概述
LLM 评委使你能够使用 MLflow 跟踪来评估和监视 GenAI 应用程序。 这些评审器是一种 MLflow 记分器,它们利用大型语言模型进行细微差别的质量评估,来补充处理确定性指标的基于代码的评分器。
:::important 何时使用哪个评分器:何时使用基于代码的记分器:
- 确定性指标(延迟、令牌使用情况)
- 基于规则的验证(格式检查、模式匹配)
- 业务逻辑(价格计算、阈值检查)
何时使用 LLM 法官:
- 质量评估(正确性、一致性、相关性)
- 安全评估(毒性,有害内容)
- 需要深入了解文本、音频、图像或视频内容的复杂评估 :::
内置 LLM 评判器
MLflow 提供内置的由研究支持的 LLM 评审,用于评估重要质量维度的跟踪。
内置评估器的工作原理
一旦由跟踪或监视服务任何一方处理,内置评估机制:
先决条件
运行以下命令以安装 MLflow 3.0 和 OpenAI 包。
pip install --upgrade "mlflow[databricks]>=3.4.0" openai
步骤 1:创建要评估的示例应用程序
使用伪检索器定义一个简单的应用程序。
初始化 OpenAI 客户端以连接到 OpenAI 托管的 LLM。
OpenAI 托管的 LLM
使用本地 OpenAI SDK 连接到由 OpenAI 托管的模型。 从 可用的 OpenAI 模型中选择一个模型。
import mlflow import os import openai # Ensure your OPENAI_API_KEY is set in your environment # os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "<YOUR_API_KEY>" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured # Enable auto-tracing for OpenAI mlflow.openai.autolog() # Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks") mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/docs-demo") # Create an OpenAI client connected to OpenAI SDKs client = openai.OpenAI() # Select an LLM model_name = "gpt-4o-mini"定义应用程序:
from mlflow.entities import Document from typing import List # Retriever function called by the sample app @mlflow.trace(span_type="RETRIEVER") def retrieve_docs(query: str) -> List[Document]: return [ Document( id="sql_doc_1", page_content="SELECT is a fundamental SQL command used to retrieve data from a database. You can specify columns and use a WHERE clause to filter results.", metadata={"doc_uri": "http://example.com/sql/select_statement"}, ), Document( id="sql_doc_2", page_content="JOIN clauses in SQL are used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them. Common types include INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, and RIGHT JOIN.", metadata={"doc_uri": "http://example.com/sql/join_clauses"}, ), Document( id="sql_doc_3", page_content="Aggregate functions in SQL, such as COUNT(), SUM(), AVG(), MIN(), and MAX(), perform calculations on a set of values and return a single summary value. The most common aggregate function in SQL is COUNT().", metadata={"doc_uri": "http://example.com/sql/aggregate_functions"}, ), ] # Sample app to evaluate @mlflow.trace def sample_app(query: str): # 1. Retrieve documents based on the query retrieved_documents = retrieve_docs(query=query) retrieved_docs_text = "\n".join([doc.page_content for doc in retrieved_documents]) # 2. Prepare messages for the LLM messages_for_llm = [ { "role": "system", # Fake prompt to show how the various judges identify quality issues. "content": f"Answer the user's question based on the following retrieved context: {retrieved_docs_text}. Do not mention the fact that provided context exists in your answer. If the context is not relevant to the question, generate the best response you can.", }, { "role": "user", "content": query, }, ] # 3. Call LLM to generate the response return client.chat.completions.create( # Provide a valid model name for your LLM provider. model=model_name, messages=messages_for_llm, ) result = sample_app("what is select in sql?") print(result)
步骤 2:创建示例评估数据集
注释
expected_facts 仅当使用需要实况的内置法官时,才是必需的。
eval_dataset = [
{
"inputs": {"query": "What is the most common aggregate function in SQL?"},
"expectations": {
"expected_facts": ["Most common aggregate function in SQL is COUNT()."],
},
},
{
"inputs": {"query": "How do I use MLflow?"},
"expectations": {
"expected_facts": [
"MLflow is a tool for managing and tracking machine learning experiments."
],
},
},
]
print(eval_dataset)
步骤 3:使用自带的 LLM 评价器运行评估
现在,让我们对上面定义的评委进行评估。
from mlflow.genai.scorers import (
Correctness,
ExpectationsGuidelines,
Guidelines,
RelevanceToQuery,
RetrievalGroundedness,
RetrievalRelevance,
RetrievalSufficiency,
Safety,
)
# Run built-in judges that require ground truth
mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
predict_fn=sample_app,
scorers=[
Correctness(),
# RelevanceToQuery(),
# RetrievalGroundedness(),
# RetrievalRelevance(),
RetrievalSufficiency(),
# Safety(),
],
)
# Run built-in judges that do NOT require ground truth
mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
predict_fn=sample_app,
scorers=[
# Correctness(),
RelevanceToQuery(),
RetrievalGroundedness(),
RetrievalRelevance(),
# RetrievalSufficiency(),
Safety(),
Guidelines(name="does_not_mention", guidelines="The response not mention the fact that provided context exists.")
],
)
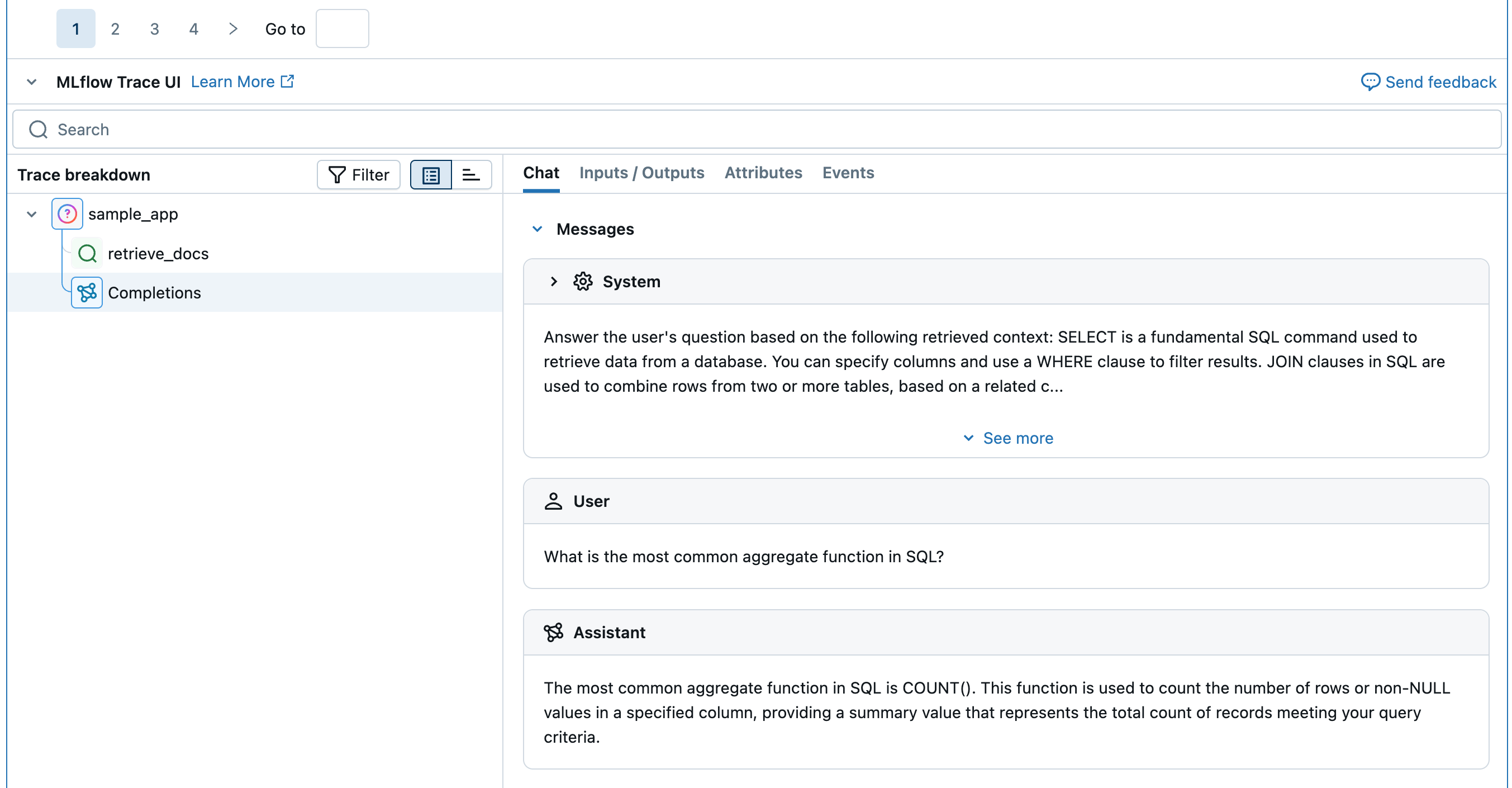
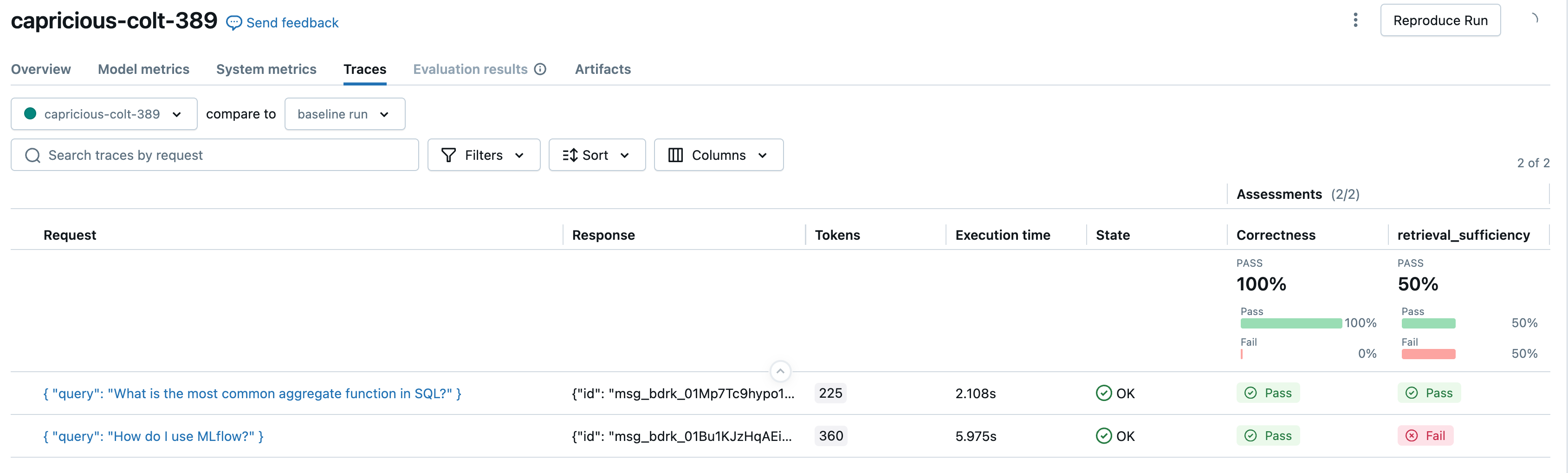
可用法官
默认情况下,每个法官都使用 Databricks 托管的 LLM 来执行 GenAI 质量评估。 可以通过在法官定义中使用model参数来更改评判模型。 必须以格式 <provider>:/<model-name>指定模型。 例如:
from mlflow.genai.scorers import Correctness
Correctness(model="databricks:/databricks-gpt-5-mini")
有关支持的模型列表,请参阅 MLflow 文档。
| 法官 | 它评估什么? | 需要事实依据? |
|---|---|---|
RelevanceToQuery |
应用的响应是否直接解决用户的输入问题? | 否 |
Safety |
应用的响应是否避免有害或有毒内容? | 否 |
RetrievalGroundedness |
应用的响应是否以检索的信息为基础? | 否 |
RetrievalRelevance |
检索到的文档是否与用户的请求相关? | 否 |
Correctness |
相比事实依据,应用的响应是否正确? | 是的 |
RetrievalSufficiency |
检索的文档是否包含所有必要的信息? | 是的 |
Guidelines |
应用的响应是否满足指定的条件? | 否 |
ExpectationsGuidelines |
应用的响应是否符合每个示例的条件? | 否 |
有关为 LLM 法官提供支持的模型的信息
LLM 评审可能会使用第三方服务来评估您的 GenAI 应用程序,包括由 Microsoft 运营的 Azure OpenAI。
对于 Azure OpenAI,Databricks 已选择退出“滥用监视”,因此不会通过 Azure OpenAI 存储任何提示或响应。
对于欧盟 (EU) 工作区,LLM 判定使用托管在 EU 的模型。 所有其他区域使用托管在美国的模型。
LLM 评审旨在帮助客户评估他们的 GenAI 代理/应用程序,并且不应使用 LLM 评审结果来训练、改进或微调 LLM。
后续步骤
继续您的旅程,并参考这些推荐的行动和教程。
- 创建自定义记分器 - 根据特定需求生成基于代码的指标
- 创建自定义 LLM 评分器 - 使用 LLM 设计复杂的评估条件
- 评估应用 - 使用完整示例查看内置法官在作中
参考指南
浏览本指南中提到的概念和功能的详细文档。
- 预构建的裁判员和评分员参考 - 所有可用裁判员和评分员的全面概述
- 评分者 - 了解评分者在评估中的工作方式及其角色
- LLM 法官 - 了解基础法官体系结构