Nota:
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar iniciar sesión o cambiar directorios.
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar cambiar los directorios.
适用于 Python v1 的 Azure 机器学习 SDK 和机器学习 CLI 提供多种方法用于监视、组织和跟踪训练运行与试验运行。 ML 运行历史记录是可解释和可重复的 ML 开发过程的重要部分。
本文演示如何完成以下任务:
- 监视运行性能。
- 标记和查找运行。
- 对运行历史记录运行搜索。
- 取消运行或使其失败。
- 创建子运行。
- 通过电子邮件通知监视运行状态。
提示
如果要了解如何监视 Azure 机器学习服务及关联的 Azure 服务,请参阅如何监视 Azure 机器学习。 如果要了解如何监视部署为 Web 服务的模型,请参阅收集模型数据和使用 Application Insights 进行监视。
先决条件
需要准备好以下各项:
Azure 订阅。 如果没有 Azure 订阅,可在开始前创建一个试用帐户。 立即试用免费版或付费版 Azure 机器学习。
一个 Azure 机器学习工作区。
适用于 Python 的 Azure 机器学习 SDK(1.0.21 或更高版本)。 若要安装或更新到最新版本的 SDK,请参阅安装或更新 SDK。
若要检查 Azure 机器学习 SDK 的版本,请使用以下代码:
print(azureml.core.VERSION)Azure CLI 和 Azure 机器学习的 CLI 扩展。
重要
本文中的一些 Azure CLI 命令使用适用于 Azure 机器学习的
azure-cli-ml或 v1 扩展。 对 v1 扩展的支持将于 2025 年 9 月 30 日结束。 在该日期之前,你将能够安装和使用 v1 扩展。建议在 2025 年 9 月 30 日之前转换为
ml或 v2 扩展。 有关 v2 扩展的详细信息,请参阅 Azure ML CLI 扩展和 Python SDK v2。
监视运行性能
启动运行及其日志记录过程
通过从 azureml.core 包导入 Workspace、Experiment、Run 和 ScriptRunConfig 类来设置试验。
import azureml.core from azureml.core import Workspace, Experiment, Run from azureml.core import ScriptRunConfig ws = Workspace.from_config() exp = Experiment(workspace=ws, name="explore-runs")使用
start_logging()方法启动运行及其日志记录过程。notebook_run = exp.start_logging() notebook_run.log(name="message", value="Hello from run!")
监视运行的状态
使用
get_status()方法获取运行的状态。print(notebook_run.get_status())若要获取运行 ID、执行时间和有关运行的其他详细信息,请使用
get_details()方法。print(notebook_run.get_details())成功完成运行后,使用
