Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article helps you determine when to enable soft delete, versioning, both, or neither.
Both blob soft delete and blob versioning can help you protect from deletes and overwrites. These features can be used independently or together, depending on your workload, cost sensitivity, and recovery needs. To learn about other ways to protect blobs and containers, see data protection overview.
Our recommendation
Blob storage customers storing critical data should enable soft delete and versioning for layered protection against unintended deletions and overwrites. Soft delete ensures your data remains recoverable for a configurable number of days. Blob versioning offers more flexibility for managing previous versions and recovery options such as being able to read previous versions and recover from metadata or property changes. Refer to the following details to find out what is right for you.
Overview of features
| Feature | Protects against | Retention duration | Storage behavior | Hierarchical namespace (HNS) considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soft delete | Deletes and overwrites for flat namespace accounts. Deletes for hierarchical namespace accounts. | Up to 365 days (configurable) | Creates a soft-deleted snapshot for each overwrite. Creates a soft-deleted blob for each delete. | Soft delete only protects delete operations for HNS-enabled accounts. With the Set Blob Expiry API, an expired file can't be restored by using the blob soft delete feature. |
| Versioning | Deletes and overwrites for flat namespace accounts. | Indefinite (until explicitly deleted) | Creates a new version on each write. | Versioning is not available for HNS-enabled accounts. |
Note
Both features are disabled by default and must be enabled at the storage account level.
When to use soft delete
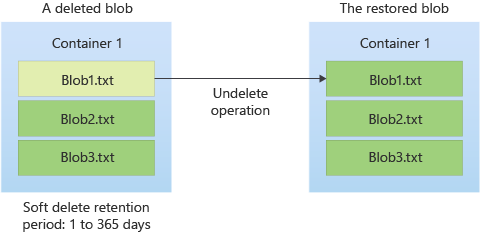
Enable soft delete if:
- You want to recover blobs that were accidentally deleted or overwritten. For hierarchical namespace enabled accounts, soft delete only protects from deletes, not overwrites.
- You need a time-limited safety net for blob recovery, equal to your retention days setting.
Considerations
- A soft-deleted snapshot is created for every overwrite operation. Blob soft delete doesn't protect against operations to write blob metadata or properties.
- A soft-deleted blob is created for every delete operation. Each soft-deleted blob is billed at the full size of the blob at the time of the operation.
- Avoid exceeding 1,000 soft-deleted snapshots per blob during the retention period to prevent performance degradation during blob listing operations.
- Retention is limited to a maximum of 365 days.
- If soft delete is enabled, there is no way to permanently delete until the soft delete retention expires. All deletes are "soft" and when the retention period expires, the soft-deleted blob is permanently deleted.
- If soft delete is disabled, all deletes are permanent, but the existing soft-deleted data are retained until the retention period expires.
- The contents of soft-deleted blobs are not accessible via Read APIs. To access the data, you must first undelete the blob.
