Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this tutorial, you learn how to upload an image to Azure Blob Storage and process it using Azure Functions and Computer Vision. You also learn how to implement Azure Function triggers and bindings as part of this process. Together, these services analyze an uploaded image that contains text, extract the text out of it, and then store the text in a database row for later analysis or other purposes.
Azure Blob Storage is Azure's massively scalable object storage solution for the cloud. Blob Storage is designed for storing images and documents, streaming media files, managing backup and archive data, and much more. You can read more about Blob Storage on the overview page.
Azure Functions is a serverless computer solution that allows you to write and run small blocks of code as highly scalable, serverless, event driven functions. You can read more about Azure Functions on the overview page.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Upload images and files to Blob Storage
- Use an Azure Function event trigger to process data uploaded to Blob Storage
- Use Azure AI services to analyze an image
- Write data to Table Storage using Azure Function output bindings
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for trial.
- Visual Studio 2022
Create the storage account and container
The first step is to create the storage account to hold the uploaded blob data, which in this scenario is images that contain text. A storage account offers several different services, but this tutorial utilizes Blob Storage and Table Storage.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
In the search bar at the top of the portal, search for Storage and select the result labeled Storage accounts.
On the Storage accounts page, select + Create in the top left.
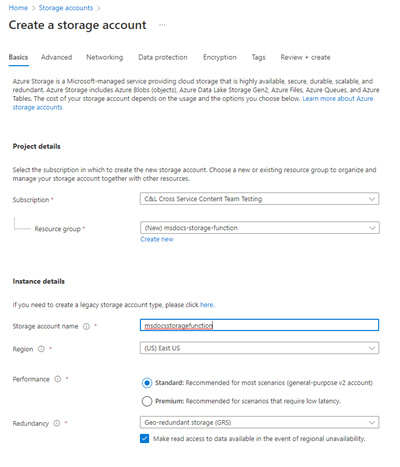
On the Create a storage account page, enter the following values:
- Subscription: Choose your desired subscription.
- Resource Group: Select Create new and enter a name of
msdocs-storage-function, and then choose OK. - Storage account name: Enter a value of
msdocsstoragefunction. The Storage account name must be unique across Azure, so you might need to add numbers after the name, such asmsdocsstoragefunction123. - Region: Select the region that is closest to you.
- Performance: Choose Standard.
- Redundancy: Leave the default value selected.
Select Review + Create at the bottom and Azure validates the information you entered. Once the settings are validated, choose Create and Azure begins provisioning the storage account, which might take a moment.
Create the container
After the storage account is provisioned, select Go to Resource. The next step is to create a storage container inside of the account to hold uploaded images for analysis.
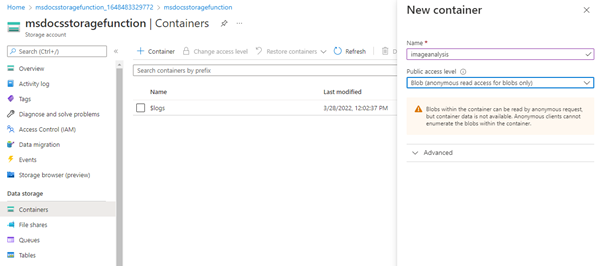
On the navigation panel, choose Containers.
On the Containers page, select + Container at the top. In the slide out panel, enter a Name of imageanalysis, and make sure the Public access level is set to Blob (anonymous read access for blobs only). Then select Create.
You should see your new container appear in the list of containers.
Retrieve the connection string
The last step is to retrieve our connection string for the storage account.
