适用于:✔️ Windows VM ✔️ 灵活规模集
Azure 磁盘加密使用 Azure 密钥保管库来控制和管理磁盘加密密钥和机密。 有关 Key Vault 的详细信息,请参阅 Azure Key Vault 入门和保护 Key Vault。
警告
- 如果之前是结合使用 Azure 磁盘加密和 Microsoft Entra ID 来加密 VM,必须继续使用这种方式来加密 VM。 有关详细信息,请参阅使用 Microsoft Entra ID 为 Azure 磁盘加密创建和配置密钥保管库(以前的版本)。
创建和配置用于 Azure 磁盘加密的 Key Vault 需要三个步骤:
注意
必须在 Azure Key Vault 访问策略设置中选择该选项,才能为卷加密启用对 Azure 磁盘加密的访问。 如果你已在密钥保管库上启用防火墙,则必须转到密钥保管库上的“网络”选项卡并启用对 Microsoft 受信任的服务的访问。
- 创建资源组(如果需要)。
- 创建密钥保管库。
- 设置密钥保管库高级访问策略。
以下快速入门说明了这些步骤:
还可以根据需要生成或导入密钥加密密钥 (KEK)。
注意
本文中的步骤在 Azure 磁盘加密先决条件 CLI 脚本和 Azure 磁盘加密先决条件 PowerShell 脚本中自动执行。
先决条件
安装工具并连接到 Azure
可以使用 Azure CLI、Azure PowerShell Az 模块或 Azure 门户来完成本文中的步骤。
虽然可以通过浏览器访问门户,但 Azure CLI 和 Azure PowerShell 需要本地安装;有关详细信息,请参阅适用于 Windows 的 Azure 磁盘加密:安装工具。
连接到 Azure 帐户
使用 Azure CLI 或 Azure PowerShell 之前,必须先连接到 Azure 订阅。 为此,可以使用 Azure CLI 登录、使用 Azure PowerShell 登录或在出现提示时向 Azure 门户提供凭据。
az cloud set -n AzureChinaCloud
az login
Connect-AzAccount -Environment AzureChinaCloud
Create a resource group
If you already have a resource group, you can skip to Create a key vault.
A resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed.
Create a resource group using the az group create Azure CLI command, the New-AzResourceGroup Azure PowerShell command, or from the Azure portal.
Azure CLI
az group create --name "myResourceGroup" --location chinaeast
Azure PowerShell
New-AzResourceGroup -Name "myResourceGroup" -Location "ChinaEast"
Create a key vault
If you already have a key vault, you can skip to Set key vault advanced access policies.
Create a key vault using the az keyvault create Azure CLI command, the New-AzKeyvault Azure PowerShell command, the Azure portal, or a Resource Manager template.
Warning
To ensure that encryption secrets don't cross regional boundaries, you must create and use a key vault that's in the same region and tenant as the VMs to be encrypted.
Each Key Vault must have a unique name. Replace <your-unique-keyvault-name> with the name of your key vault in the following examples.
Azure CLI
When creating a key vault by using the Azure CLI, add the "--enabled-for-disk-encryption" flag.
az keyvault create --name "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" --resource-group "myResourceGroup" --location "chinaeast" --enabled-for-disk-encryption
Azure PowerShell
When creating a key vault using Azure PowerShell, add the "-EnabledForDiskEncryption" flag.
New-AzKeyvault -name "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" -ResourceGroupName "myResourceGroup" -Location "chinaeast" -EnabledForDiskEncryption
Resource Manager template
You can also create a key vault by using the Resource Manager template.
Click Deploy to Azure.
Select the subscription, resource group, resource group location, Key Vault name, Object ID, legal terms, and agreement, and then click Review + create.
Set key vault advanced access policies
Important
Newly-created key vaults have soft-delete on by default. If you are using a pre-existing key vault, you must enable soft-delete. See Azure Key Vault soft-delete overview.
The Azure platform needs access to the encryption keys or secrets in your key vault to make them available to the VM for booting and decrypting the volumes.
If you didn't enable your key vault for disk encryption, deployment, or template deployment at the time of creation (as demonstrated in the previous step), you must update its advanced access policies.
Azure CLI
Use az keyvault update to enable disk encryption for the key vault.
Enable Key Vault for disk encryption: Enabled-for-disk-encryption is required.
az keyvault update --name "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" --resource-group "MyResourceGroup" --enabled-for-disk-encryption "true"Enable Key Vault for deployment, if needed: Enables the Microsoft.Compute resource provider to retrieve secrets from this key vault when this key vault is referenced in resource creation, for example when creating a virtual machine.
az keyvault update --name "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" --resource-group "MyResourceGroup" --enabled-for-deployment "true"Enable Key Vault for template deployment, if needed: Allow Resource Manager to retrieve secrets from the vault.
az keyvault update --name "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" --resource-group "MyResourceGroup" --enabled-for-template-deployment "true"
Azure PowerShell
Use the key vault PowerShell cmdlet Set-AzKeyVaultAccessPolicy to enable disk encryption for the key vault.
