Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes common problems with Azure Stream Analytics input connections, how to troubleshoot those problems, and how to correct them.
Many troubleshooting steps require you to turn on resource logs for your Stream Analytics job. If you don't have resource logs turned on, see Troubleshoot Azure Stream Analytics by using resource logs.
Job doesn't receive input events
Verify your connectivity to inputs and outputs. Use the Test Connection button for each input and output.
Examine your input data:
Use the Sample Data button for each input. Download the input sample data.
Inspect the sample data to understand the schema and data types.
Check Event Hub metrics to ensure that events are being sent. Message metrics should be greater than zero if Event Hubs is receiving messages.
Ensure that you selected a time range in the input preview. Choose Select time range, and then enter a sample duration before testing your query.
Malformed input events cause deserialization errors
Deserialization problems happen when the input stream of your Stream Analytics job contains malformed messages. For example, a missing parenthesis or brace in a JSON object, or an incorrect time-stamp format in the time field, can cause a malformed message.
When a Stream Analytics job receives a malformed message from an input, it drops the message and notifies you with a warning. A warning symbol appears on the Inputs tile of your Stream Analytics job. The warning symbol exists as long as the job is in a running state.
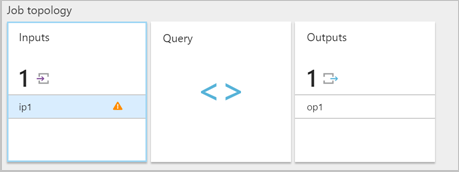
Turn on resource logs to view the details of the error and the message (payload) that caused the error. There are multiple reasons why deserialization errors can occur. For more information about specific deserialization errors, see Input data errors. If resource logs aren't turned on, a brief notification appears in the Azure portal.
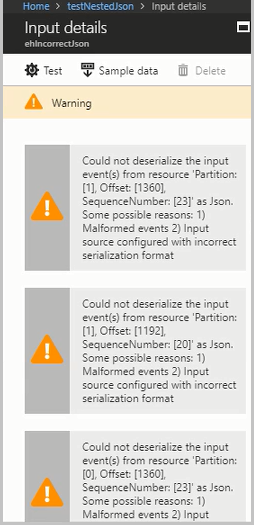
If the message payload is greater than 32 KB or is in binary format, run the CheckMalformedEvents.cs code available in the GitHub samples repository. This code reads the partition ID offset and prints the data located in that offset.
Other common reasons for input deserialization errors are:
- An integer column that has a value greater than
9223372036854775807. - Strings instead of an array of objects or line-separated objects. Valid example:
*[{'a':1}]*. Invalid example:*"'a' :1"*. - Using an Event Hubs capture blob in Avro format as input in your job.
- Having two columns in a single input event that differ only in case. Example:
*column1*and*COLUMN1*.
Partition count changes
The partition count of event hubs can be changed. If the partition count of an event hub is changed, you need to stop and restart the Stream Analytics job.
The following error appears when the partition count of an event hub is changed while the job is running: Microsoft.Streaming.Diagnostics.Exceptions.InputPartitioningChangedException.
Job exceeds the maximum Event Hubs receivers
A best practice for using Event Hubs is to use multiple consumer groups for job scalability. The number of readers in the Stream Analytics job for a specific input affects the number of readers in a single consumer group.
The precise number of receivers is based on internal implementation details for the scale-out topology logic. The number isn't exposed externally. The number of readers can change when a job is started or upgraded.
The following error message appears when the number of receivers exceeds the maximum. The message includes a list of existing connections made to Event Hubs under a consumer group. The tag AzureStreamAnalytics indicates that the connections are from an Azure streaming service.
The streaming job failed: Stream Analytics job has validation errors: Job will exceed the maximum amount of Event Hubs Receivers.
The following information may be helpful in identifying the connected receivers: Exceeded the maximum number of allowed receivers per partition in a consumer group which is 5. List of connected receivers –
AzureStreamAnalytics_c4b65e4a-f572-4cfc-b4e2-cf237f43c6f0_1,
AzureStreamAnalytics_c4b65e4a-f572-4cfc-b4e2-cf237f43c6f0_1,
AzureStreamAnalytics_c4b65e4a-f572-4cfc-b4e2-cf237f43c6f0_1,
AzureStreamAnalytics_c4b65e4a-f572-4cfc-b4e2-cf237f43c6f0_1,
AzureStreamAnalytics_c4b65e4a-f572-4cfc-b4e2-cf237f43c6f0_1.
Note
When the number of readers changes during a job upgrade, transient warnings are written to audit logs. Stream Analytics jobs automatically recover from these transient problems.
To add a new consumer group in your Event Hubs instance, follow these steps:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Locate your event hub.
Under the Entities heading, select Event Hubs.
Select the event hub by name.
On the Event Hubs Instance page, under the Entities heading, select Consumer groups. A consumer group with the name $Default is listed.
Select + Consumer Group to add a new consumer group.
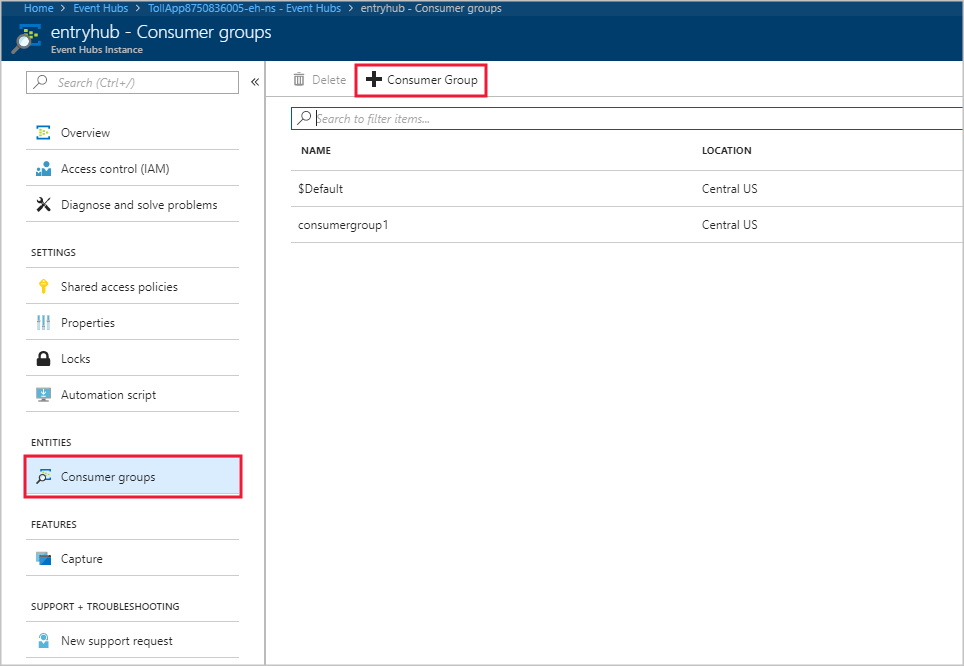
When you created the input in the Stream Analytics job to point to the event hub, you specified the consumer group there. Event Hubs uses $Default if no consumer group is specified. After you create a consumer group, edit the event hub input in the Stream Analytics job and specify the name of the new consumer group.
Readers per partition exceed the Event Hubs limit
If your streaming query syntax references the same resource for event hub input multiple times, the job engine can use multiple readers per query from that same consumer group. When there are too many references to the same consumer group, the job can exceed the limit of five and throw an error. In those circumstances, you can further divide by using multiple inputs across multiple consumer groups.
Scenarios in which the number of readers per partition exceeds the Event Hubs limit of five include:
Multiple
SELECTstatements: If you use multipleSELECTstatements that refer to the same event hub input, eachSELECTstatement causes a new receiver to be created.UNION: When you useUNION, it's possible to have multiple inputs that refer to the same event hub and consumer group.SELF JOIN: When you use aSELF JOINoperation, it's possible to refer to the same event hub multiple times.
The following best practices can help mitigate scenarios in which the number of readers per partition exceeds the Event Hubs limit of five.
Split your query into multiple steps by using a WITH clause
The WITH clause specifies a temporary named result set that a FROM clause in the query can reference. You define the WITH clause in the execution scope of a single SELECT statement.
For example, instead of this query:
SELECT foo
INTO output1
FROM inputEventHub
SELECT bar
INTO output2
FROM inputEventHub
…
Use this query:
WITH data AS (
SELECT * FROM inputEventHub
)
SELECT foo
INTO output1
FROM data
SELECT bar
INTO output2
FROM data
…
Ensure that inputs bind to different consumer groups
For queries in which three or more inputs are connected to the same Event Hubs consumer group, create separate consumer groups. This task requires the creation of additional Stream Analytics inputs.
Create separate inputs with different consumer groups
You can create separate inputs with different consumer groups for the same event hub. In the following example of a UNION query, InputOne and InputTwo refer to the same Event Hubs source. Any query can have separate inputs with different consumer groups. The UNION query is only one example.
WITH
DataOne AS
(
SELECT * FROM InputOne
),
DataTwo AS
(
SELECT * FROM InputTwo
),
SELECT foo FROM DataOne
UNION
SELECT foo FROM DataTwo
Readers per partition exceed the IoT Hub limit
Stream Analytics jobs use the built-in Event Hubs-compatible endpoint in Azure IoT Hub to connect and read events from IoT Hub. If your readers per partition exceed the limits of IoT Hub, you can use the solutions for Event Hubs to resolve it. You can create a consumer group for the built-in endpoint through the IoT Hub portal endpoint session or through the IoT Hub SDK.
Get help
For further assistance, try the Microsoft Q&A page for Azure Stream Analytics.