Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This tutorial is part two of a series. In it, you'll learn about the benefits of read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS) by simulating a failure.
In order to simulate a failure, you can use either static routing or Fiddler. Both methods will allow you to simulate failure for requests to the primary endpoint of your RA-GZRS storage account, leading the application to read from the secondary endpoint instead.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a trial account before you begin.
In part two of the series, you learn how to:
- Run and pause the application
- Simulate a failure with an invalid static route or Fiddler
- Simulate primary endpoint restoration
Prerequisites
Before you begin this tutorial, complete the previous tutorial: Make your application data highly available with Azure storage.
To simulate a failure with static routing, you'll use an elevated command prompt.
To simulate a failure using Fiddler, download and install Fiddler
Simulate a failure with an invalid static route
You can create an invalid static route for all requests to the primary endpoint of your RA-GZRS storage account. In this tutorial, the local host is used as the gateway for routing requests to the storage account. Using the local host as the gateway causes all requests to your storage account primary endpoint to loop back inside the host, which results in a failed request. Follow the following steps to simulate a failure, and primary endpoint restoration with an invalid static route.
Start and pause the application
Use the instructions in the previous tutorial to launch the sample and download the test file, confirming that it comes from primary storage. Depending on your target platform, you can then manually pause the sample or wait at a prompt.
Simulate failure
While the application is paused, open a command prompt on Windows as an administrator or run terminal as root on Linux.
Get information about the storage account primary endpoint domain by entering the following command on a command prompt or terminal, replacing STORAGEACCOUNTNAME with the name of your storage account.
nslookup STORAGEACCOUNTNAME.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn
Copy to the IP address of your storage account to a text editor for later use.
To get the IP address of your local host, type ipconfig on the Windows command prompt, or ifconfig on the Linux terminal.
To add a static route for a destination host, type the following command on a Windows command prompt or Linux terminal, replacing <destination_ip> with your storage account IP address and <gateway_ip> with your local host IP address.
Linux
sudo route add <destination_ip> gw <gateway_ip>
Windows
route add <destination_ip> <gateway_ip>
In the window with the running sample, resume the application or press the appropriate key to download the sample file and confirm that it comes from secondary storage. You can then pause the sample again or wait at the prompt.
Simulate primary endpoint restoration
To simulate the primary endpoint becoming functional again, delete the invalid static route from the routing table. This allows all requests to the primary endpoint to be routed through the default gateway. Type the following command on a Windows command prompt or Linux terminal.
Linux
sudo route del <destination_ip> gw <gateway_ip>
Windows
route delete <destination_ip>
You can then resume the application or press the appropriate key to download the sample file again, this time confirming that it once again comes from primary storage.
Simulate a failure with Fiddler
To simulate failure with Fiddler, you inject a failed response for requests to the primary endpoint of your RA-GZRS storage account.
The following sections depict how to simulate a failure and primary endpoint restoration with fiddler.
Launch fiddler
Open Fiddler, select Rules and Customize Rules.
The Fiddler ScriptEditor launches and displays the SampleRules.js file. This file is used to customize Fiddler.
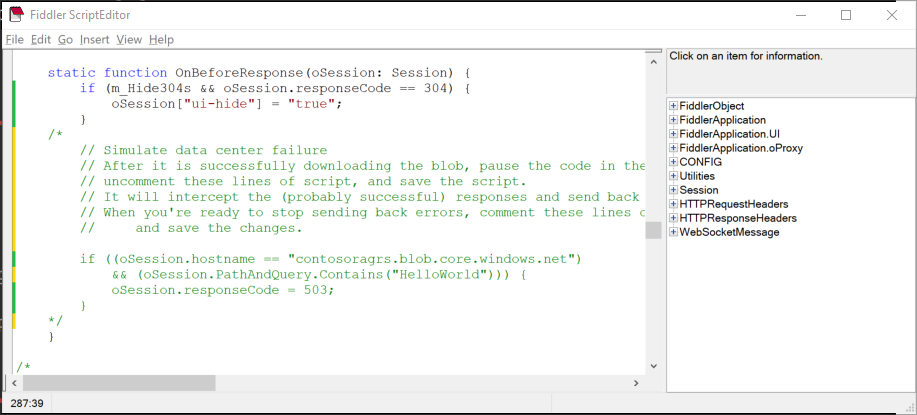
Paste the following code sample in the OnBeforeResponse function, replacing STORAGEACCOUNTNAME with the name of your storage account. Depending on the sample, you may also need to replace HelloWorld with the name of the test file being downloaded, or remove that part of the condition if it doesn't apply. The new code is commented out to ensure that it doesn't run immediately.
Once complete, select File and Save to save your changes. Leave the ScriptEditor window open for use in the following steps.
/*
// Simulate data center failure
// After it is successfully downloading the blob, pause the code in the sample,
// uncomment these lines of script, and save the script.
// It will intercept the (probably successful) responses and send back a 503 error.
// When you're ready to stop sending back errors, comment these lines of script out again
// and save the changes.
if ((oSession.hostname == "STORAGEACCOUNTNAME.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn")
// depending on the sample, you may need to modify or remove the line below
&& (oSession.PathAndQuery.Contains("HelloWorld"))) {
oSession.responseCode = 503;
}
*/
Start and pause the application
Use the instructions in the previous tutorial to launch the sample and download the test file, confirming that it comes from primary storage. Depending on your target platform, you can then manually pause the sample or wait at a prompt.
Simulate failure
While the application is paused, switch back to Fiddler and uncomment the custom rule you saved in the OnBeforeResponse function. Be sure to select File and Save to save your changes so the rule will take effect. This code looks for requests to the RA-GZRS storage account and, if the path contains the name of the sample file, returns a response code of 503 - Service Unavailable.
In the window with the running sample, resume the application or press the appropriate key to download the sample file and confirm that it comes from secondary storage. You can then pause the sample again or wait at the prompt.
Simulate primary endpoint restoration
In Fiddler, remove or comment out the custom rule again. Select File and Save to ensure the rule will no longer be in effect.
In the window with the running sample, resume the application or press the appropriate key to download the sample file and confirm that it comes from primary storage once again. You can then exit the sample.
Next steps
In part two of the series, you learned about simulating a failure to test read-access geo-redundant storage.
To learn more about how RA-GZRS storage works, and its associated risks, see Designing HA apps with RA-GZRS.