Nota:
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar iniciar sesión o cambiar directorios.
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar cambiar los directorios.
Azure AI 搜索提供了几种减少矢量索引大小的方法。 这些方法的范围从矢量压缩到对搜索服务上存储的内容更具选择性的方法。
注释
现在建议对 RAG 工作流进行 代理检索 ,但经典 RAG 更简单。 如果它满足应用程序要求,它仍然是一个不错的选择。
在本教程中,你将修改现有的搜索索引,以便使用:
- 窄数据类型
- 标量量化
- 通过在搜索结果中选择退出矢量来减少存储
本教程重现索引管道创建的搜索索引。 所有这些更新都会影响现有内容,因此需要重新运行索引器。 但是,不要删除搜索索引,而是创建第二个索引索引,以便在添加新功能后比较矢量索引大小的减少。
本教程中介绍的技术总共可以减少约一半的矢量存储。
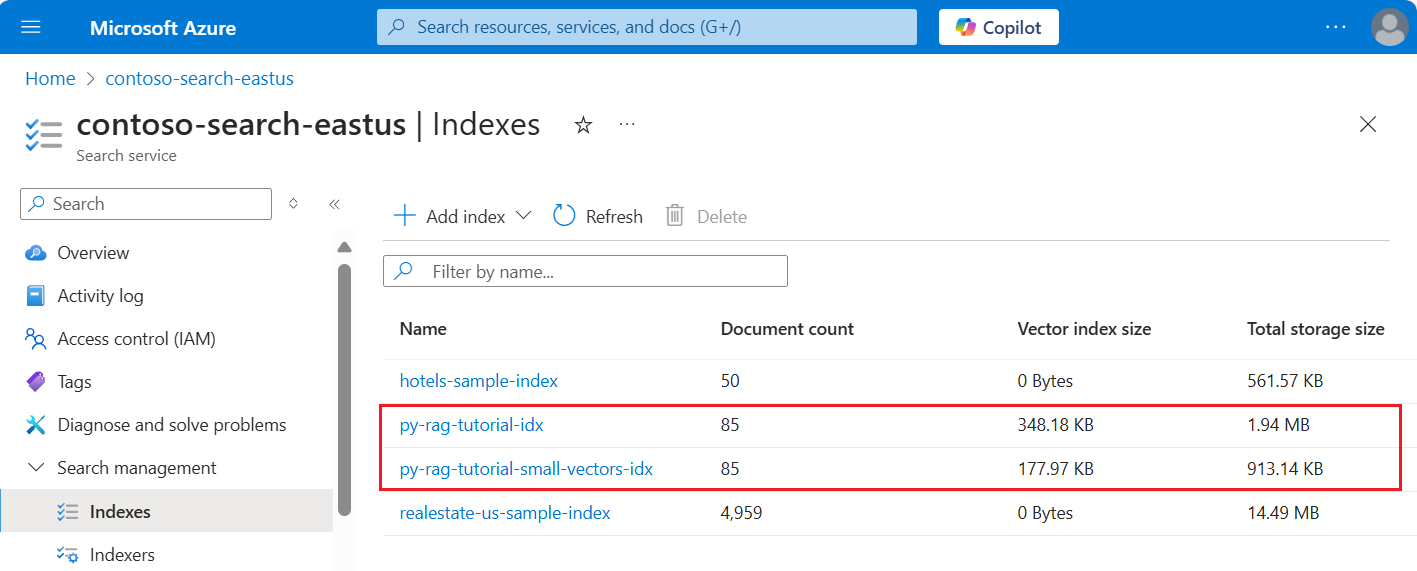
以下屏幕截图将上一教程中的第一个索引与在此教程中生成的索引进行比较。
先决条件
本教程实质上是重新运行索引管道。 你需要本教程中所述的所有 Azure 资源和权限。
为了进行比较,你应在 Azure AI 搜索服务上具有现有的 py-rag-tutorial-idx 索引。 它的大小应接近 2 MB,矢量索引部分应为 348 KB。
你还应具有以下对象:
py-rag-tutorial-ds(数据源)
py-rag-tutorial-ss(技能集)
下载示例
从 GitHub 下载 Jupyter 笔记本,以将请求发送到 Azure AI 搜索。 有关详细信息,请参阅从 GitHub 下载文件。
更新索引以减少存储
Azure AI 搜索具有多种减少矢量大小的方法,可降低矢量工作负载的成本。 在此步骤中,创建使用以下功能的新索引:
矢量压缩。 标量量化提供此功能。
消除可选存储。 如果您只需要用于查询请求的矢量,而不需要在响应结果的有效负载中使用,那么可以删除用于搜索结果的矢量副本。
有限数据类型。 可以在text_vector字段中指定
Collection(Edm.Half),以将传入的 float32 维度存储为 float16,这将占用索引中更少的空间。
所有这些功能都在搜索索引中指定。 加载索引后,比较原始索引与新索引之间的差异。
将新索引命名为
py-rag-tutorial-small-vectors-idx。对新索引使用以下定义。 此架构与最大化相关性中的上一个架构更新的区别在于标量量化的新类和新压缩部分、text_vector 字段的新数据类型 (
Collection(Edm.Half)) 和设置为 false 的新属性stored。from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential from azure.identity import get_bearer_token_provider from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexClient from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import ( SearchField, SearchFieldDataType, VectorSearch, HnswAlgorithmConfiguration, VectorSearchProfile, AzureOpenAIVectorizer, AzureOpenAIVectorizerParameters, ScalarQuantizationCompression, ScalarQuantizationParameters, SearchIndex, SemanticConfiguration, SemanticPrioritizedFields, SemanticField, SemanticSearch, ScoringProfile, TagScoringFunction, TagScoringParameters ) credential = DefaultAzureCredential() index_name = "py-rag-tutorial-small-vectors-idx" index_client = SearchIndexClient(endpoint=AZURE_SEARCH_SERVICE, credential=credential) fields = [ SearchField(name="parent_id", type=SearchFieldDataType.String), SearchField(name="title", type=SearchFieldDataType.String), SearchField(name="locations", type=SearchFieldDataType.Collection(SearchFieldDataType.String), filterable=True), SearchField(name="chunk_id", type=SearchFieldDataType.String, key=True, sortable=True, filterable=True, facetable=True, analyzer_name="keyword"), SearchField(name="chunk", type=SearchFieldDataType.String, sortable=False, filterable=False, facetable=False), SearchField(name="text_vector", type="Collection(Edm.Half)", vector_search_dimensions=1024, vector_search_profile_name="myHnswProfile", stored= False) ] # Configure the vector search configuration vector_search = VectorSearch( algorithms=[ HnswAlgorithmConfiguration(name="myHnsw"), ], profiles=[ VectorSearchProfile( name="myHnswProfile", algorithm_configuration_name="myHnsw", compression_name="myScalarQuantization", vectorizer_name="myOpenAI", ) ], vectorizers=[ AzureOpenAIVectorizer( vectorizer_name="myOpenAI", kind="azureOpenAI", parameters=AzureOpenAIVectorizerParameters( resource_url=AZURE_OPENAI_ACCOUNT, deployment_name="text-embedding-3-large", model_name="text-embedding-3-large" ), ), ], compressions=[ ScalarQuantizationCompression( compression_name="myScalarQuantization", rerank_with_original_vectors=True, default_oversampling=10, parameters=ScalarQuantizationParameters(quantized_data_type="int8"), ) ] ) semantic_config = SemanticConfiguration( name="my-semantic-config", prioritized_fields=SemanticPrioritizedFields( title_field=SemanticField(field_name="title"), keywords_fields=[SemanticField(field_name="locations")], content_fields=[SemanticField(field_name="chunk")] ) ) semantic_search = SemanticSearch(configurations=[semantic_config]) scoring_profiles = [ ScoringProfile( name="my-scoring-profile", functions=[ TagScoringFunction( field_name="locations", boost=5.0, parameters=TagScoringParameters( tags_parameter="tags", ), ) ] ) ] index = SearchIndex(name=index_name, fields=fields, vector_search=vector_search, semantic_search=semantic_search, scoring_profiles=scoring_profiles) result = index_client.create_or_update_index(index) print(f"{result.name} created")
创建或重复使用数据源
下面是上一教程中数据源的定义。 如果搜索服务中已有此数据源,则可以跳过新数据源的创建。
from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexerClient
from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import (
SearchIndexerDataContainer,
SearchIndexerDataSourceConnection
)
# Create a data source
indexer_client = SearchIndexerClient(endpoint=AZURE_SEARCH_SERVICE, credential=credential)
container = SearchIndexerDataContainer(name="nasa-ebooks-pdfs-all")
data_source_connection = SearchIndexerDataSourceConnection(
name="py-rag-tutorial-ds",
type="azureblob",
connection_string=AZURE_STORAGE_CONNECTION,
container=container
)
data_source = indexer_client.create_or_update_data_source_connection(data_source_connection)
print(f"Data source '{data_source.name}' created or updated")
创建或重复使用技能集
与上一教程相比,技能集也保持不变。 此处再次展示,以便你可以检查它。
from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import (
SplitSkill,
InputFieldMappingEntry,
OutputFieldMappingEntry,
AzureOpenAIEmbeddingSkill,
EntityRecognitionSkill,
SearchIndexerIndexProjection,
SearchIndexerIndexProjectionSelector,
SearchIndexerIndexProjectionsParameters,
IndexProjectionMode,
SearchIndexerSkillset,
CognitiveServicesAccountKey
)
# Create a skillset
skillset_name = "py-rag-tutorial-ss"
split_skill = SplitSkill(
description="Split skill to chunk documents",
text_split_mode="pages",
context="/document",
maximum_page_length=2000,
page_overlap_length=500,
inputs=[
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="text", source="/document/content"),
],
outputs=[
OutputFieldMappingEntry(name="textItems", target_name="pages")
],
)
embedding_skill = AzureOpenAIEmbeddingSkill(
description="Skill to generate embeddings via Azure OpenAI",
context="/document/pages/*",
resource_url=AZURE_OPENAI_ACCOUNT,
deployment_name="text-embedding-3-large",