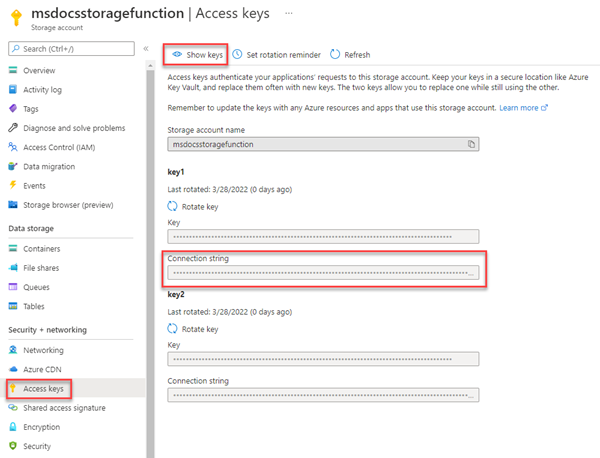
On the left navigation panel, select Access Keys.
On the Access Keys page, select Show keys. Copy the value of the Connection String under the key1 section and paste the key somewhere to use for later. Make a note of the storage account name
msdocsstoragefunctionfor later as well.
These values are necessary when we need to connect our Azure Function to this storage account.
Create the Computer Vision service
Next, create the Computer Vision service account that processes our uploaded files. Computer Vision is part of Azure AI services and offers various features for extracting data out of images. You can learn more about Computer Vision on the overview page.
In the search bar at the top of the portal, search for Computer and select the result labeled Computer vision.
On the Computer vision page, select + Create.
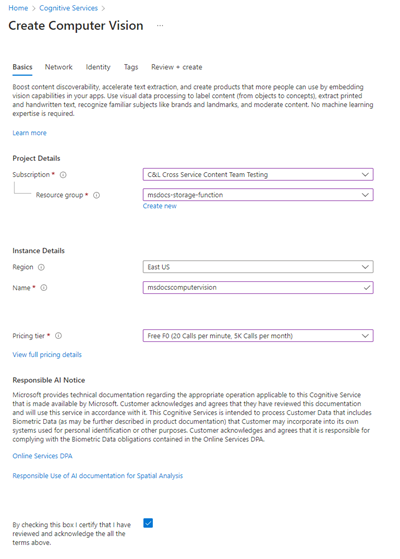
On the Create Computer Vision page, enter the following values:
- Subscription: Choose your desired Subscription.
- Resource Group: Use the
msdocs-storage-functionresource group you created earlier. - Region: Select the region that is closest to you.
- Name: Enter in a name of
msdocscomputervision. - Pricing Tier: Choose Free if it is available, otherwise choose Standard S1.
- Check the Responsible AI Notice box if you agree to the terms
Select Review + Create at the bottom. Azure takes a moment validate the information you entered. Once the settings are validated, choose Create and Azure begins provisioning the Computer Vision service, which might take a moment.
When the operation completes, select Go to Resource.
Retrieve the keys
Next, we need to find the secret key and endpoint URL for the Computer Vision service to use in our Azure Function app.
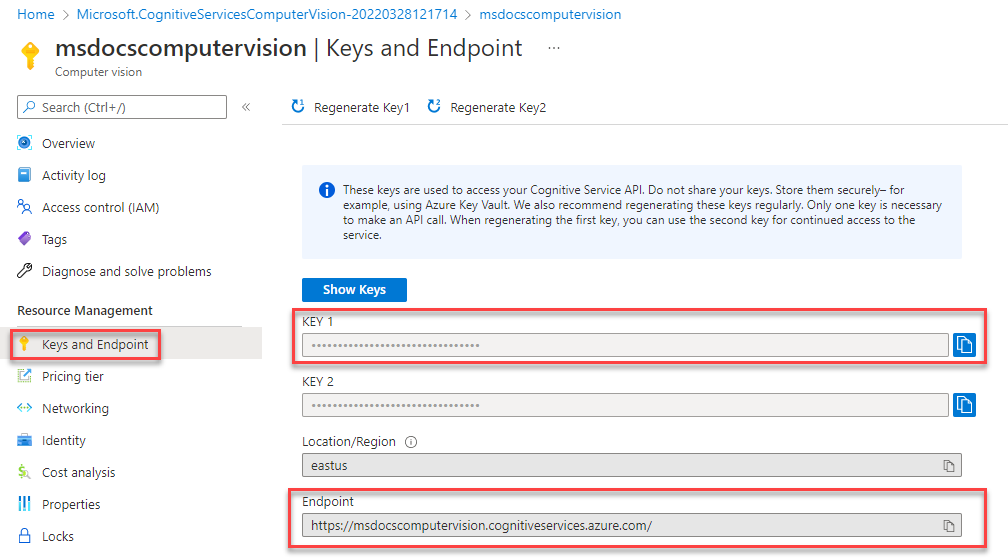
On the Computer Vision overview page, select Keys and Endpoint.
On the Keys and EndPoint page, copy the Key 1 value and the EndPoint values and paste them somewhere to use for later.
Download and configure the sample project
The code for the Azure Function used in this tutorial can be found in this GitHub repository. You can also clone the project using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/msdocs-storage-bind-function-service.git \
cd msdocs-storage-bind-function-service/dotnet
The sample project code accomplishes the following tasks:
- Retrieves environment variables to connect to the storage account and Computer Vision service
- Accepts the uploaded file as a blob parameter
- Analyzes the blob using the Computer Vision service
- Sends the analyzed image text to a new table row using output bindings
Once you download and opened the project, there are a few essential concepts to understand in the main Run method shown below. The Azure function utilizes Trigger and Output bindings, which are applied using attributes on the Run method signature.
The Table attribute uses two parameters. The first parameter specifies the name of the table to write the parsed image text value returned by the function. The second Connection parameter pulls a Table Storage connection string from the environment variables so that our Azure function has access to it.
The BlobTrigger attribute is used to bind our function to the upload event in Blob Storage, and supplies that uploaded blob to the Run function. The blob trigger has two parameters of its own - one for the name of the blob container to monitor for uploads, and one for the connection string of our storage account again.
// Azure Function name and output Binding to Table Storage
[FunctionName("ProcessImageUpload")]
[return: Table("ImageText", Connection = "StorageConnection")]
// Trigger binding runs when an image is uploaded to the blob container below
public async Task<ImageContent> Run([BlobTrigger("imageanalysis/{name}",
Connection = "StorageConnection")]Stream myBlob, string name, ILogger log)
{
// Get connection configurations
string subscriptionKey = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ComputerVisionKey");
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ComputerVisionEndpoint");
string imgUrl = $"https://{ Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("StorageAccountName")}
.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/imageanalysis/{name}";
ComputerVisionClient client = new ComputerVisionClient(
new ApiKeyServiceClientCredentials(subscriptionKey)) { Endpoint = endpoint };
// Get the analyzed image contents
var textContext = await AnalyzeImageContent(client, imgUrl);
return new ImageContent {
PartitionKey = "Images",
RowKey = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), Text = textContext
};
}
public class ImageContent
{
public string PartitionKey { get; set; }
public string RowKey { get; set; }
public string Text { get; set; }
}
This code also retrieves essential configuration values from environment variables, such as the storage account connection string and Computer Vision key. We'll add these environment variables to our Azure Function environment after it's deployed.
The ProcessImage function also utilizes a second method called AnalyzeImage. This code uses the URL Endpoint and Key of our Computer Vision account to make a request to that server to process our image. The request returns all of the text discovered in the image, which is written to Table Storage using the output binding on the Run method.
static async Task<string> ReadFileUrl(ComputerVisionClient client, string urlFile)
{
// Analyze the file using Computer Vision Client
var textHeaders = await client.ReadAsync(urlFile);
string operationLocation = textHeaders.OperationLocation;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
// Complete code omitted for brevity, view in sample project
return text.ToString();
}
Running locally
If you'd like to run the project locally, you can populate the environment variables using the local.settings.json file. Inside of this file, fill in the placeholder values with the values you saved earlier when creating the Azure resources.
Although the Azure Function code runs locally, it still connects to the live services out on Azure, rather than using any local emulators.
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "UseDevelopmentStorage=true",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "dotnet",
"StorageConnection": "your-storage-account-connection-string",
"StorageAccountName": "your-storage-account-name",
"ComputerVisionKey": "your-computer-vision-key",
"ComputerVisionEndPoint": "your-computer-vision-endpoint"
}
}
Deploy the code to Azure Functions
You are now ready to deploy our application to Azure by using Visual Studio. You can also create the Azure Functions app in Azure at the same time as part of the deployment process.
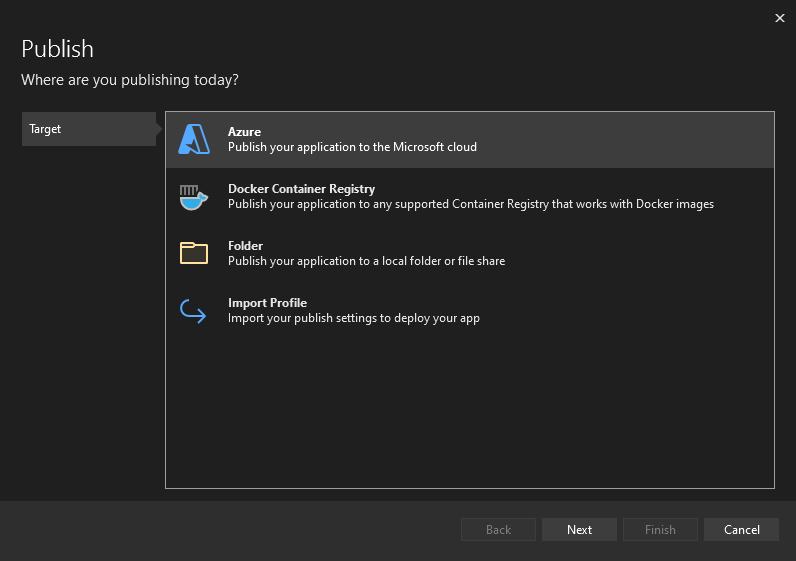
To begin, right select the ProcessImage project node and select Publish.
On the Publish dialog screen, select Azure and choose Next.
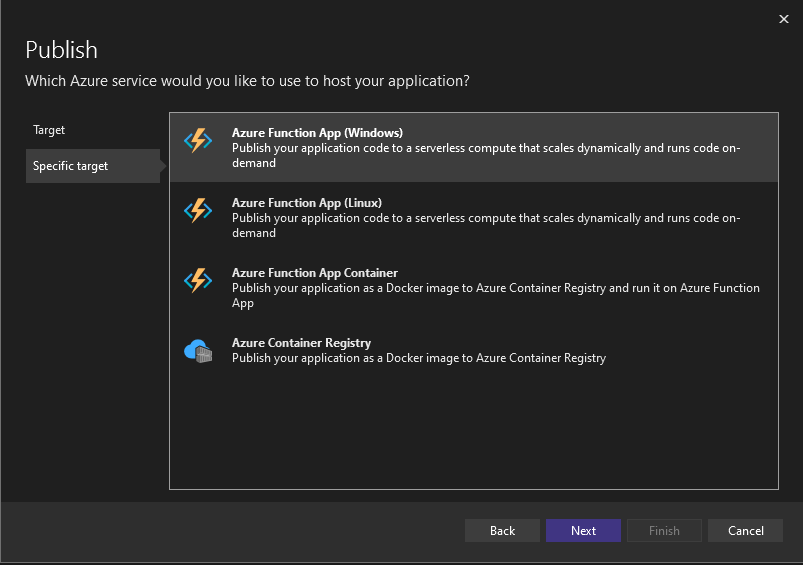
Select Azure Function App (Windows) or Azure Function App (Linux) on the next screen, and then choose Next again.