Enable Key Vault for disk encryption: EnabledForDiskEncryption is required for Azure Disk encryption.
Set-AzKeyVaultAccessPolicy -VaultName "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup" -EnabledForDiskEncryptionEnable Key Vault for deployment, if needed: Enables the Microsoft.Compute resource provider to retrieve secrets from this key vault when this key vault is referenced in resource creation, for example when creating a virtual machine.
Set-AzKeyVaultAccessPolicy -VaultName "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup" -EnabledForDeploymentEnable Key Vault for template deployment, if needed: Enables Azure Resource Manager to get secrets from this key vault when this key vault is referenced in a template deployment.
Set-AzKeyVaultAccessPolicy -VaultName "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup" -EnabledForTemplateDeployment
Azure portal
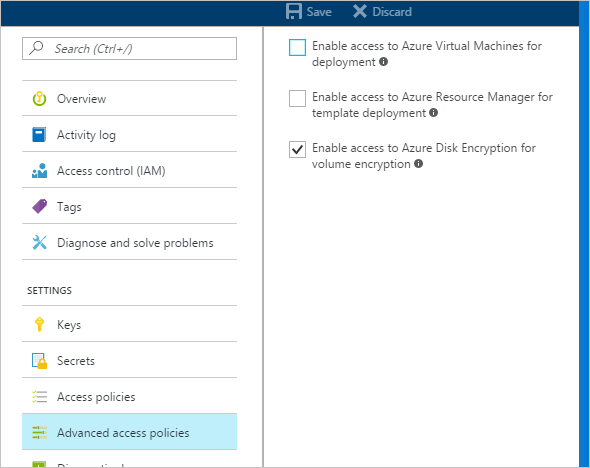
Select your key vault and go to Access Policies.
Under "Enable Access to", select the box labeled Azure Disk Encryption for volume encryption.
Select Azure Virtual Machines for deployment and/or Azure Resource Manager for template deployment, if needed.
Click Save.
Azure Disk Encryption and auto-rotation
Although Azure Key Vault now has key auto-rotation, it isn't currently compatible with Azure Disk Encryption. Specifically, Azure Disk Encryption will continue to use the original encryption key, even after it has been auto-rotated.
Rotating an encryption key won't break Azure Disk Encryption, but disabling the "old" encryption key (in other words, the key Azure Disk Encryption is still using) will.
Set up a key encryption key (KEK)
Important
The account running to enable disk encryption over the key vault must have "reader" permissions.
If you want to use a key encryption key (KEK) for an additional layer of security for encryption keys, add a KEK to your key vault. When a key encryption key is specified, Azure Disk Encryption uses that key to wrap the encryption secrets before writing to Key Vault.
You can generate a new KEK by using the Azure CLI az keyvault key create command, the Azure PowerShell Add-AzKeyVaultKey cmdlet, or the Azure portal. You must generate an RSA key type; Azure Disk Encryption doesn't currently support using Elliptic Curve keys.
Your key vault KEK URLs must be versioned. Azure enforces this restriction of versioning. For valid secret and KEK URLs, see the following examples:
- Example of a valid secret URL:
https://contosovault.vault.azure.cn/secrets/EncryptionSecretWithKek/xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx - Example of a valid KEK URL:
https://contosovault.vault.azure.cn/keys/diskencryptionkek/xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Azure CLI
Use the Azure CLI az keyvault key create command to generate a new KEK and store it in your key vault.
az keyvault key create --name "myKEK" --vault-name "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" --kty RSA --size 4096
You may instead import a private key by using the Azure CLI az keyvault key import command:
In either case, you supply the name of your KEK to the Azure CLI az vm encryption enable --key-encryption-key parameter.
az vm encryption enable -g "MyResourceGroup" --name "myVM" --disk-encryption-keyvault "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" --key-encryption-key "myKEK"
Azure PowerShell
Use the Azure PowerShell Add-AzKeyVaultKey cmdlet to generate a new KEK and store it in your key vault.
Add-AzKeyVaultKey -Name "myKEK" -VaultName "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" -Destination "Software" -Size 4096
You may instead import a private key using the Azure PowerShell az keyvault key import command.
In either case, you will supply the ID of your KEK key Vault and the URL of your KEK to the Azure PowerShell Set-AzVMDiskEncryptionExtension -KeyEncryptionKeyVaultId and -KeyEncryptionKeyUrl parameters. This example assumes that you are using the same key vault for both the disk encryption key and the KEK.
$KeyVault = Get-AzKeyVault -VaultName "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" -ResourceGroupName "myResourceGroup"
$KEK = Get-AzKeyVaultKey -VaultName "<your-unique-keyvault-name>" -Name "myKEK"
Set-AzVMDiskEncryptionExtension -ResourceGroupName MyResourceGroup -VMName "MyVM" -DiskEncryptionKeyVaultUrl $KeyVault.VaultUri -DiskEncryptionKeyVaultId $KeyVault.ResourceId -KeyEncryptionKeyVaultId $KeyVault.ResourceId -KeyEncryptionKeyUrl $KEK.Id -SkipVmBackup -VolumeType All