model_name="text-embedding-3-large",
dimensions=1536,
inputs=[
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="text", source="/document/pages/*"),
],
outputs=[
OutputFieldMappingEntry(name="embedding", target_name="text_vector")
],
)
entity_skill = EntityRecognitionSkill(
description="Skill to recognize entities in text",
context="/document/pages/*",
categories=["Location"],
default_language_code="en",
inputs=[
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="text", source="/document/pages/*")
],
outputs=[
OutputFieldMappingEntry(name="locations", target_name="locations")
]
)
index_projections = SearchIndexerIndexProjection(
selectors=[
SearchIndexerIndexProjectionSelector(
target_index_name=index_name,
parent_key_field_name="parent_id",
source_context="/document/pages/*",
mappings=[
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="chunk", source="/document/pages/*"),
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="text_vector", source="/document/pages/*/text_vector"),
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="locations", source="/document/pages/*/locations"),
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="title", source="/document/metadata_storage_name"),
],
),
],
parameters=SearchIndexerIndexProjectionsParameters(
projection_mode=IndexProjectionMode.SKIP_INDEXING_PARENT_DOCUMENTS
),
)
cognitive_services_account = CognitiveServicesAccountKey(key=AZURE_AI_FOUNDRY_KEY)
skills = [split_skill, embedding_skill, entity_skill]
skillset = SearchIndexerSkillset(
name=skillset_name,
description="Skillset to chunk documents and generating embeddings",
skills=skills,
index_projection=index_projections,
cognitive_services_account=cognitive_services_account
)
client = SearchIndexerClient(endpoint=AZURE_SEARCH_SERVICE, credential=credential)
client.create_or_update_skillset(skillset)
print(f"{skillset.name} created")
创建新的索引器并加载索引
尽管可以使用新索引重置和重新运行现有索引器,但创建新索引器同样容易。 使用两个索引和索引器可以保留执行历史记录,并能够进行更深入的比较。
此索引器与以前的索引器相同,只不过它指定了本教程中的新索引。
from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import (
SearchIndexer
)
# Create an indexer
indexer_name = "py-rag-tutorial-small-vectors-idxr"
indexer_parameters = None
indexer = SearchIndexer(
name=indexer_name,
description="Indexer to index documents and generate embeddings",
target_index_name="py-rag-tutorial-small-vectors-idx",
skillset_name="py-rag-tutorial-ss",
data_source_name="py-rag-tutorial-ds",
parameters=indexer_parameters
)
# Create and run the indexer
indexer_client = SearchIndexerClient(endpoint=AZURE_SEARCH_SERVICE, credential=credential)
indexer_result = indexer_client.create_or_update_indexer(indexer)
print(f' {indexer_name} is created and running. Give the indexer a few minutes before running a query.')
最后一步,切换到 Azure 门户以比较两个索引的矢量存储要求。 你应该会看到类似于下面屏幕截图内容的结果。
本教程中创建的索引对文本矢量使用半精度浮点数 (float16)。 与使用单精度浮点数 (float32) 的前一个索引相比,这会将矢量存储要求减少一半。 标量压缩和一组矢量的省略贡献了剩余的存储节省。 有关减少矢量大小的详细信息,请参阅选择用于优化矢量存储和处理的方法。
请考虑重温上一教程中的查询,以便比较查询速度和实用性。 每当重复查询时,LLM 输出中应会出现一些变化,但通常实现的存储节省技术不应降低搜索结果的质量。
后续步骤
我们建议下一步使用此加速器: