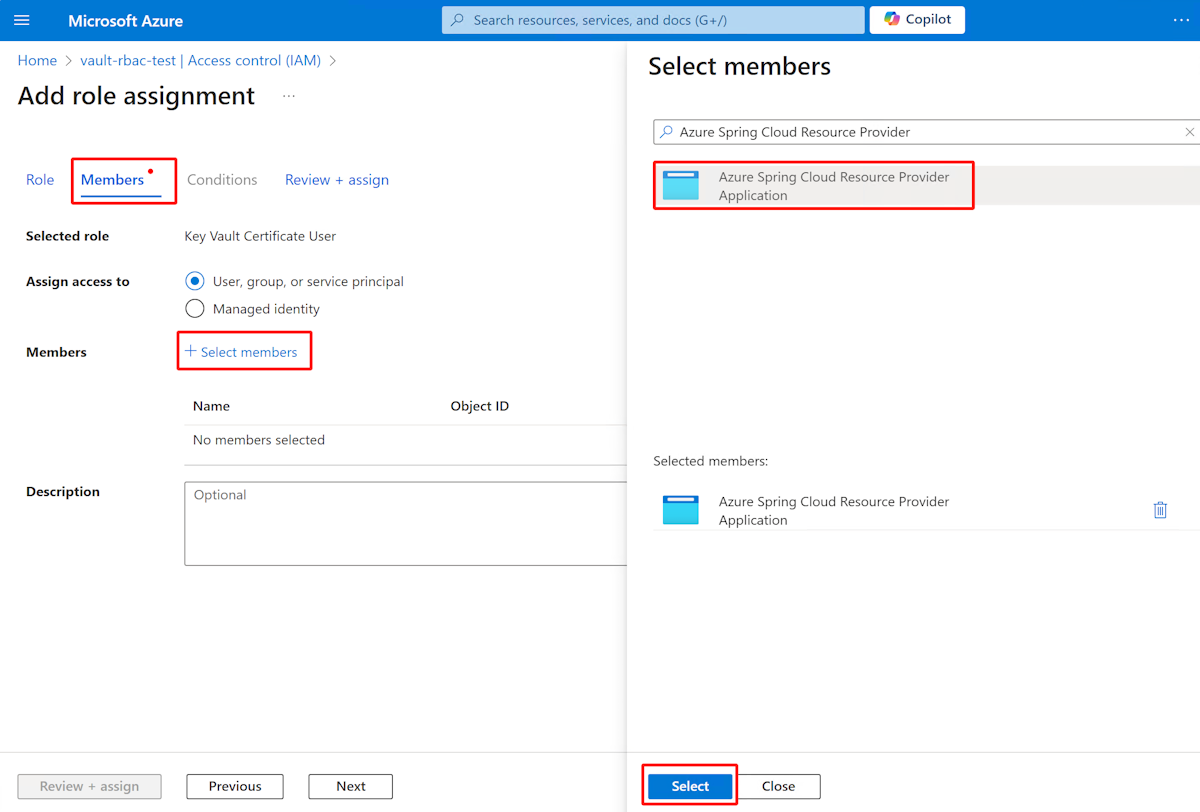
Use the following steps to grant access:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select Key vaults, then select the key vault you import your certificate from.
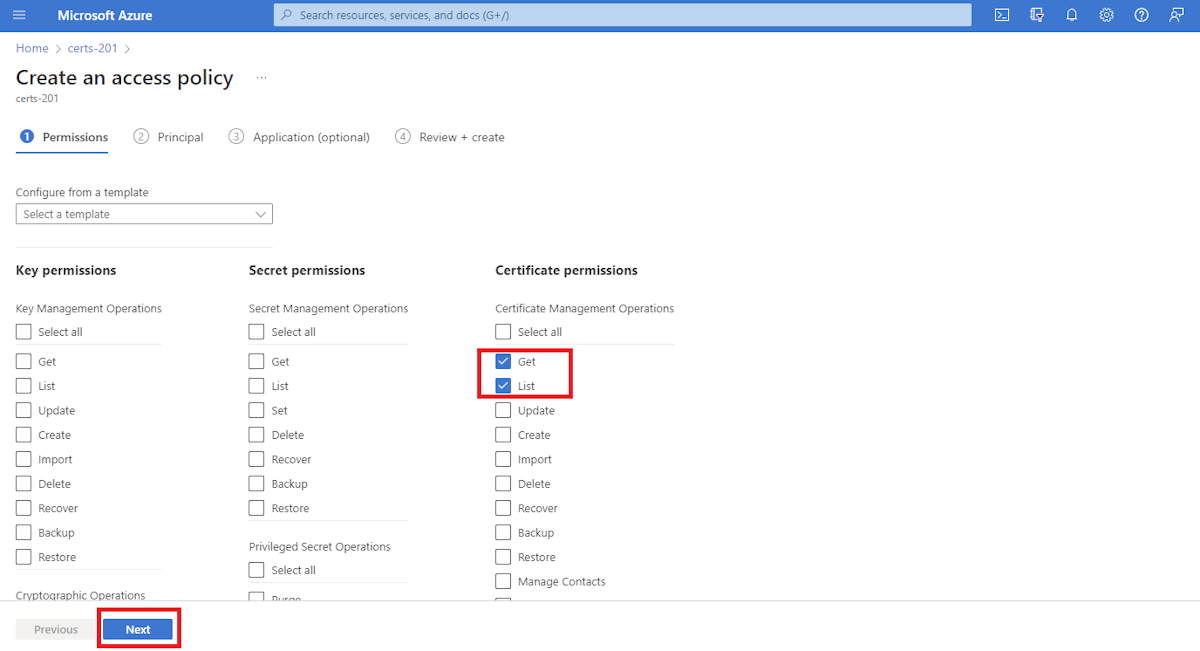
In the navigation pane, select Access policies, then select Create.
Select Certificate permissions, then select Get and List.
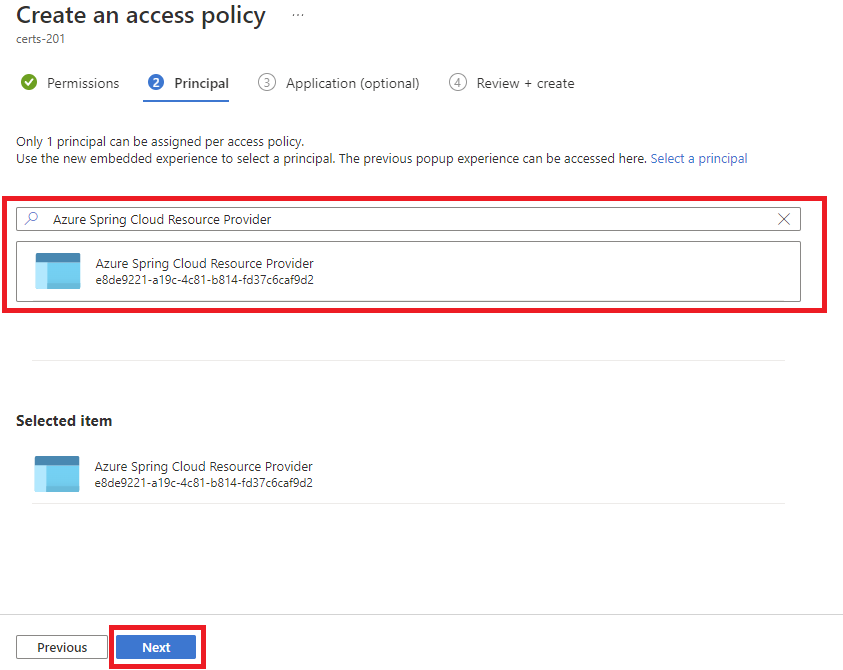
Under Principal, select Azure Spring Cloud Resource Provider.
Select Review + Create, then select Create.
After you grant access to your key vault, you can import your certificate using the following steps:
Go to your service instance.
From the left navigation pane of your instance, select TLS/SSL settings.
Select Import Key Vault Certificate in the Public Key Certificates section.
Select your key vault in the Key vaults section, select your certificate in the Certificate section, and then select Select.
Provide a value for Certificate name, select Enable auto sync if needed, and then select Apply. For more information, see the Auto sync certificate section of Map an existing custom domain to Azure Spring Apps.
After you successfully import your certificate, you see it in the list of Public Key Certificates.
Note
The Azure Key Vault and Azure Spring Apps instances should be in the same tenant.
Import a local certificate file
You can import a certificate file stored locally using these steps:
- Go to your service instance.
- From the left navigation pane of your instance, select TLS/SSL settings.
- Select Upload public certificate in the Public Key Certificates section.
After you successfully import your certificate, you see it in the list of Public Key Certificates.
Load a certificate
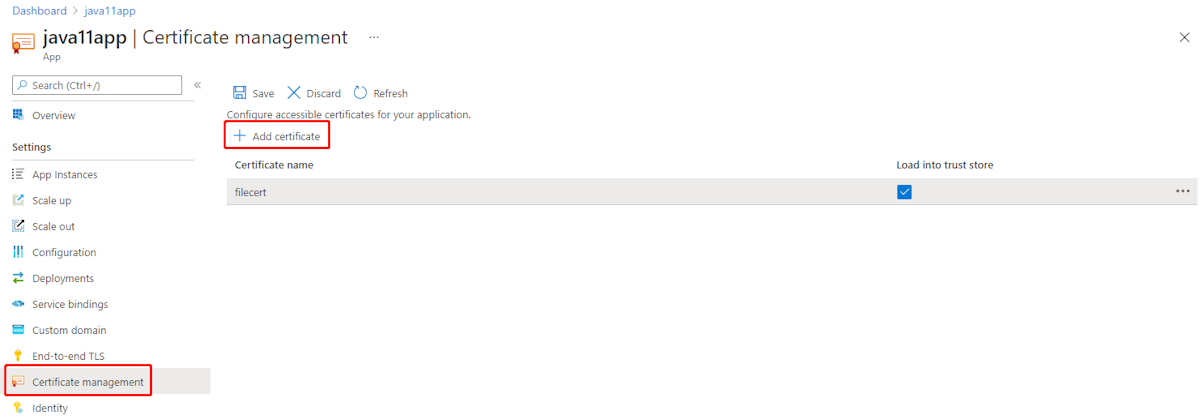
To load a certificate into your application in Azure Spring Apps, start with these steps:
- Go to your application instance.
- From the left navigation pane of your app, select Certificate management.
- Select Add certificate to choose certificates accessible for the app.
Load a certificate from code
Your loaded certificates are available in the /etc/azure-spring-cloud/certs/public folder. Use the following Java code to load a public certificate in an application in Azure Spring Apps.
CertificateFactory factory = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X509");
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("/etc/azure-spring-cloud/certs/public/<certificate name>");
X509Certificate cert = (X509Certificate) factory.generateCertificate(is);
// use the loaded certificate
Load a certificate into the trust store
For a Java application, you can choose Load into trust store for the selected certificate. The certificate is automatically added to the Java default TrustStores to authenticate a server in TLS/SSL authentication.
The following log from your app shows that the certificate is successfully loaded.
Load certificate from specific path. alias = <certificate alias>, thumbprint = <certificate thumbprint>, file = <certificate name>