Nota:
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar iniciar sesión o cambiar directorios.
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar cambiar los directorios.
重要
此功能目前以公共预览版提供。 可以在预览页面上确认加入状态。 请参阅 管理 Azure Databricks 预览版。
本页介绍如何为外部用户嵌入工作、如何配置 Azure Databricks 工作区以安全共享嵌入式仪表板,以及如何使用示例应用程序开始。 为外部用户嵌入使用服务主体和作用域访问令牌对嵌入式仪表板进行身份验证和授权。 此方法允许你与组织外部的查看者(例如合作伙伴和客户)共享仪表板,而无需为这些用户预配 Azure Databricks 帐户。
若要了解其他嵌入选项,包括为组织中的用户嵌入仪表板,请参阅 “嵌入仪表板”。
外部用户的嵌入工作原理
在为外部用户嵌入仪表板时,下图和编号的步骤说明了如何对用户进行身份验证和仪表板填充用户范围的结果。
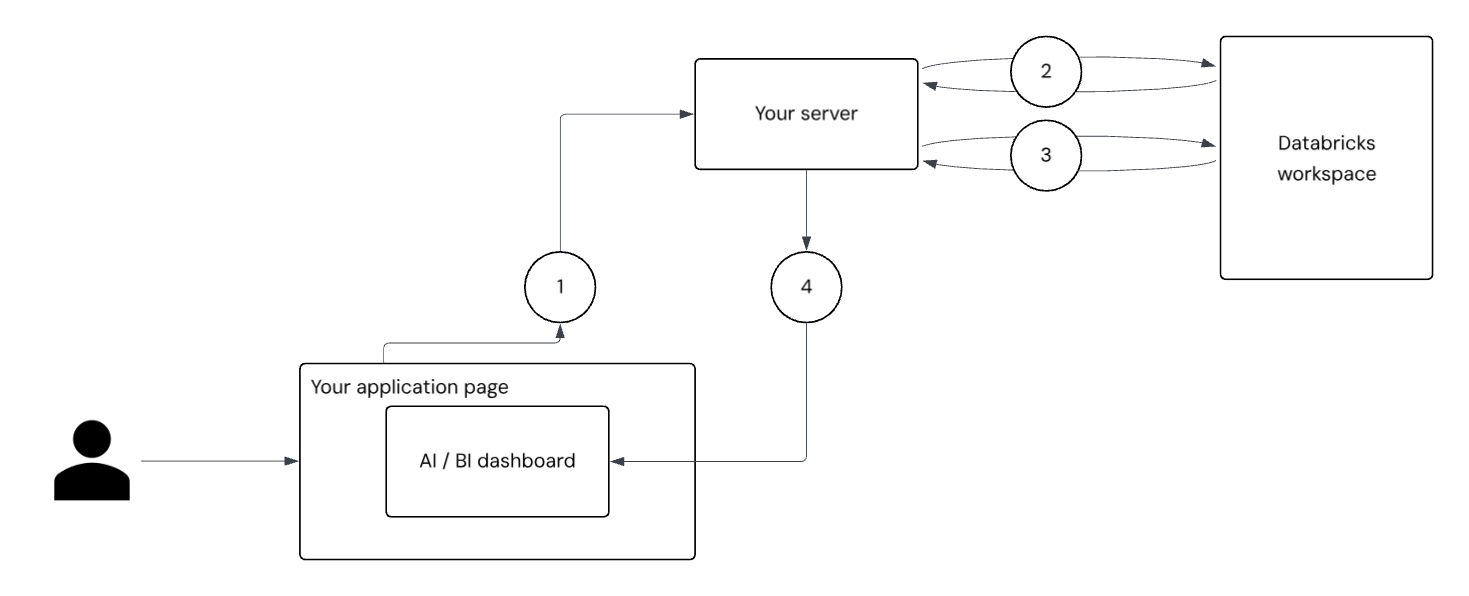
用户身份验证和请求: 用户登录到应用程序。 应用程序的前端将经过身份验证的请求发送到服务器以获取仪表板访问令牌。
服务主体身份验证: 服务器使用服务主体机密从 Databricks 服务器请求和接收 OAuth 令牌。 这是一个范围广泛的令牌,可以调用 Azure Databricks 代表服务主体访问的所有仪表板 API。 服务器使用此令牌调用
/tokeninfo终结点,并传入基本用户信息,例如external_viewer_id和external_value。 请参阅 安全向单个用户展示仪表板。用户范围的令牌生成: 使用终结点和 Databricks OpenID Connect (OIDC) 终结点的响应
/tokeninfo,服务器会生成一个新的严格范围的令牌,用于对传入的用户信息进行编码。仪表板呈现和数据筛选:应用程序页在构造过程中实例化
DatabricksDashboard@databricks/aibi-client并传递用户范围的令牌。 仪表板使用用户的上下文呈现。 此令牌授权访问、支持审核external_viewer_id以及用于external_value数据筛选。 仪表板数据集中的查询可以引用__aibi_external_value以应用每用户筛选器,确保每个查看器只查看允许查看的数据。
安全地向单个用户显示仪表板
配置应用程序服务器,以便根据 external_viewer_id每个用户生成唯一的用户范围令牌。 这使你可以通过审核日志跟踪仪表板视图和使用情况。 与 external_viewer_id 一个 external_value配对,该变量充当全局变量,可以插入到仪表板数据集中使用的 SQL 查询中。 这样,便可以筛选每个用户的仪表板上显示的数据。
external_viewer_id 传递到仪表板审核日志,不得包含个人身份信息。 此值还应是每个用户的唯一值。
external_value 用于查询处理, 可以 包含个人身份信息。
以下示例演示如何在数据集查询中使用外部值作为筛选器:
SELECT *
FROM sales
WHERE region = __aibi_external_value
设置概述
本部分包括为在外部位置嵌入仪表板而需要执行的步骤的高级概念概述。
若要在外部应用程序中嵌入仪表板,请先在 Azure Databricks 中创建 服务主体 并生成机密。 必须向服务主体授予对仪表板及其基础数据的读取访问权限。 服务器使用服务主体机密检索可以代表服务主体访问仪表板 API 的令牌。 使用此令牌,服务器调用 /tokeninfo API 终结点(OpenID Connect(OIDC)终结点,该终结点返回基本用户配置文件信息,包括 external_value 和 external_viewer_id 值。 这些值使你可以将请求与单个用户相关联。
使用从服务主体获取的令牌,服务器将生成范围限定为访问仪表板的特定用户的新令牌。 此用户范围的令牌将传递到应用程序页,应用程序从DatabricksDashboard库中实例化@databricks/aibi-client对象。 令牌包含支持审核和强制筛选的用户特定信息,以便每个用户只看到他们有权访问的数据。 从用户的角度来看,登录到应用程序会自动提供对嵌入仪表板的访问权限,并具有正确的数据可见性。
速率限制和性能注意事项
外部嵌入的速率限制为每秒 20 个仪表板加载。 可以同时打开 20 多个仪表板,但不能同时开始加载超过 20 个仪表板。
先决条件
若要实现外部嵌入,请确保满足以下先决条件:
- 必须在已发布的仪表板上至少具有 CAN MANAGE 权限。 请参阅 教程:如有必要,使用示例仪表板 快速创建和发布示例仪表板。
- 必须安装 Databricks CLI 0.205 或更高版本。 有关说明 ,请参阅安装或更新 Databricks CLI 。 若要配置和使用 OAuth 身份验证,请参阅 OAuth 用户到计算机(U2M)身份验证。
- 工作区管理员必须定义可托管嵌入式仪表板的已批准域的列表。 有关说明,请参阅 “管理仪表板嵌入 ”。
- 用于托管嵌入式仪表板的外部应用程序。 可以使用自己的应用程序或使用提供的示例应用程序。
步骤 1:创建服务主体
创建服务主体以充当 Azure Databricks 中的外部应用程序的标识。 此服务主体代表应用程序对请求进行身份验证。
若要创建服务主体,请执行以下作:
以工作区管理员身份登录到 Azure Databricks 工作区。
单击 Azure Databricks 工作区顶部栏中的用户名,然后选择“设置”。
在左窗格中单击“ 标识”并访问 。
在服务主体旁边,单击管理。
单击“添加服务主体”。
单击“新增” 。
输入服务主体的描述性名称。
单击 添加。
打开刚从 “服务主体 列表”页创建的服务主体。 如有必要,请使用 “筛选 文本输入”字段按名称搜索它。
在 “服务主体详细信息 ”页上,记录 应用程序 ID。验证是否已选中 Databricks SQL 访问 和 工作区访问 复选框。
步骤 2:创建 OAuth 机密
为服务主体生成机密并收集外部应用程序所需的以下配置值:
- 服务主体(客户端)ID
- 客户密钥
服务主体使用 OAuth 机密在从外部应用程序请求访问令牌时验证其标识。