When to use versioning
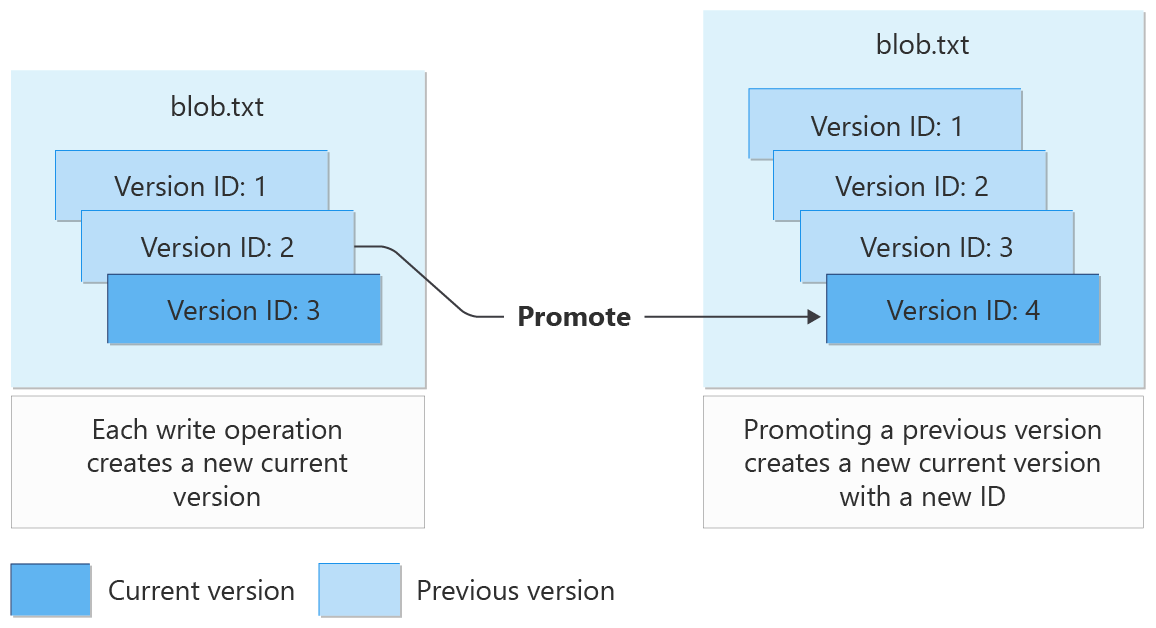
Enable versioning if:
You want to maintain a complete history of changes to a blob. For versioning, both overwrites and deletes create a previous version. Deletion removes the current version, but the previous versions remain.
You want to save changes to metadata and properties as previous versions.
You need long-term or indefinite retention of previous blob states.
You want to maintain quick access to previous versions without having to undelete.
Considerations
Each write operation (Put Blob, Put Block List, Set Blob Metadata, and Copy Blob) creates a new version of the blob.
Versions are retained until explicitly deleted, offering long-term recovery options.
Avoid exceeding 1,000 versions per blob to maintain optimal performance and prevent performance degradation during blob listing operations.
You can delete specific versions at any time. Separate roles are required to delete current versions and previous versions. That separation can be helpful to avoid mistakes. The same identity can have both of these roles assigned. Learn more.
You can configure a lifecycle management policy to control the lifecycle of your versions and define retention conditions.
Versioning is not available for accounts with hierarchical namespace enabled.
When to use both
Enable both soft delete and versioning if:
- You need comprehensive protection against both accidental deletions and overwrites.
- You operate in a regulated environment requiring layered data protection.
- You want to ensure recovery options even if versions are deleted.
- You want to create a grace period where, when previous versions are deleted, they are retained for some period of time (soft delete retention).
Considerations
When versioning is enabled, deletion of the current version makes it a previous version. When soft delete is enabled, deletion of the previous version makes it a soft-deleted previous version. (Learn more)
Soft delete retention only applies to deletion of previous versions.
Avoid exceeding 1,000 versions per blob to maintain optimal performance and prevent performance degradation during blob listing operations.
Each feature retains data in a different way. You can set different retention periods for versioning and soft delete to balance cost and risk of data loss.
When to use neither
You might choose to disable both features if:
- Your application has its own backup and recovery mechanisms.
- You have strict cost constraints and low risk of accidental data loss.
- Your data is temporary or test data and protection is not necessary.
Blob accessibility after deletion
Whether soft delete, versioning, or both are enabled on the account, this section describes how to access the data after a blob is deleted.
If versioning is enabled, you must specify a version ID to read a previous version. Use the Copy Blob operation to copy a previous version to a new current version.
If soft delete is enabled, you must undelete the blob.
If versioning and soft delete are enabled and the previous version you want to access has been soft-deleted, you must first undelete the blob. The Undelete Blob operation always restores all soft-deleted versions of the blob. Then you can use the Copy Blob operation to copy a previous version to a new current version.
Cost considerations
Enabling soft delete or versioning for frequently overwritten data might result in increased storage capacity charges and increased latency when listing blobs. Block-level updates using Put Block and Put Block List can reduce storage costs. If you make no changes to a blob, version, or snapshot's tier, then you are billed for unique blocks of data across that blob its versions, and snapshots. You are billed for active data until the blob, versions, and snapshots are permanently deleted. Learn more