complete()方法将其标记为已完成。notebook_run.complete() print(notebook_run.get_status())如果使用 Python 的
with...as设计模式,则当运行超出范围时,该运行会自动将自身标记为已完成。 无需手动将它标记为已完成。with exp.start_logging() as notebook_run: notebook_run.log(name="message", value="Hello from run!") print(notebook_run.get_status()) print(notebook_run.get_status())
标记和查找运行
在 Azure 机器学习中,可以使用属性与标记来帮助组织运行,以及查询运行以获取重要信息。
添加属性和标记
若要将可搜索的元数据添加到运行,请使用
add_properties()方法。 例如,以下代码将"author"属性添加到运行:local_run.add_properties({"author":"azureml-user"}) print(local_run.get_properties())属性是不可变的,因此它们将创建一条永久记录用于审核目的。 以下代码示例会导致出错,因为我们已在前面的代码中添加了
"azureml-user"作为"author"属性值:try: local_run.add_properties({"author":"different-user"}) except Exception as e: print(e)与属性不同,标记是可变的。 若要为试验的使用者添加可搜索且有意义的信息,请使用
tag()方法。local_run.tag("quality", "great run") print(local_run.get_tags()) local_run.tag("quality", "fantastic run") print(local_run.get_tags())还可以添加简单的字符串标记。 当这些标记作为键出现在标记字典中时,它们的值为
None。local_run.tag("worth another look") print(local_run.get_tags())查询属性和标记
可以查询试验中的运行,以返回与特定属性和标记匹配的运行列表。
list(exp.get_runs(properties={"author":"azureml-user"},tags={"quality":"fantastic run"})) list(exp.get_runs(properties={"author":"azureml-user"},tags="worth another look"))
取消运行或使其失败
如果发现错误,或者完成运行花费的时间太长,可以取消该运行。
若要使用 SDK 取消运行,请使用 cancel() 方法:
src = ScriptRunConfig(source_directory='.', script='hello_with_delay.py')
local_run = exp.submit(src)
print(local_run.get_status())
local_run.cancel()
print(local_run.get_status())
如果运行已完成但包含错误(例如,使用了错误的训练脚本),可以使用 fail() 方法将其标记为失败。
local_run = exp.submit(src)
local_run.fail()
print(local_run.get_status())
创建子运行