生成机密:
单击“服务主体详细信息”页上的“机密”。
单击“ 生成机密”。
输入新机密的生存期值(例如,介于 1 到 730 天之间)。
立即复制机密。 退出此屏幕后,无法再次查看此机密。
步骤 3:向服务主体分配权限
你创建的服务主体充当通过应用程序提供仪表板访问权限的标识。 仅当 仪表板未 使用共享数据权限发布时,其权限才适用。 如果使用共享数据权限,发布者的凭据可以访问数据。 有关更多详细信息和建议,请参阅 嵌入身份验证方法。
单击工作区边栏中 的仪表板 以打开仪表板列表页。
单击要嵌入的仪表板的名称。 此时会打开已发布的仪表板。
单击“共享”。
使用 “共享 ”对话框中的文本输入字段查找服务主体,然后单击它。 将权限级别设置为 CAN RUN。 然后,单击“添加” 。
记录 仪表板 ID。 可以在仪表板的 URL(例如,
https://<your-workspace-url>/dashboards/<dashboard-id>)中找到仪表板 ID。 请参阅 Databricks 工作区详细信息。
注释
如果发布具有单个数据权限的仪表板,则必须向服务主体授予对仪表板中使用的数据的访问权限。 计算访问始终使用发布者的凭据,因此无需向服务主体授予计算权限。
若要读取和显示数据,服务主体必须至少 SELECT 对仪表板中引用的表和视图拥有特权。 请参阅谁可以管理特权?
步骤 4:使用示例应用进行身份验证和生成令牌
使用示例应用程序练习外部嵌入仪表板。 应用程序包括启动必要的令牌交换以生成作用域令牌的说明和代码。 以下代码块没有依赖项。 复制并保存以下应用程序之一。
Python
在名为 . example.py. 的文件中复制并保存此项。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
import sys
import json
import base64
import urllib.request
import urllib.parse
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Config
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
CONFIG = {
"instance_url": os.environ.get("INSTANCE_URL"),
"dashboard_id": os.environ.get("DASHBOARD_ID"),
"service_principal_id": os.environ.get("SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_ID"),
"service_principal_secret": os.environ.get("SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_SECRET"),
"external_viewer_id": os.environ.get("EXTERNAL_VIEWER_ID"),
"external_value": os.environ.get("EXTERNAL_VALUE"),
"workspace_id": os.environ.get("WORKSPACE_ID"),
"port": int(os.environ.get("PORT", 3000)),
}
basic_auth = base64.b64encode(
f"{CONFIG['service_principal_id']}:{CONFIG['service_principal_secret']}".encode()
).decode()
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# HTTP Request Helper
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
def http_request(url, method="GET", headers=None, body=None):
headers = headers or {}
if body is not None and not isinstance(body, (bytes, str)):
raise ValueError("Body must be bytes or str")
req = urllib.request.Request(url, method=method, headers=headers)
if body is not None:
if isinstance(body, str):
body = body.encode()
req.data = body
try:
with urllib.request.urlopen(req) as resp:
data = resp.read().decode()
try:
return {"data": json.loads(data)}
except json.JSONDecodeError:
return {"data": data}
except urllib.error.HTTPError as e:
raise RuntimeError(f"HTTP {e.code}: {e.read().decode()}") from None
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Token logic
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
def get_scoped_token():
# 1. Get all-api token
oidc_res = http_request(
f"{CONFIG['instance_url']}/oidc/v1/token",
method="POST",
headers={
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
"Authorization": f"Basic {basic_auth}",
},
body=urllib.parse.urlencode({
"grant_type": "client_credentials",
"scope": "all-apis"