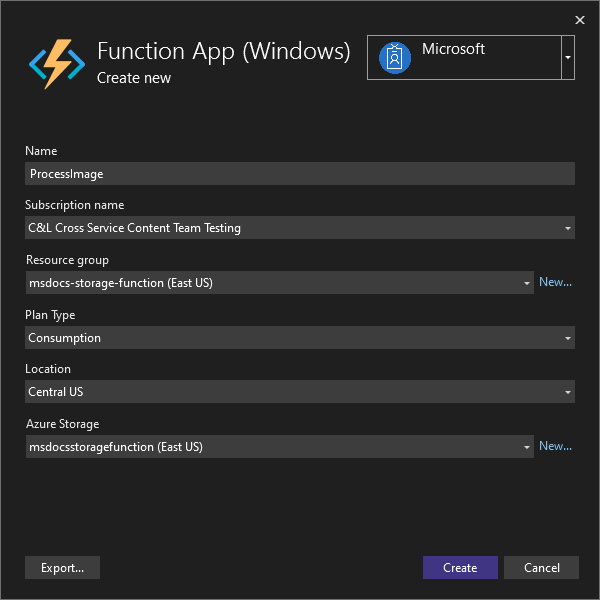
On the Functions instance step, make sure to choose the subscription you'd like to deploy to. Next, select the green + symbol on the right side of the dialog.
A new dialog opens. Enter the following values for your new Function App.
- Name: Enter msdocsprocessimage or something similar.
- Subscription Name: Choose whatever subscription you'd like to use.
- Resource Group: Choose the
msdocs-storage-functionresource group you created earlier. - Plan Type: Select Consumption.
- Location: Choose the region closest to you.
- Azure Storage: Select the storage account you created earlier.
Once you fill in all of those values, select Create. Visual Studio and Azure begin provisioning the requested resources, which takes a few moments to complete.
Once the process finishes, select Finish to close out the dialog workflow.
The final step to deploy the Azure Function is to select Publish in the upper right of the screen. Publishing the function might also take a few moments to complete. Once it finishes, your application is running on Azure.
Connect the services
The Azure Function was deployed successfully, but it cannot connect to our storage account and Computer Vision services yet. The correct keys and connection strings must first be added to the configuration settings of the Azure Functions app.
At the top of the Azure portal, search for function and select Function App from the results.
On the Function App screen, select the Function App you created in Visual Studio.
On the Function App overview page, select Configuration on the left navigation to open a page where we can manage various types of configuration settings for our app. For now, we are interested in Application Settings section.
The next step is to add settings for our storage account name and connection string, the Computer Vision secret key, and the Computer Vision endpoint.
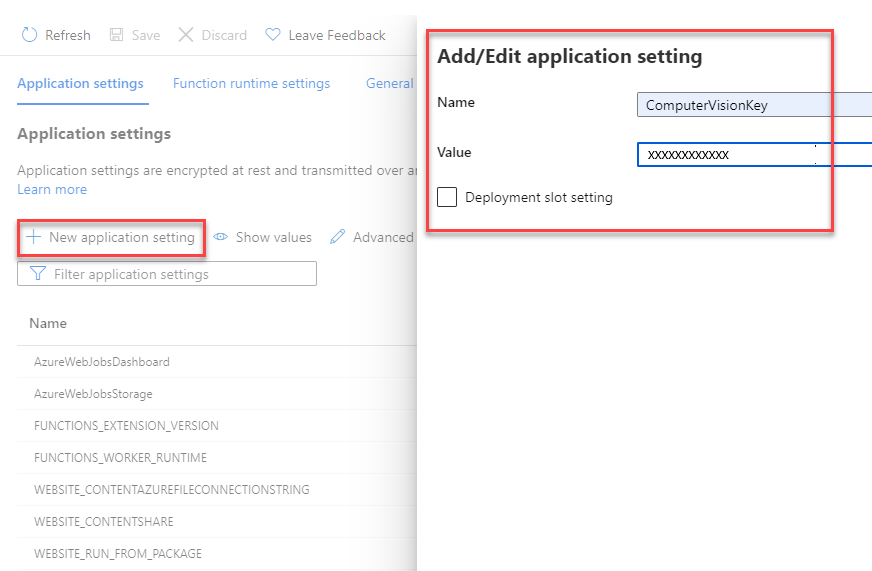
On the Application settings tab, select + New application setting. In the flyout that appears, enter the following values:
- Name: Enter a value of ComputerVisionKey.
- Value: Paste in the Computer Vision key you saved from earlier.
Select OK to add this setting to your app.
Next, let's repeat this process for the endpoint of our Computer Vision service, using the following values:
- Name: Enter a value of ComputerVisionEndpoint.
- Value: Paste in the endpoint URL you saved from earlier.
Repeat this step again for the storage account connection, using the following values:
- Name: Enter a value of StorageConnection.
- Value: Paste in the connection string you saved from earlier.
Finally, repeat this process one more time for the storage account name, using the following values:
- Name: Enter a value of StorageAccountName.
- Value: Enter in the name of the storage account you created.
After you add these application settings, make sure to select Save at the top of the configuration page. When the save completes, you can hit Refresh as well to make sure the settings are picked up.
All of the required environment variables to connect our Azure function to different services are now in place.
Upload an image to Blob Storage
You are now ready to test out our application! You can upload a blob to the container, and then verify that the text in the image was saved to Table Storage.
First, at the top of the Azure portal, search for Storage and select storage account. On the storage account page, select the account you created earlier.
Next, select Containers on the left nav, and then navigate into the ImageAnalysis container you created earlier. From here you can upload a test image right inside the browser.
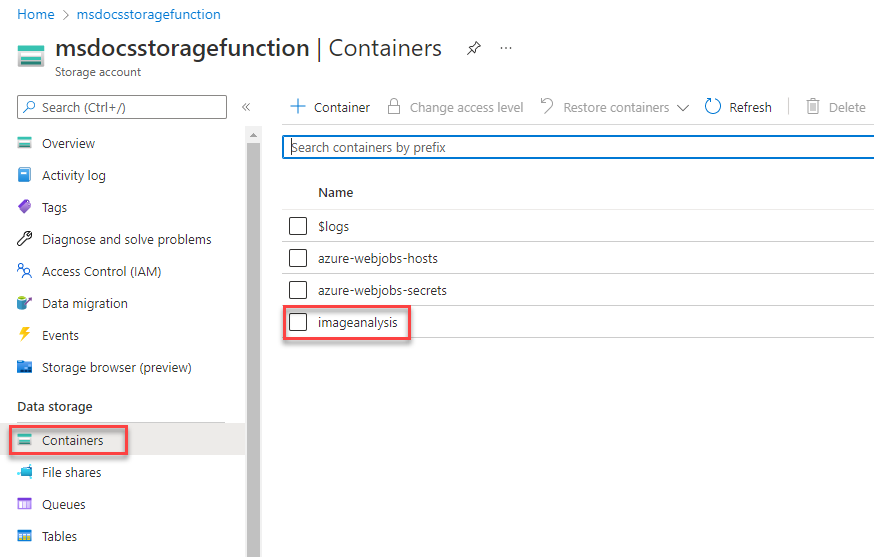
You can find a few sample images included in the images folder at the root of the downloadable sample project, or you can use one of your own.
At the top of the ImageAnalysis page, select Upload. In the flyout that opens, select the folder icon to open up a file browser. Choose the image you'd like to upload, and then select Upload.
