适用于:✅Azure 数据资源管理器
函数 series_fit_lowess_fl() 是一个用户定义的函数 (UDF),它对一个序列应用 LOWESS 回归。 此函数采用包含多个序列(动态数值阵列)的表,并生成一条 LOWESS 曲线,它是原始序列的平滑化版本。
先决条件
- 必须在群集上启用 Python 插件。 这是函数中使用的内联 Python 所必需的。
语法
T | invoke series_fit_lowess_fl(y_series, y_fit_series, [ fit_size ], [ x_series ], [ x_istime ])
详细了解语法约定。
参数
| 客户 | 类型 | 必需 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| y_series | string |
✔️ | 包含依赖变量的输入表列的名称。 此列是要拟合的序列。 |
| y_fit_series | string |
✔️ | 用于存储已拟合序列的列的名称。 |
| fit_size | int |
对于每个点,其各自的 fit_size 最近点会应用局部回归。 默认值为 5。 | |
| x_series | string |
包含独立变量的列的名称,即 x 轴(或时间轴)。 此参数为可选,只有间距不均匀的序列才需要。 默认值为空字符串,因为对于间距均匀的序列的回归,x 是冗余的。 | |
| x_istime | bool |
仅当指定了 x_series 并且它是日期/时间的向量时,才需要此布尔参数。 默认为 false。 |
函数定义
可以通过将函数的代码嵌入为查询定义的函数,或将其创建为数据库中的存储函数来定义函数,如下所示:
使用以下 let 语句定义函数。 不需要任何权限。
let series_fit_lowess_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_size:int=5, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_size', fit_size, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_size = kargs["fit_size"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
import statsmodels.api as sm
def lowess_fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, fsize):
y = ts_row[y_col]
fraction = fsize/len(y)
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
lowess = sm.nonparametric.lowess
z = lowess(y, x, return_sorted=False, frac=fraction)
return list(z)
result = df
result[y_fit_series] = df.apply(lowess_fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, fit_size))
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
// Write your query to use the function here.
示例
以下示例使用 invoke 运算符运行函数。
常规时序上的 LOWESS 回归
若要使用查询定义的函数,请在嵌入的函数定义后调用它。
let series_fit_lowess_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_size:int=5, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_size', fit_size, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_size = kargs["fit_size"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
import statsmodels.api as sm
def lowess_fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, fsize):
y = ts_row[y_col]
fraction = fsize/len(y)
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
lowess = sm.nonparametric.lowess
z = lowess(y, x, return_sorted=False, frac=fraction)
return list(z)
result = df
result[y_fit_series] = df.apply(lowess_fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, fit_size))
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
//
// Apply 9 points LOWESS regression on regular time series
//
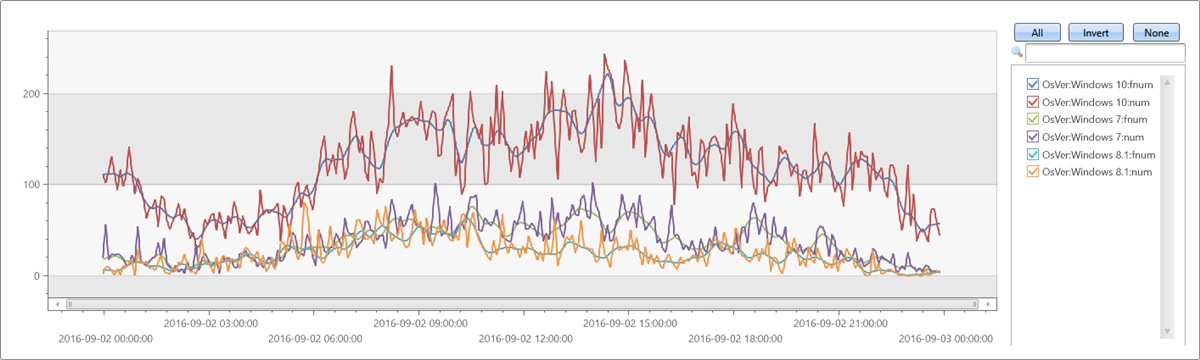
let max_t = datetime(2016-09-03);
demo_make_series1
| make-series num=count() on TimeStamp from max_t-1d to max_t step 5m by OsVer
| extend fnum = dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_lowess_fl('num', 'fnum', 9)
| render timechart
输出
测试不规则时序
若要使用查询定义的函数,请在嵌入的函数定义后调用它。
let series_fit_lowess_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_size:int=5, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_size', fit_size, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_size = kargs["fit_size"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
import statsmodels.api as sm
def lowess_fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, fsize):
y = ts_row[y_col]
fraction = fsize/len(y)
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
lowess = sm.nonparametric.lowess
z = lowess(y, x, return_sorted=False, frac=fraction)
return list(z)
result = df
result[y_fit_series] = df.apply(lowess_fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, fit_size))
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
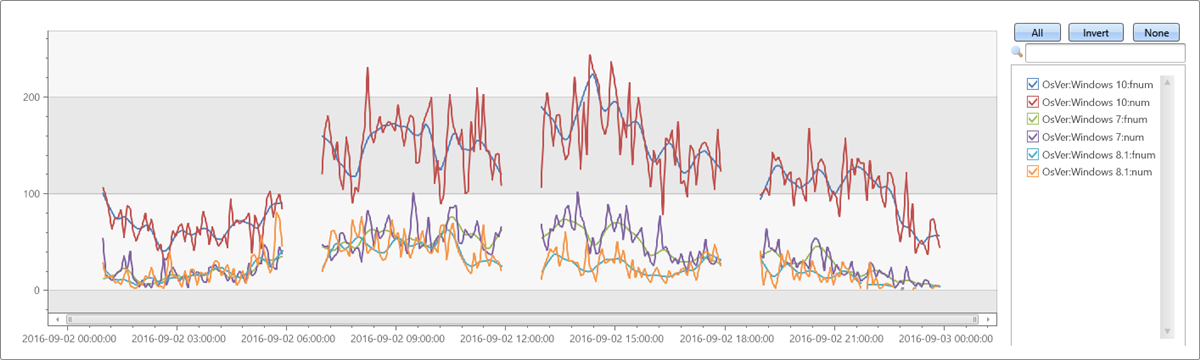
let max_t = datetime(2016-09-03);
demo_make_series1
| where TimeStamp between ((max_t-1d)..max_t)
| summarize num=count() by bin(TimeStamp, 5m), OsVer
| order by TimeStamp asc
| where hourofday(TimeStamp) % 6 != 0 // delete every 6th hour to create irregular time series
| summarize TimeStamp=make_list(TimeStamp), num=make_list(num) by OsVer
| extend fnum = dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_lowess_fl('num', 'fnum', 9, 'TimeStamp', True)
| render timechart
输出
将多项式拟合与 LOWESS 进行比较
若要使用查询定义的函数,请在嵌入的函数定义后调用它。
let series_fit_lowess_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_size:int=5, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_size', fit_size, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_size = kargs["fit_size"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
import statsmodels.api as sm
def lowess_fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, fsize):
y = ts_row[y_col]
fraction = fsize/len(y)
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
lowess = sm.nonparametric.lowess
z = lowess(y, x, return_sorted=False, frac=fraction)
return list(z)
result = df
result[y_fit_series] = df.apply(lowess_fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, fit_size))
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
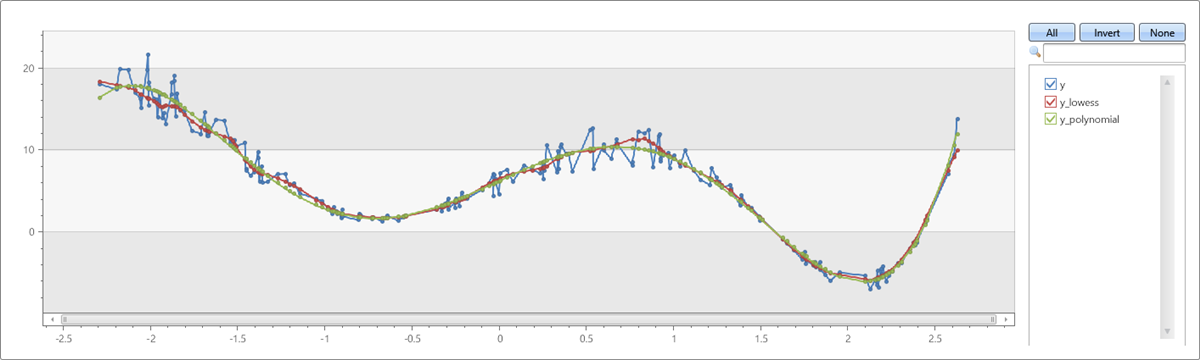
range x from 1 to 200 step 1
| project x = rand()*5 - 2.3
| extend y = pow(x, 5)-8*pow(x, 3)+10*x+6
| extend y = y + (rand() - 0.5)*0.5*y
| summarize x=make_list(x), y=make_list(y)
| extend y_lowess = dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_lowess_fl('y', 'y_lowess', 15, 'x')
| extend series_fit_poly(y, x, 5)
| project x, y, y_lowess, y_polynomial=series_fit_poly_y_poly_fit
| render linechart
输出