本教程介绍如何使用 Azure 中继功能构建 WCF 中继客户端应用程序和服务。 正如原始的 WCF,服务是公开一个或多个终结点的构造。 每个终结点公开一个或多个服务操作。 服务的终结点用于指定可在其中找到服务的地址、包含客户端必须与服务进行通信的信息的绑定,以及定义服务向其客户端提供的功能的协定。 WCF 和 WCF 中继之间的主要区别在于:终结点在云中公开,而不是在本地计算机中公开。
按顺序完成本教程的每个部分后,你将获得一个正常运行的服务。 此外,你还会获得一个可以调用服务操作的客户端。
在本教程中,你将执行以下任务:
- 安装本教程的必备组件。
- 创建中继命名空间。
- 创建 WCF 服务协定。
- 实现 WCF 协定。
- 托管并运行 WCF 服务以向中继服务注册。
- 创建服务协定的 WCF 客户端。
- 配置 WCF 客户端。
- 实现 WCF 客户端。
- 运行应用程序。
先决条件
若要完成本教程,需要具备以下先决条件:
- Azure 订阅。 如果没有 Azure 订阅,请在开始之前创建一个试用版订阅。
- Visual Studio 2015 或更高版本。 本教程中的示例使用 Visual Studio 2019。
- 用于 .NET 的 Azure SDK。 从 SDK 下载页安装它。
创建中继命名空间
第一步是创建命名空间并获取共享访问签名 (SAS) 密钥。 命名空间为每个通过中继服务公开的应用程序提供应用程序边界。 创建服务命名空间时,系统会自动生成 SAS 密钥。 服务命名空间与 SAS 密钥的组合为 Azure 提供了用于验证应用程序访问权限的凭据。
登录 Azure 门户。
在左侧菜单中,选择“所有服务” 。 选择“集成”,搜索“中继”,将鼠标移到“中继”上方,然后选择“创建”。
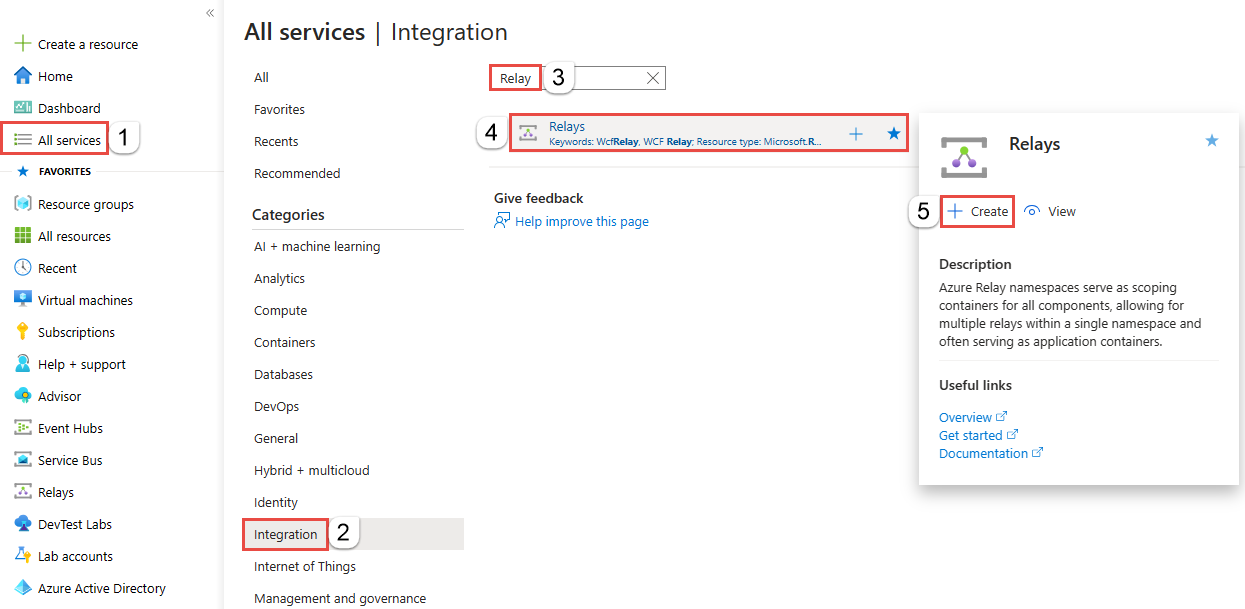
在“创建命名空间”页上,执行以下步骤:
选择要在其中创建命名空间的 Azure 订阅。
对于资源组,选择一个要在其中放置命名空间的现有资源组,或创建一个新资源组。
输入中继命名空间的名称。
选择应托管该命名空间的区域。
在页面底部选择查看 + 创建。
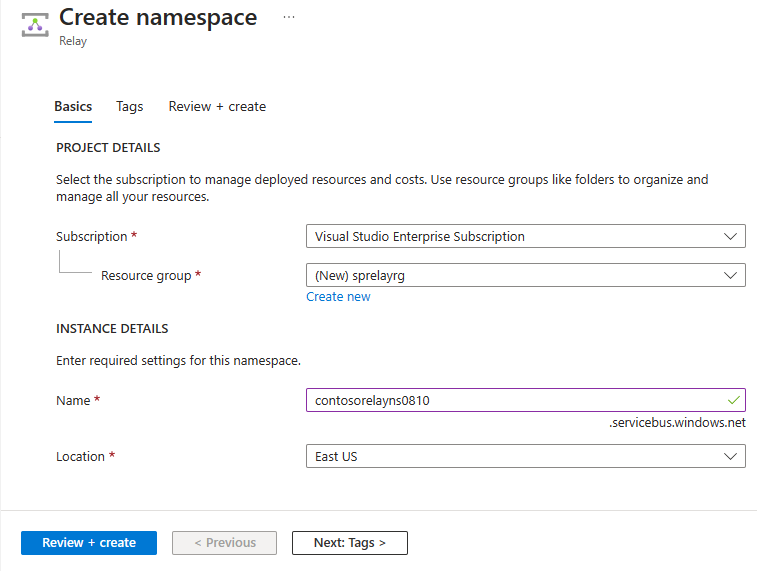
在“查看 + 创建”页面上,选择“创建”。
几分钟后,将看到该命名空间的“中继”页面。
获取管理凭据
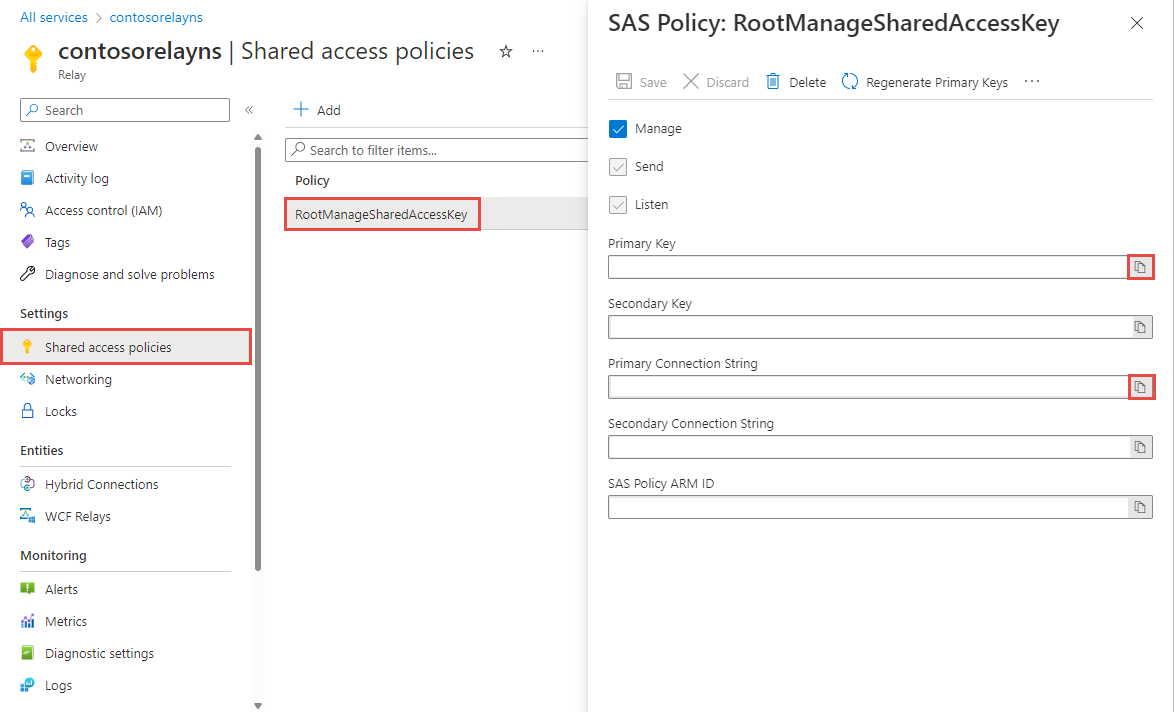
在“中继”页上,选择左侧菜单的“共享访问策略”。
在“共享访问策略”页,选择“RootManageSharedAccessKey” 。
在“SAS 策略:RootManageSharedAccessKey”下,选择“主连接字符串”旁边的“复制”按钮。 此操作会将连接字符串复制到剪贴板,供以后使用。 将此值粘贴到记事本或其他某个临时位置。
重复上述步骤,将主密钥的值复制和粘贴到临时位置,供以后使用。
定义 WCF 服务协定
服务协定指定服务支持的操作。 操作是 Web 服务方法或函数。 约定通过定义 C++、C# 或 Visual Basic 接口来创建。 接口中的每个方法都对应一个特定的服务操作。 必须将 ServiceContractAttribute 属性应用于每个接口,并且必须将 OperationContractAttribute 属性应用于每个操作。 如果具有 ServiceContractAttribute 属性的接口中的方法没有 OperationContractAttribute 属性,则该方法是不公开的。 该过程后面的示例中提供了这些任务的代码。 有关协定和服务的更多讨论,请参阅设计和实现服务。
使用接口创建中继协定
以管理员身份启动 Microsoft Visual Studio。 为此,请右键单击 Visual Studio 程序图标,并选择“以管理员身份运行”。
在 Visual Studio 中选择“创建新项目”。
在“创建新项目”中,选择适用于 C# 的“控制台应用(.NET Framework)”,然后选择“下一步”。
将项目命名为 EchoService 并选择“创建”。
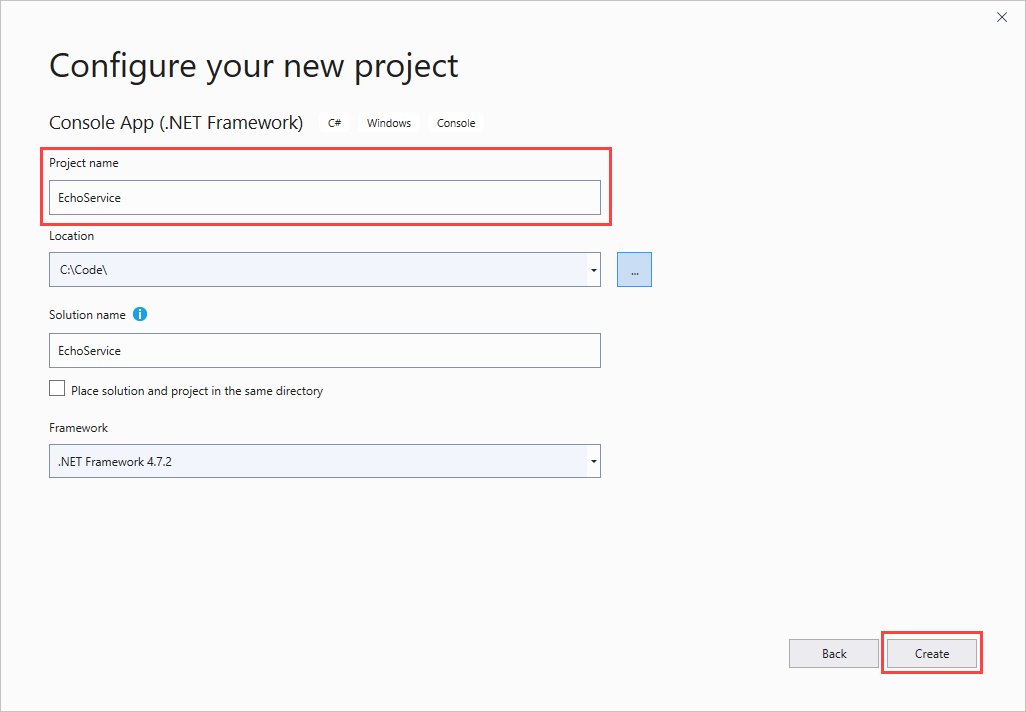
在“解决方案资源管理器”中,右键单击项目,并选择“管理 NuGet 包”。 在“NuGet 包管理器”中选择“浏览”,然后搜索并选择“WindowsAzure.ServiceBus”。 选择“安装”并接受使用条款。
该包自动添加对服务总线库和 WCF
System.ServiceModel的引用。 System.ServiceModel 是用于以编程方式访问 WCF 基本功能的命名空间。 服务总线使用 WCF 的许多对象和属性来定义服务约定。在 Program.cs 顶部添加以下
using语句:using System.ServiceModel; using Microsoft.ServiceBus;将命名空间名称从其默认名称
EchoService更改为Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples。重要
本教程使用 C# 命名空间
Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples,它是基于协定的管理类型的命名空间,此类型用于配置 WCF 客户端部分中的配置文件。 在生成此示例时,可以指定所需的任何命名空间。 但是,只有在应用程序配置文件中相应地修改协定和服务的命名空间之后,本教程才会生效。 在 App.config 文件中指定的命名空间必须与在 C# 文件中指定的命名空间相同。直接在
Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples命名空间声明后面(但在命名空间内)定义一个名为IEchoContract的新接口,然后将ServiceContractAttribute属性应用于该接口,命名空间值为https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/。 在命名空间声明的后面粘贴以下代码:[ServiceContract(Name = "IEchoContract", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")] public interface IEchoContract { }该命名空间值不同于在整个代码范围内使用的命名空间。 相反,该命名空间值用作此协定的唯一标识符。 显式指定命名空间可防止将默认的命名空间值添加到约定名称中。
注意
通常情况下,服务协定命名空间包含一个包括版本信息的命名方案。 服务协定命名空间中包括的版本信息可以使服务通过将新服务协定定义为新命名空间并将其公开到新的终结点上,来隔离重大更改。 以这种方式,客户端可以继续使用旧的服务协定,而无需进行更新。 版本信息可能包含日期或内部版本号。 有关详细信息,请参阅 服务版本控制。 对于本教程,服务协定命名空间的命名方案不包含版本信息。
在
IEchoContract接口中,为IEchoContract协定在接口中公开的单个操作声明一个方法,然后将OperationContractAttribute属性应用到你希望将其作为公共 WCF 中继协定的一部分进行公开的方法中,如下所示:[OperationContract] string Echo(string text);直接在
IEchoContract接口定义之后声明从IEchoContract中继承并同样继承到IClientChannel接口的通道,如下所示:public interface IEchoChannel : IEchoContract, IClientChannel { }通道是主机和客户端用来互相传递信息的 WCF 对象。 随后,将针对通道编写代码,以在两个应用程序之间回显信息。
选择“生成”>“生成解决方案”,或按 Ctrl+Shift+B 以确认到目前为止操作的准确性 。
WCF 协定的示例
以下代码显示了定义 WCF 中继协定的基本接口。
using System;
using System.ServiceModel;
namespace Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples
{
[ServiceContract(Name = "IEchoContract", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")]
public interface IEchoContract
{
[OperationContract]
String Echo(string text);
}
public interface IEchoChannel : IEchoContract, IClientChannel { }
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
}
既然已创建接口,可以实现该接口。
实现 WCF 协定
创建 Azure 中继首先需要使用接口创建协定。 有关创建接口的详细信息,请参阅上一部分。 下一个过程实现接口。 此任务包括创建名为 EchoService 的类,用于实现用户定义的 IEchoContract 接口。 实现接口后,即可使用 App.config 配置文件配置接口。 配置文件包含应用程序所需的信息。 此信息包括服务的名称、协定的名称,以及用来与中继服务通信的协议类型。 该过程后面的示例中提供了这些任务所用的代码。 有关如何实现服务协定的更多常规讨论,请参阅实现服务协定。
在
IEchoContract接口定义的正下方创建名为EchoService的新类。EchoService类实现IEchoContract接口。class EchoService : IEchoContract { }与其他接口实现类似,可以在另一个文件中实现定义。 但是,在本教程中,实现所在的文件与接口定义和
Main()方法所在的文件相同。将 ServiceBehaviorAttribute 属性应用于