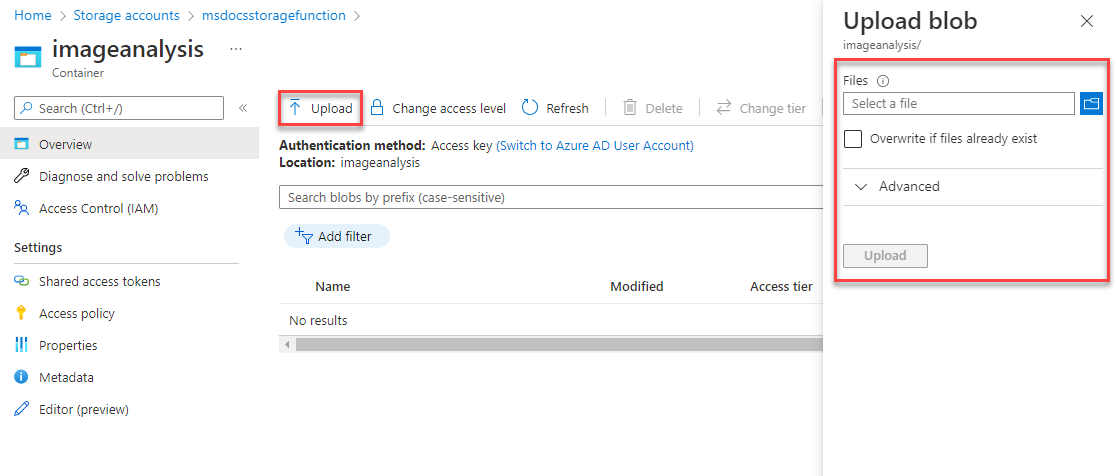
The file should appear inside of your blob container. Next, you can verify that the upload triggered the Azure Function, and that the text in the image was analyzed and saved to Table Storage properly.
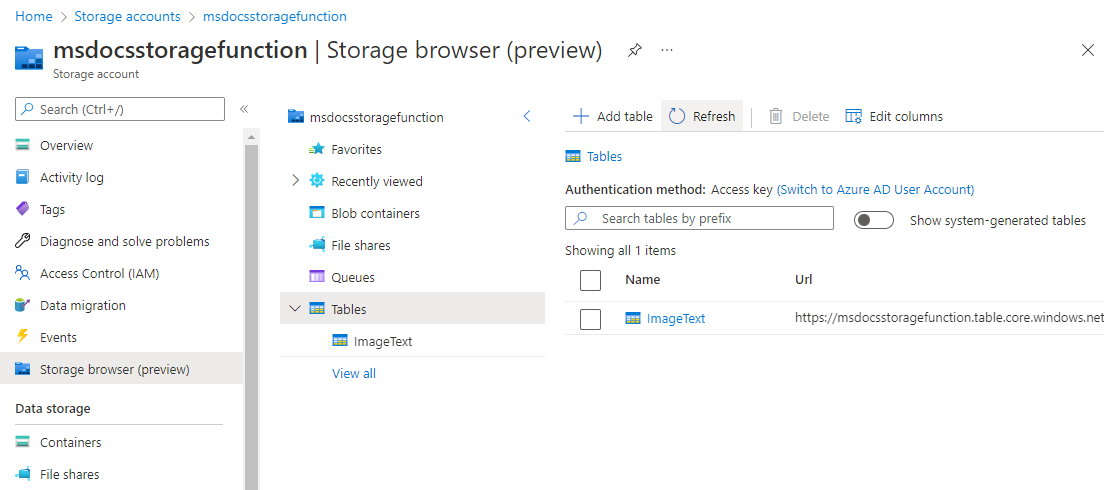
Using the breadcrumbs at the top of the page, navigate up one level in your storage account. Locate and select Storage browser on the left nav, and then select Tables.
An ImageText table should now be available. Select on the table to preview the data rows inside of it. You should see an entry for the processed image text of our upload. You can verify this using either the Timestamp, or by viewing the content of the Text column.
Congratulations! You succeeded in processing an image that was uploaded to Blob Storage using Azure Functions and Computer Vision.
Clean up resources
If you're not going to continue to use this application, you can delete the resources you created by removing the resource group.
- Select Resource groups from the main navigation
- Select the
msdocs-storage-functionresource group from the list. - Select the Delete resource group button at the top of the resource group overview page.
- Enter the resource group name msdocs-storage-function in the confirmation dialog.
- Select delete. The process to delete the resource group might take a few minutes to complete.