})
)
oidc_token = oidc_res["data"]["access_token"]
# 2. Get token info
token_info_url = (
f"{CONFIG['instance_url']}/api/2.0/lakeview/dashboards/"
f"{CONFIG['dashboard_id']}/published/tokeninfo"
f"?external_viewer_id={urllib.parse.quote(CONFIG['external_viewer_id'])}"
f"&external_value={urllib.parse.quote(CONFIG['external_value'])}"
)
token_info = http_request(
token_info_url,
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {oidc_token}"}
)["data"]
# 3. Generate scoped token
params = token_info.copy()
authorization_details = params.pop("authorization_details", None)
params.update({
"grant_type": "client_credentials",
"authorization_details": json.dumps(authorization_details)
})
scoped_res = http_request(
f"{CONFIG['instance_url']}/oidc/v1/token",
method="POST",
headers={
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
"Authorization": f"Basic {basic_auth}",
},
body=urllib.parse.urlencode(params)
)
return scoped_res["data"]["access_token"]
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# HTML generator
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
def generate_html(token):
return f"""<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Dashboard Demo</title>
<style>
body {{ font-family: system-ui; margin: 0; padding: 20px; background: #f5f5f5; }}
.container {{ max-width: 1200px; margin: 0 auto; height:calc(100vh - 40px) }}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="dashboard-content" class="container"></div>
<script type="module">
import {{ DatabricksDashboard }} from "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@databricks/aibi-client@0.0.0-alpha.7/+esm";
const dashboard = new DatabricksDashboard({{
instanceUrl: "{CONFIG['instance_url']}",
workspaceId: "{CONFIG['workspace_id']}",
dashboardId: "{CONFIG['dashboard_id']}",
token: "{token}",
container: document.getElementById("dashboard-content")
}});
dashboard.initialize();
</script>
</body>
</html>"""
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# HTTP server
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
class RequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
if self.path != "/":
self.send_response(404)
self.send_header("Content-Type", "text/plain")
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(b"Not Found")
return
try:
token = get_scoped_token()
html = generate_html(token)
status = 200
except Exception as e:
html = f"<h1>Error</h1><p>{e}</p>"
status = 500
self.send_response(status)
self.send_header("Content-Type", "text/html")
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(html.encode())
def start_server():
missing = [k for k, v in CONFIG.items() if not v]
if missing:
print(f"Missing: {', '.join(missing)}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
server = HTTPServer(("localhost", CONFIG["port"]), RequestHandler)