IEchoContract接口。 该属性指定服务名称和命名空间。 完成后,EchoService类将如下所示:[ServiceBehavior(Name = "EchoService", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")] class EchoService : IEchoContract { }在
EchoService类中,实现IEchoContract接口中定义的Echo方法。public string Echo(string text) { Console.WriteLine("Echoing: {0}", text); return text; }选择“生成”>“生成解决方案”,或按 Ctrl+Shift+B 。
定义服务主机的配置
该配置文件类似于 WCF 配置文件。 其中包括服务名称、终结点和绑定。 终结点是 Azure 中继公开的、让客户端和主机相互通信的位置。 绑定是用于通信的协议类型。 此处的主要差别在于,配置的服务终结点是指 NetTcpRelayBinding 绑定,它不是 .NET Framework 的一部分。 NetTcpRelayBinding 是由服务定义的绑定之一。
在“解决方案资源管理器”中,双击“App.config”在 Visual Studio 编辑器中将其打开。
在
<appSettings>元素中,将占位符替换为你的 Azure 中继命名空间的名称以及在先前步骤中复制的 SAS 密钥。在
<system.serviceModel>标记中,添加<services>元素。 可以在单个配置文件中定义多个中继应用程序。 但是,本教程只定义一个。<?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <system.serviceModel> <services> </services> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>在
<services>元素中,添加<service>元素来定义服务名称。<service name="Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples.EchoService"> </service>在
<service>元素中,定义终结点协定的位置,以及终结点绑定的类型。<endpoint contract="Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples.IEchoContract" binding="netTcpRelayBinding"/>终结点用于定义客户端会在何处查找主机应用程序。 接下来,本教程使用此步骤创建一个通过 Azure 中继完全公开主机的 URI。 绑定声明我们将 TCP 用作协议,以与中继服务进行通信。
选择“生成”>“生成解决方案”,或按 Ctrl+Shift+B 以确认到目前为止操作的准确性 。
服务协定的实现示例
下面的代码显示服务协定的实现。
[ServiceBehavior(Name = "EchoService", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")]
class EchoService : IEchoContract
{
public string Echo(string text)
{
Console.WriteLine("Echoing: {0}", text);
return text;
}
}
以下代码显示了与该服务主机关联的 App.config 文件的基本格式。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service name="Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples.EchoService">
<endpoint contract="Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples.IEchoContract" binding="netTcpRelayBinding" />
</service>
</services>
<extensions>
<bindingExtensions>
<add name="netTcpRelayBinding"
type="Microsoft.ServiceBus.Configuration.NetTcpRelayBindingCollectionElement, Microsoft.ServiceBus, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35"/>
</bindingExtensions>
</extensions>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
托管并运行 WCF 服务以向中继服务注册
此步骤介绍如何运行 Azure 中继服务。
创建中继凭据
在