创建子运行可将相关的运行组合到一起,例如,以完成不同的超参数优化迭代。
注意
只能使用 SDK 创建子运行。
此代码示例使用 hello_with_children.py 脚本,通过 child_run() 方法从已提交的运行内部创建包含五个子运行的批:
!more hello_with_children.py
src = ScriptRunConfig(source_directory='.', script='hello_with_children.py')
local_run = exp.submit(src)
local_run.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)
print(local_run.get_status())
with exp.start_logging() as parent_run:
for c,count in enumerate(range(5)):
with parent_run.child_run() as child:
child.log(name="Hello from child run", value=c)
注意
当子运行超出范围时,会自动标记为已完成。
若要高效地创建许多子运行,请使用 create_children() 方法。 由于每次创建操作都会造成网络调用,因此,创建一批运行比逐个创建更为高效。
提交子运行
也可以从父运行提交子运行。 通过此操作可创建父运行和子运行的层次结构。 你无法创建没有父运行的子运行:即使父运行只启动子运行而不执行任何操作,仍需要创建层次结构。 所有运行的状态都是独立的:即使一个或多个子运行已取消或失败,父运行也可以处于 "Completed" 成功状态。
你可能会希望子运行使用与父运行不同的运行配置。 例如,对父运行使用常规的基于 CPU 的配置,而对子运行使用基于 GPU 的配置。 另一种常见的需求是向每个子运行传递不同的参数和数据。 若要自定义子运行,请为该子运行创建一个 ScriptRunConfig 对象。
重要
若要从远程计算上的父运行提交子运行,必须先登录到父运行代码中的工作区。 默认情况下,远程运行中的运行上下文对象没有用于提交子运行的凭据。 使用服务主体或托管标识凭据进行登录。 有关身份验证的详细信息,请参阅设置身份验证。
以下代码:
- 从工作区
ws中检索名为"gpu-cluster"的计算资源 - 循环访问要传递给子
ScriptRunConfig对象的不同参数值 - 使用自定义计算资源和参数创建并提交新的子运行
- 阻止至所有子运行完成为止
# parent.py
# This script controls the launching of child scripts
from azureml.core import Run, ScriptRunConfig
compute_target = ws.compute_targets["gpu-cluster"]
run = Run.get_context()
child_args = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange']
for arg in child_args:
run.log('Status', f'Launching {arg}')
child_config = ScriptRunConfig(source_directory=".", script='child.py', arguments=['--fruit', arg], compute_target=compute_target)
