Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: ✔️ Linux VMs ✔️ Uniform scale sets
Note
The following article is for Uniform Virtual Machine Scale Sets. We recommend using Flexible Virtual Machine Scale Sets for new workloads. Learn more about this new orchestration mode in our Flexible Virtual Machine Scale Sets overview.
A Virtual Machine Scale Set allows you to deploy and manage a set of auto-scaling virtual machines. You can scale the number of VMs in the scale set manually, or define rules to autoscale based on resource usage like CPU, memory demand, or network traffic. An Azure load balancer then distributes traffic to the VM instances in the scale set. In this quickstart, you create a Virtual Machine Scale Set and deploy a sample application with an Azure Resource Manager template (ARM template).
An Azure Resource Manager template is a JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) file that defines the infrastructure and configuration for your project. The template uses declarative syntax. You describe your intended deployment without writing the sequence of programming commands to create the deployment.
ARM templates let you deploy groups of related resources. In a single template, you can create the Virtual Machine Scale Set, install applications, and configure autoscale rules. With the use of variables and parameters, this template can be reused to update existing, or create additional, scale sets. You can deploy templates through the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell, or from continuous integration / continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines.
If your environment meets the prerequisites and you're familiar with using ARM templates, select the Deploy to Azure button. The template will open in the Azure portal.
Prerequisites
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a Trial before you begin.
Review the template
The template used in this quickstart is from Azure Quickstart Templates.
These resources are defined in the template:
- Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks
- Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses
- Microsoft.Network/loadBalancers
- Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets
- Microsoft.Insights/autoscaleSettings
Define a scale set
To create a scale with a template, you define the appropriate resources. The core parts of the Virtual Machine Scale Set resource type are:
| Property | Description of property | Example template value |
|---|---|---|
| type | Azure resource type to create | Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets |
| name | The scale set name | myScaleSet |
| location | The location to create the scale set | China North 2 |
| sku.name | The VM size for each scale set instance | Standard_A1 |
| sku.capacity | The number of VM instances to initially create | 2 |
| upgradePolicy.mode | VM instance upgrade mode when changes occur | Automatic |
| imageReference | The platform or custom image to use for the VM instances | Canonical Ubuntu Server 16.04-LTS |
| osProfile.computerNamePrefix | The name prefix for each VM instance | myvmss |
| osProfile.adminUsername | The username for each VM instance | azureuser |
| osProfile.adminPassword | The password for each VM instance | P@ssw0rd! |
To customize a scale set template, you can change the VM size or initial capacity. Another option is to use a different platform or a custom image.
Add a sample application
To test your scale set, install a basic web application. When you deploy a scale set, VM extensions can provide post-deployment configuration and automation tasks, such as installing an app. Scripts can be downloaded from Azure storage or GitHub, or provided to the Azure portal at extension run-time. To apply an extension to your scale set, you add the extensionProfile section to the preceding resource example. The extension profile typically defines the following properties:
- Extension type
- Extension publisher
- Extension version
- Location of configuration or install scripts
- Commands to execute on the VM instances
The template uses the Custom Script Extension to install Bottle, a Python web framework, and a simple HTTP server.
Two scripts are defined in fileUris - installserver.sh, and workserver.py. These files are downloaded from GitHub, then commandToExecute runs bash installserver.sh to install and configure the app.
Deploy the template
You can deploy the template by selecting the following Deploy to Azure button. This button opens the Azure portal, loads the complete template, and prompts for a few parameters such as a scale set name, instance count, and admin credentials.
You can also deploy a Resource Manager template by using Azure CLI:
# Create a resource group
az group create --name myResourceGroup --location chinanorth2
# Deploy template into resource group
az deployment group create \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--template-uri https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-quickstart-templates/master/application-workloads/python/vmss-bottle-autoscale/azuredeploy.json
Answer the prompts to provide a scale set name, instance count, and admin credentials for the VM instances. It takes a few minutes for the scale set and supporting resources to be created.
Validate the deployment
To see your scale set in action, access the sample web application in a web browser. Obtain the public IP address of the load balancer with az network public-ip list as follows:
az network public-ip list \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--query [*].ipAddress -o tsv
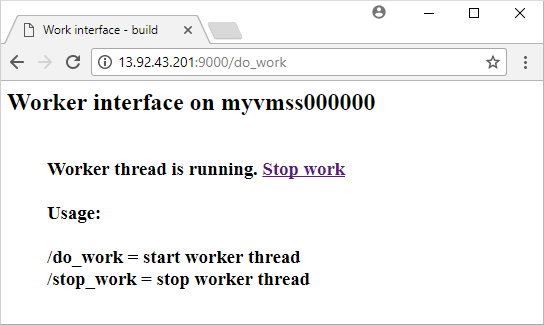
Enter the public IP address of the load balancer in to a web browser in the format http://publicIpAddress:9000/do_work. The load balancer distributes traffic to one of your VM instances, as shown in the following example:
Clean up resources
When no longer needed, you can use az group delete to remove the resource group, scale set, and all related resources as follows. The --no-wait parameter returns control to the prompt without waiting for the operation to complete. The --yes parameter confirms that you wish to delete the resources without an additional prompt to do so.
az group delete --name myResourceGroup --yes --no-wait
Next steps
In this quickstart, you created a Linux scale set with an ARM template and used the Custom Script Extension to install a basic Python web server on the VM instances. To learn more, continue to the tutorial for how to create and manage Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets.