print(f":rocket: Server running on http://localhost:{CONFIG['port']}")
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_server()
JavaScript
在名为 . example.js. 的文件中复制并保存此项。
#!/usr/bin/env node
const http = require('http');
const https = require('https');
const { URL, URLSearchParams } = require('url');
// This constant is just a mapping of environment variables to their respective
// values.
const CONFIG = {
instanceUrl: process.env.INSTANCE_URL,
dashboardId: process.env.DASHBOARD_ID,
servicePrincipalId: process.env.SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_ID,
servicePrincipalSecret: process.env.SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_SECRET,
externalViewerId: process.env.EXTERNAL_VIEWER_ID,
externalValue: process.env.EXTERNAL_VALUE,
workspaceId: process.env.WORKSPACE_ID,
port: process.env.PORT || 3000,
};
const basicAuth = Buffer.from(`${CONFIG.servicePrincipalId}:${CONFIG.servicePrincipalSecret}`).toString('base64');
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Main
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
function startServer() {
const missing = Object.keys(CONFIG).filter((key) => !CONFIG[key]);
if (missing.length > 0) throw new Error(`Missing: ${missing.join(', ')}`);
const server = http.createServer(async (req, res) => {
// This is a demo server, we only support GET requests to the root URL.
if (req.method !== 'GET' || req.url !== '/') {
res.writeHead(404, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Not Found');
return;
}
let html = '';
let status = 200;
try {
const token = await getScopedToken();
html = generateHTML(token);
} catch (error) {
html = `<h1>Error</h1><p>${error.message}</p>`;
status = 500;
} finally {
res.writeHead(status, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html' });
res.end(html);
}
});
server.listen(CONFIG.port, () => {
console.log(`🚀 Server running on http://localhost:${CONFIG.port}`);
});
process.on('SIGINT', () => process.exit(0));
process.on('SIGTERM', () => process.exit(0));
}
async function getScopedToken() {
// 1. Get all-api token. This will allow you to access the /tokeninfo
// endpoint, which contains the information required to generate a scoped token
const {
data: { access_token: oidcToken },
} = await httpRequest(`${CONFIG.instanceUrl}/oidc/v1/token`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
Authorization: `Basic ${basicAuth}`,
},
body: new URLSearchParams({
grant_type: 'client_credentials',
scope: 'all-apis',
}),
});
// 2. Get token info. This information is **required** for generating a token that is correctly downscoped.
// A correctly downscoped token will only have access to a handful of APIs, and within those APIs, only
// a the specific resources required to render the dashboard.
//
// This is essential to prevent leaking a privileged token.
//
// At the time of writing, OAuth tokens in Databricks are valid for 1 hour.
const tokenInfoUrl = new URL(
`${CONFIG.instanceUrl}/api/2.0/lakeview/dashboards/${CONFIG.dashboardId}/published/tokeninfo`,
);
tokenInfoUrl.searchParams.set('external_viewer_id', CONFIG.externalViewerId);
tokenInfoUrl.searchParams.set('external_value', CONFIG.externalValue);
const { data: tokenInfo } = await httpRequest(tokenInfoUrl.toString(), {
headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${oidcToken}` },
});
// 3. Generate scoped token. This call is very similar to what was issued before, but now we are providing the scoping to make the generated token
// safe to pass to a browser.
const { authorization_details, ...params } = tokenInfo;
const {
data: { access_token },
} = await httpRequest(`${CONFIG.instanceUrl}/oidc/v1/token`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
Authorization: `Basic ${basicAuth}`,
},
body: new URLSearchParams({
grant_type: 'client_credentials',
...params,
authorization_details: JSON.stringify(authorization_details),
}),
});
return access_token;
}
startServer();
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Helper functions
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Helper function to create HTTP requests.
* @param {string} url - The URL to make the request to.
* @param {Object} options - The options for the request.
* @param {string} options.method - The HTTP method to use.
* @param {Object} options.headers - The headers to include in the request.
* @param {Object} options.body - The body to include in the request.
* @returns {Promise<Object>} A promise that resolves to the response data.
*/
function httpRequest(url, { method = 'GET', headers = {}, body } = {}) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const isHttps = url.startsWith('https://');
const lib = isHttps ? https : http;
const options = new URL(url);
options.method = method;
options.headers = headers;
const req = lib.request(options, (res) => {
let data = '';
res.on('data', (chunk) => (data += chunk));
res.on('end', () => {
if (res.statusCode >= 200 && res.statusCode < 300) {
try {
resolve({ data: JSON.parse(data) });
} catch {
resolve({ data });
}
} else {
reject(new Error(`HTTP ${res.statusCode}: ${data}`));
}
});
});
req.on('error', reject);
if (body) {
if (typeof body === 'string' || Buffer.isBuffer(body)) {
req.write(body);
} else if (body instanceof URLSearchParams) {
req.write(body.toString());
} else {
req.write(JSON.stringify(body));
}
}
req.end();
});
}
function generateHTML(token) {
return `<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Dashboard Demo</title>
<style>
body { font-family: system-ui; margin: 0; padding: 20px; background: #f5f5f5; }
.container { max-width: 1200px; margin: 0 auto; height:calc(100vh - 40px) }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="dashboard-content" class="container"></div>
<script type="module">
/**
* We recommend bundling the dependency instead of using a CDN. However, for demonstration purposes,
* we are just using a CDN.
*
* We do not recommend one CDN over another and encourage decoupling the dependency from third-party code.
*/
import { DatabricksDashboard } from "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@databricks/aibi-client@0.0.0-alpha.7/+esm";
const dashboard = new DatabricksDashboard({
instanceUrl: "${CONFIG.instanceUrl}",
workspaceId: "${CONFIG.workspaceId}",
dashboardId: "${CONFIG.dashboardId}",
token: "${token}",
container: document.getElementById("dashboard-content")
});
dashboard.initialize();
</script>
</body>
</html>`;
}
步骤 5:运行示例应用程序
替换以下值,然后从终端运行代码块。 值 不应 用尖括号括起来(< >):
- 使用 工作区 URL 查找并替换以下值:
<your-instance><workspace_id><dashboard_id>
- 将以下值替换为创建服务主体时创建的值(步骤 2):
<service_principal_id>-
<service_principal_secret>(客户端密码)
- 将以下值替换为与外部应用程序用户关联的标识符:
<some-external-viewer><some-external-value>
- 替换为
</path/to/example>在上一步中创建的.py或.js文件的路径。 包括文件扩展名。
注释
不要在 EXTERNAL_VIEWER_ID 值中包含任何个人身份信息(PII)。
INSTANCE_URL='https://<your-instance>.databricks.com' \
WORKSPACE_ID='<workspace_id>' \
DASHBOARD_ID='<dashboard_id>' \
SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_ID='<service-principal-id>' \
SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_SECRET='<service-principal_secret>' \
EXTERNAL_VIEWER_ID='<some-external-viewer>' \
EXTERNAL_VALUE='<some-external-value>' \
~</path/to/example>
# Terminal will output: :rocket: Server running on http://localhost:3000