Main()中,创建两个变量,将命名空间和从控制台窗口中读取的 SAS 密钥存储在其中。Console.Write("Your Service Namespace: "); string serviceNamespace = Console.ReadLine(); Console.Write("Your SAS key: "); string sasKey = Console.ReadLine();随后将使用 SAS 密钥来访问你的项目。 命名空间作为参数传递给
CreateServiceUri以创建服务 URI。使用 TransportClientEndpointBehavior 对象声明使用 SAS 密钥作为凭据类型。 在最后一步中添加的代码后直接添加以下代码。
TransportClientEndpointBehavior sasCredential = new TransportClientEndpointBehavior(); sasCredential.TokenProvider = TokenProvider.CreateSharedAccessSignatureTokenProvider("RootManageSharedAccessKey", sasKey);
为服务创建基本地址
在上一部分添加的代码后面,为服务的基址创建 Uri 实例。 此 URI 指定服务总线方案、命名空间,以及服务接口的路径。
Uri address = ServiceBusEnvironment.CreateServiceUri("sb", serviceNamespace, "EchoService");
值“sb”是服务总线方案的缩写。 它指示我们正在使用 TCP 作为协议。 先前当 NetTcpRelayBinding 被指定为绑定时,在配置文件中也指示了此方案。
对于本教程中,URI 是 sb://putServiceNamespaceHere.chinacloudapi.cn/EchoService。
创建并配置服务主机
仍在
Main()中,将连接模式设置为AutoDetect。ServiceBusEnvironment.SystemConnectivity.Mode = ConnectivityMode.AutoDetect;连接模式描述服务用于与中继服务进行通信的协议;连接模式为 HTTP 或 TCP。 使用默认设置
AutoDetect,服务尝试通过 TCP(如果可用)或 HTTP(如果 TCP 不可用)连接到 Azure 中继。 结果与服务为客户端通信指定的协议不同。 为客户端通信指定的协议由所使用的绑定所决定。 例如,服务可以使用 BasicHttpRelayBinding 绑定,该绑定指定其终结点通过 HTTP 与客户端通信。 同一个服务可以指定ConnectivityMode.AutoDetect,以便服务通过 TCP 与 Azure 中继通信。使用之前在本部分中创建的 URI 创建服务主机。
ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(EchoService), address);该服务主机是可实例化服务的 WCF 对象。 在这里传递想要创建的服务类型(
EchoService类型),以及想要公开服务的地址。在 Program.cs 文件的顶部,添加对 System.ServiceModel.Description 和 Microsoft.ServiceBus.Description 的引用。
using System.ServiceModel.Description; using Microsoft.ServiceBus.Description;返回到
Main(),配置终结点以启用公开访问。IEndpointBehavior serviceRegistrySettings = new ServiceRegistrySettings(DiscoveryType.Public);此步骤告知中继服务可以通过检查项目的 Atom 馈送公开找到应用程序。 如果将
DiscoveryType设置为private,客户端仍可以访问该服务。 但是,当搜索Relay命名空间时不会显示该服务。 相反,客户端必须事先知道终结点路径。将服务凭据应用到 App.config 文件中定义的服务终结点:
foreach (ServiceEndpoint endpoint in host.Description.Endpoints) { endpoint.Behaviors.Add(serviceRegistrySettings); endpoint.Behaviors.Add(sasCredential); }如前所述,可能已经在配置文件中声明多个服务和终结点。 如果已配置,此代码将遍历配置文件并且搜索可能应用了凭据的每个终结点。 对于本教程,配置文件只有一个终结点。
打开服务主机
仍在
Main()中,添加以下行以打开服务。host.Open();通知用户该服务正在运行,并说明如何关闭服务。
Console.WriteLine("Service address: " + address); Console.WriteLine("Press [Enter] to exit"); Console.ReadLine();完成后,关闭服务主机。