# Starts the run asynchronously
run.submit_child(child_config)
# Experiment will "complete" successfully at this point.
# Instead of returning immediately, block until child runs complete
for child in run.get_children():
child.wait_for_completion()
若要高效创建多个具有相同配置、参数和输入内容的子运行,可使用 create_children() 方法。 由于每次创建操作都会造成网络调用,因此,创建一批运行比逐个创建更为高效。
在子运行内部,可以查看父运行 ID:
## In child run script
child_run = Run.get_context()
child_run.parent.id
查询子运行
若要查询特定父级的子运行,请使用 get_children() 方法。
使用 recursive = True 参数可以查询子级和孙级的嵌套树。
print(parent_run.get_children())
记录到父运行或根运行
你可以使用 Run.parent 字段访问启动当前子运行的运行。 使用 Run.parent 的一个常见用例是将日志结果合并到一个位置。 子运行以异步方式执行,而且只能保证父运行等待其子运行完成,无法保证它们顺序一致且保持同步。
# in child (or even grandchild) run
def root_run(self : Run) -> Run :
if self.parent is None :
return self
return root_run(self.parent)
current_child_run = Run.get_context()
root_run(current_child_run).log("MyMetric", f"Data from child run {current_child_run.id}")
通过电子邮件通知监视运行状态
在 Azure 门户的左侧导航栏中,选择“监视”选项卡。
选择“诊断设置”,然后选择“+ 添加诊断设置。
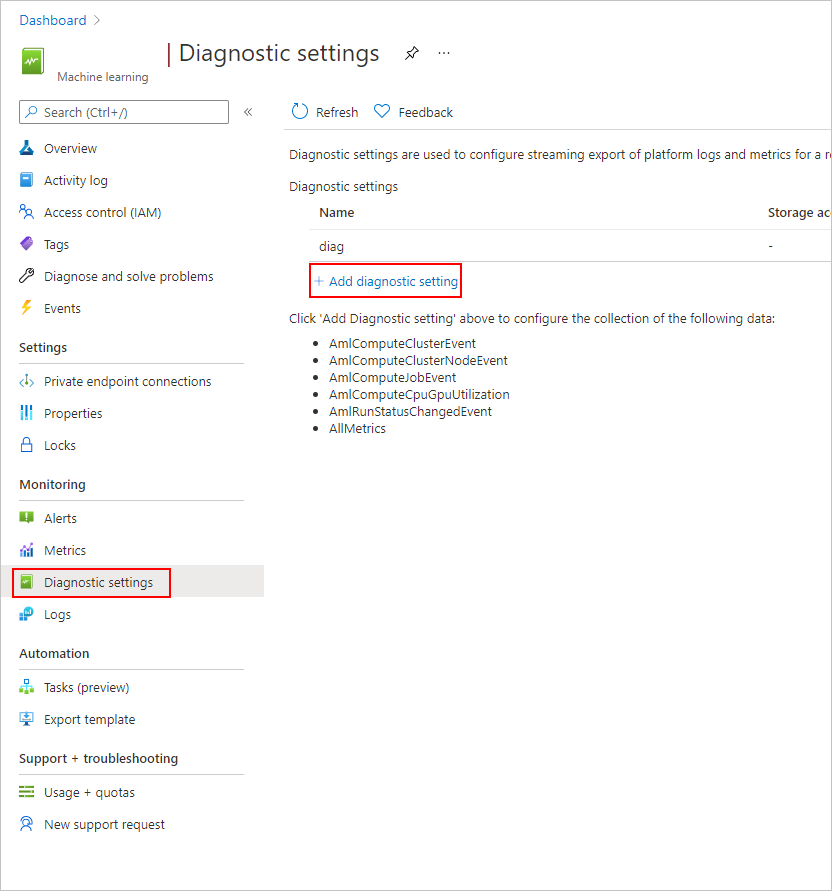
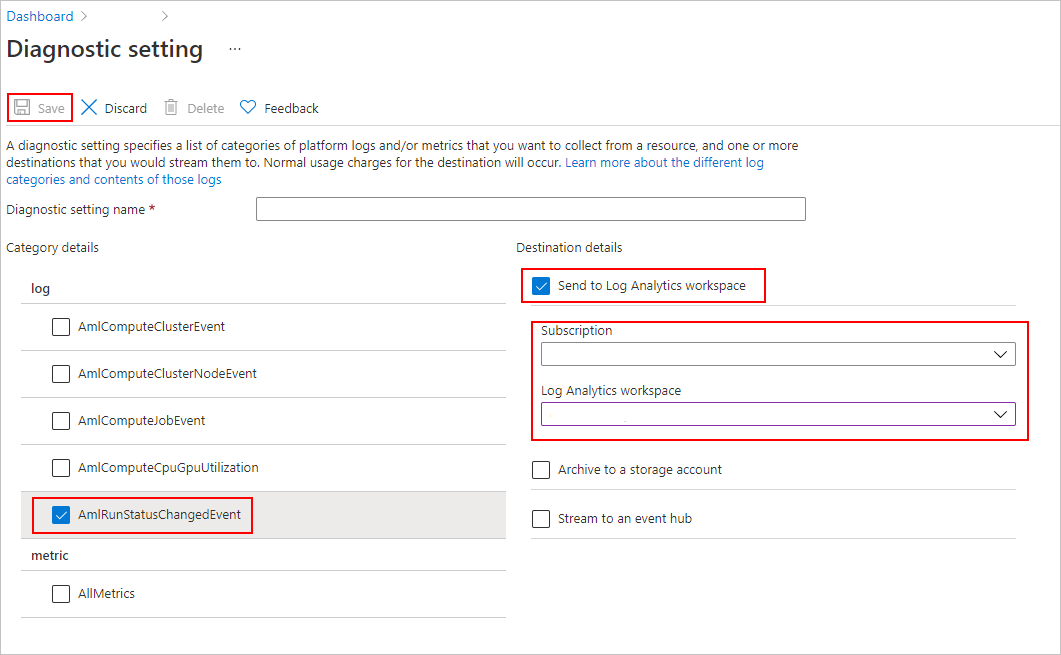
在“诊断设置”的
- “类别详细信息”下,选择“AmlRunStatusChangedEvent”。
- 在“目标详细信息”中,选择“发送到 Log Analytics 工作区”,并指定“订阅”和“Log Analytics 工作区”。
注意
Azure Log Analytics 工作区是一种不同于 Azure 机器学习服务工作区的 Azure 资源类型。 如果该列表中没有选项,则可以创建 Log Analytics 工作区。
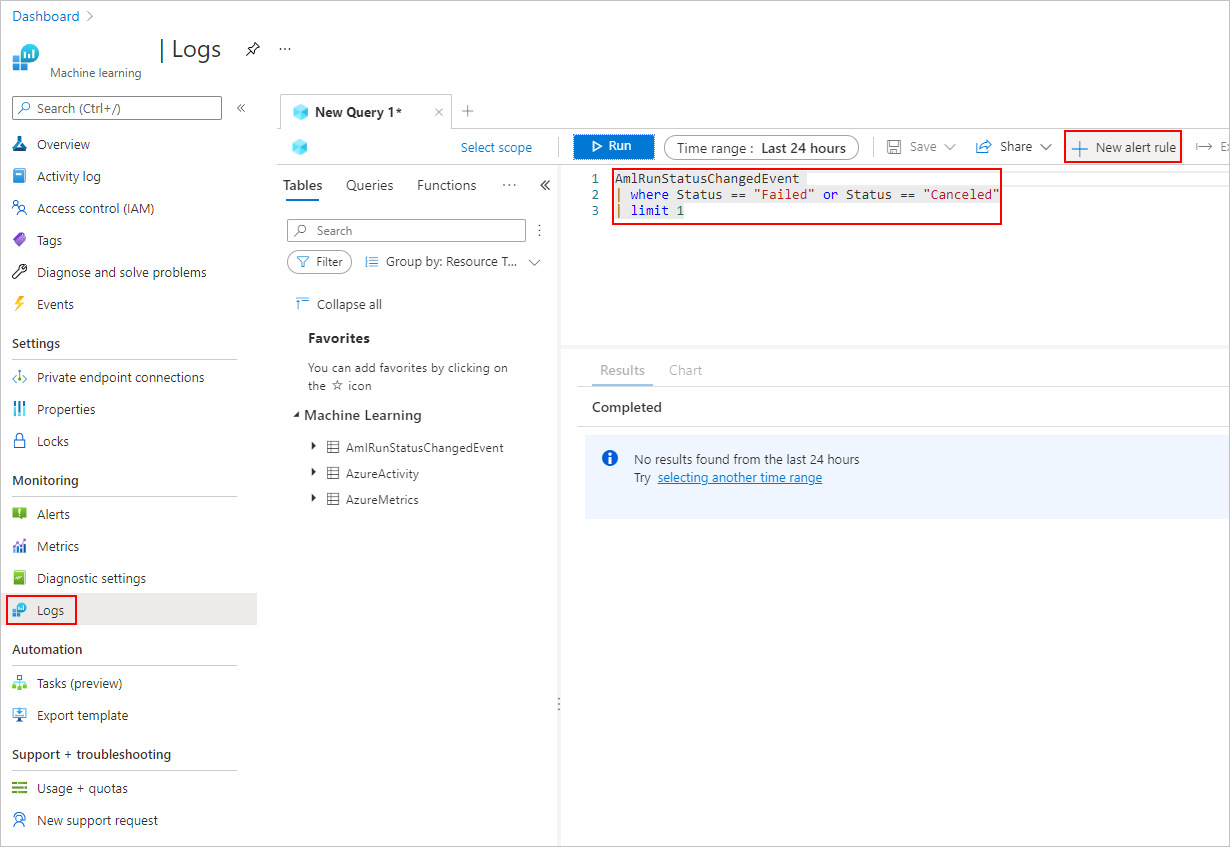
在“日志”选项卡中,添加“新的警报规则”。
示例笔记本
以下笔记本演示了本文中的概念:
若要详细了解日志记录 API,请参阅日志记录 API 笔记本。
有关使用 Azure 机器学习 SDK 管理运行的详细信息,请参阅管理运行笔记本。
后续步骤
- 若要了解如何记录试验的指标,请参阅在训练运行期间记录指标。
- 若要了解如何监视 Azure 机器学习中的资源和日志,请参阅监视 Azure 机器学习。