host.Close();按 Ctrl+Shift+B 生成项目。
在控制台应用程序中托管服务的示例
完成的服务代码应如下所示。 该代码包括本教程中前面步骤中使用的服务协定和实现,并将服务托管在控制台应用程序中。
using System;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Description;
using Microsoft.ServiceBus;
using Microsoft.ServiceBus.Description;
namespace Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples
{
[ServiceContract(Name = "IEchoContract", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")]
public interface IEchoContract
{
[OperationContract]
String Echo(string text);
}
public interface IEchoChannel : IEchoContract, IClientChannel { };
[ServiceBehavior(Name = "EchoService", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")]
class EchoService : IEchoContract
{
public string Echo(string text)
{
Console.WriteLine("Echoing: {0}", text);
return text;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ServiceBusEnvironment.SystemConnectivity.Mode = ConnectivityMode.AutoDetect;
Console.Write("Your Service Namespace: ");
string serviceNamespace = Console.ReadLine();
Console.Write("Your SAS key: ");
string sasKey = Console.ReadLine();
// Create the credentials object for the endpoint.
TransportClientEndpointBehavior sasCredential = new TransportClientEndpointBehavior();
sasCredential.TokenProvider = TokenProvider.CreateSharedAccessSignatureTokenProvider("RootManageSharedAccessKey", sasKey);
// Create the service URI based on the service namespace.
Uri address = ServiceBusEnvironment.CreateServiceUri("sb", serviceNamespace, "EchoService");
// Create the service host reading the configuration.
ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(EchoService), address);
// Create the ServiceRegistrySettings behavior for the endpoint.
IEndpointBehavior serviceRegistrySettings = new ServiceRegistrySettings(DiscoveryType.Public);
// Add the Relay credentials to all endpoints specified in configuration.
foreach (ServiceEndpoint endpoint in host.Description.Endpoints)
{
endpoint.Behaviors.Add(serviceRegistrySettings);
endpoint.Behaviors.Add(sasCredential);
}
// Open the service.
host.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Service address: " + address);
Console.WriteLine("Press [Enter] to exit");
Console.ReadLine();
// Close the service.
host.Close();
}
}
}
创建服务协定的 WCF 客户端
下一任务是创建客户端应用程序,并定义稍后要实现的服务协定。 这些步骤类似于创建服务的步骤:定义协定、编辑 App.config 文件、使用凭据连接到中继服务等。 该过程后面的示例中提供了这些任务所用的代码。
在当前 Visual Studio 解决方案中为客户端创建一个新的项目:
- 在“解决方案资源管理器”中,右键单击当前解决方案(而非项目),并选择“添加”>“新建项目”。
- 在“添加新项目”中,选择适用于 C# 的“控制台应用(.NET Framework)”,然后选择“下一步”。
- 指定“EchoClient”作为项目名称,然后选择“创建”。
在“解决方案资源管理器”中的“EchoClient”项目内,双击“Program.cs”文件以在编辑器中将其打开(如果尚未打开)。
将命名空间名称从其默认名称
EchoClient更改为Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples。安装服务总线 NuGet 包:
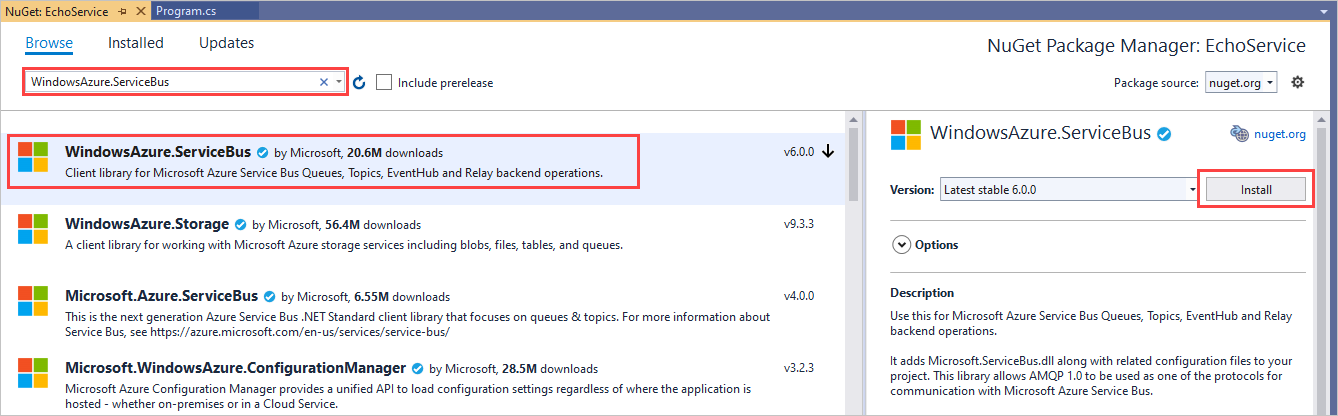
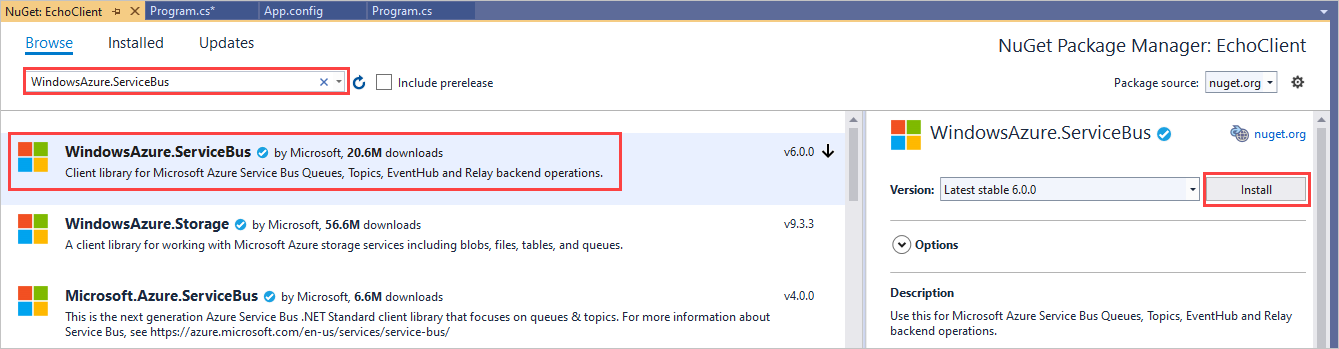
在“解决方案资源管理器”中,右键单击“EchoClient”并选择“管理 NuGet 包” 。
选择“浏览”,然后搜索并选择“WindowsAzure.ServiceBus”。 选择“安装”并接受使用条款。
为 Program.cs 文件中的 System.ServiceModel 命名空间添加
using语句。using System.ServiceModel;如下面的示例中所示,将服务协定定义添加到命名空间。 此定义等同于 Service 项目中所使用的定义。 在
Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples命名空间的顶部添加此代码。[ServiceContract(Name = "IEchoContract", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")] public interface IEchoContract { [OperationContract] string Echo(string text); } public interface IEchoChannel : IEchoContract, IClientChannel { }按 Ctrl+Shift+B 生成客户端。
EchoClient 项目的示例
以下代码演示了 EchoClient 项目中的 Program.cs 文件的当前状态。
using System;
using Microsoft.ServiceBus;
using System.ServiceModel;
namespace Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples
{
[ServiceContract(Name = "IEchoContract", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")]
public interface IEchoContract
{
[OperationContract]
string Echo(string text);
}
public interface IEchoChannel : IEchoContract, IClientChannel { }
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
}
配置 WCF 客户端
在此步骤中,可以为之前在本教程中创建的访问服务的基本客户端应用程序创建 App.config 文件。 此 App.config 文件用于定义终结点的协定、绑定和名称。 该过程后面的示例中提供了这些任务所用的代码。
在“解决方案资源管理器”中的“EchoClient”项目内,双击“App.config”以在 Visual Studio 编辑器中打开该文件 。
在
<appSettings>元素中,将占位符替换为服务命名空间的名称以及在先前步骤中复制的 SAS 密钥。在
system.serviceModel元素中添加<client>元素。<?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <system.serviceModel> <client> </client> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>此代码声明要定义 WCF 样式的客户端应用程序。
在
client元素中,定义终结点的名称、协定和绑定类型。<endpoint name="RelayEndpoint" contract="Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples.IEchoContract" binding="netTcpRelayBinding"/>此代码定义终结点的名称。 它还定义服务中定义的协定,以及客户端应用程序使用 TCP 与 Azure 中继进行通信的事实。 终结点名称在下一步中用于将此终结点配置与服务 URI 链接。
选择“文件”>“全部保存”。
App.config 文件的示例
以下代码演示 Echo 客户端的 App.config 文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<client>
<endpoint name="RelayEndpoint"
contract="Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples.IEchoContract"
binding="netTcpRelayBinding"/>
</client>
<extensions>
<bindingExtensions>
<add name="netTcpRelayBinding"
type="Microsoft.ServiceBus.Configuration.NetTcpRelayBindingCollectionElement, Microsoft.ServiceBus, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35"/>
</bindingExtensions>
</extensions>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
实现 WCF 客户端
在此部分,实现可访问之前在本教程中创建的服务的基本客户端应用程序。 与服务相似,该客户端执行许多相同的操作访问 Azure 中继:
- 设置连接模式。
- 创建用于定位主机服务的 URI。
- 定义安全凭据。
- 将凭据应用到连接。
- 打开连接。
- 执行应用程序特定的任务。
- 关闭连接。
但是,主要的区别之一在于,客户端应用程序使用通道连接到中继服务。 服务使用对 ServiceHost 的调用。 该过程后面的示例中提供了这些任务所用的代码。
实现客户端应用程序
将连接模式设置为
AutoDetect在 EchoClient 应用程序的Main()方法中添加以下代码。ServiceBusEnvironment.SystemConnectivity.Mode = ConnectivityMode.AutoDetect;定义变量以保存用于服务命名空间的值,以及从控制台读取的 SAS 密钥。
Console.Write("Your Service Namespace: "); string serviceNamespace = Console.ReadLine(); Console.Write("Your SAS Key: "); string sasKey = Console.ReadLine();创建用于定义中继项目中主机位置的 URI。
Uri serviceUri = ServiceBusEnvironment.CreateServiceUri("sb", serviceNamespace, "EchoService");创建服务命名空间终结点的凭据对象。
TransportClientEndpointBehavior sasCredential = new TransportClientEndpointBehavior(); sasCredential.TokenProvider = TokenProvider.CreateSharedAccessSignatureTokenProvider("RootManageSharedAccessKey", sasKey);创建加载在 App.config 文件中所述的配置的通道工厂。
ChannelFactory<IEchoChannel> channelFactory = new ChannelFactory<IEchoChannel>("RelayEndpoint", new EndpointAddress(serviceUri));通道工厂是创建通道(通过该通道,服务和客户端可以进行通信)的一个 WCF 对象。
应用凭据。
channelFactory.Endpoint.Behaviors.Add(sasCredential);创建并打开服务通道。
IEchoChannel channel = channelFactory.CreateChannel(); channel.Open();编写用于回显的基本用户界面和功能。
Console.WriteLine("Enter text to echo (or [Enter] to exit):"); string input = Console.ReadLine(); while (input != String.Empty) { try { Console.WriteLine("Server echoed: {0}", channel.Echo(input)); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine("Error: " + e.Message); } input = Console.ReadLine(); }代码使用通道对象的实例作为服务代理。
关闭通道,并关闭工厂。
channel.Close(); channelFactory.Close();
本教程的示例代码
完成的代码应如下所示。 此代码演示如何创建客户端应用程序、如何调用服务操作以及如何在完成操作调用后关闭客户端。
using System;
using Microsoft.ServiceBus;
using System.ServiceModel;
namespace Microsoft.ServiceBus.Samples
{
[ServiceContract(Name = "IEchoContract", Namespace = "https://samples.microsoft.com/ServiceModel/Relay/")]
public interface IEchoContract
{
[OperationContract]
String Echo(string text);
}
public interface IEchoChannel : IEchoContract, IClientChannel { }
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ServiceBusEnvironment.SystemConnectivity.Mode = ConnectivityMode.AutoDetect;
Console.Write("Your Service Namespace: ");
string serviceNamespace = Console.ReadLine();
Console.Write("Your SAS Key: ");
string sasKey = Console.ReadLine();
Uri serviceUri = ServiceBusEnvironment.CreateServiceUri("sb", serviceNamespace, "EchoService");
TransportClientEndpointBehavior sasCredential = new TransportClientEndpointBehavior();
sasCredential.TokenProvider = TokenProvider.CreateSharedAccessSignatureTokenProvider("RootManageSharedAccessKey", sasKey);
ChannelFactory<IEchoChannel> channelFactory = new ChannelFactory<IEchoChannel>("RelayEndpoint", new EndpointAddress(serviceUri));
channelFactory.Endpoint.Behaviors.Add(sasCredential);
IEchoChannel channel = channelFactory.CreateChannel();
channel.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Enter text to echo (or [Enter] to exit):");
string input = Console.ReadLine();
while (input != String.Empty)
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Server echoed: {0}", channel.Echo(input));
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: " + e.Message);
}
input = Console.ReadLine();
}
channel.Close();
channelFactory.Close();
}
}
}
运行应用程序
按 Ctrl+Shift+B 生成解决方案。 此操作生成在先前步骤中创建的客户端项目和服务项目。
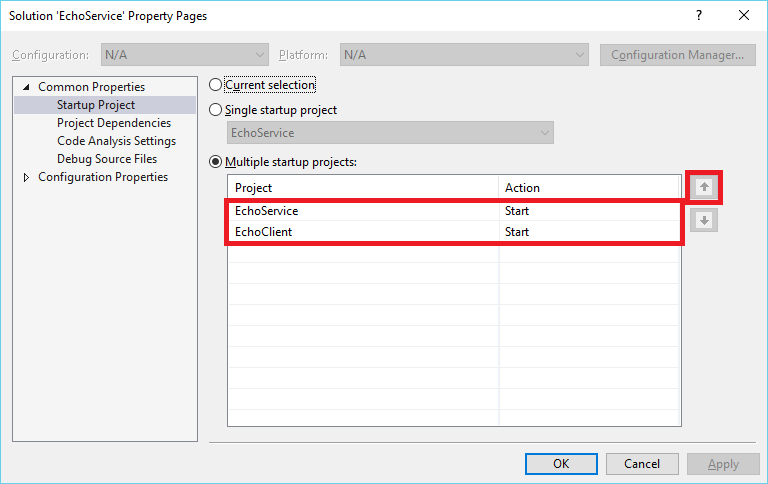
在运行客户端应用程序之前,必须确保服务应用程序正在运行。 在“解决方案资源管理器”中,右键单击“EchoService”解决方案并选择“属性” 。
在“属性页”中选择“通用属性”>“启动项目”,然后选择“多个启动项目” 。 EchoService 显示在列表的最前面。
将 EchoService 和 EchoClient 项目的“操作”框设置为“启动”。
选择“项目依赖项”。 在“项目”中选择“EchoClient”。 对于“依赖于”,请确保选择“EchoService”。
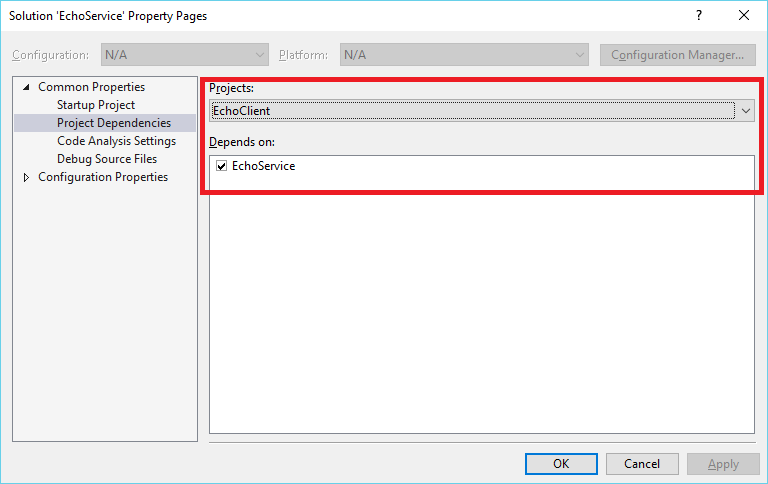
选择“确定”关闭“属性页”。
按 F5 运行这两个项目。
此时会打开两个控制台窗口并提示输入命名空间名称。 必须先运行服务,因此请在“EchoService”控制台窗口中输入命名空间,然后按 Enter。
接下来,控制台会提示输入 SAS 密钥。 输入 SAS 密钥并按 Enter。
以下是来自控制台窗口的示例输出。 此处的值只是示例。
Your Service Namespace: myNamespaceYour SAS Key: <SAS key value>服务应用程序将其正在侦听的地址打印到控制台窗口中,如下面的示例中所示。
Service address: sb://mynamespace.servicebus.chinacloudapi.cn/EchoService/Press [Enter] to exit在 EchoClient 控制台窗口中,输入之前为服务应用程序输入的相同信息。 为客户端应用程序输入相同的服务命名空间和 SAS 密钥值。
输入这些值后,客户端将打开服务通道并提示你输入如以下控制台输出示例中所示的一些文本。
Enter text to echo (or [Enter] to exit):输入要发送到服务应用程序的一些文本,然后按 Enter。 此文本通过 Echo 服务操作发送到服务并显示在服务控制台窗口中,如下面的示例输出所示。
Echoing: My sample text客户端应用程序接收
Echo操作的返回值(此为原始文本),并将其打印到控制台窗口。 以下文本是来自客户端控制台窗口的示例输出。Server echoed: My sample text可以继续以这种方式将来自客户端的短信发送至服务。 完成后,在客户端和服务控制台窗口中按 Enter 以结束这两个应用程序。
下一步
转到以下教程: