在数据工程中, 回填 是指通过设计用于处理当前或流数据的数据管道追溯处理历史数据的过程。
通常,这是一个将数据发送到现有表的独立数据流。 下图显示了向管道中的青铜表发送历史数据的回填流。
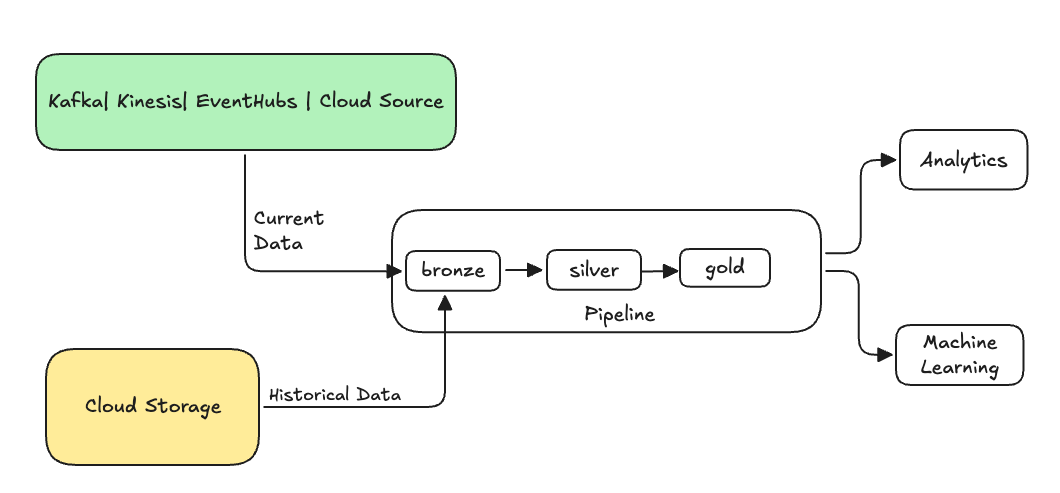
某些可能需要回填的方案:
- 处理旧系统的历史数据以训练机器学习(ML)模型或构建历史趋势分析仪表板。
- 由于上游数据源的数据质量问题,重新处理数据子集。
- 业务要求已更改,需要为初始管道未涵盖的不同时间段回填数据。
- 业务逻辑已更改,需要重新处理历史数据和当前数据。
使用该 ONCE 选项的专用追加流支持 Lakeflow Spark 声明性管道中的回填。 有关的详细信息,请参阅append_flow或ONCE。
将历史数据回填到流式处理表中时的注意事项
- 通常,会将数据追加到青铜流式表中。 下游银层和黄金层将从铜层中选取新数据。
- 确保管道可以正常处理重复的数据,以防多次追加相同的数据。
- 确保历史数据架构与当前数据架构兼容。
- 考虑数据卷大小和所需的处理时间 SLA,并相应地配置群集和批大小。
示例:向现有管道添加回填
在此示例中,假设你有一个管道,该管道从 2025 年 1 月 1 日起从云存储源引入原始事件注册数据。 稍后,你意识到要回填前三年的历史数据供下游报告和分析用例使用。 所有数据位于一个位置,按年、月和日分区,采用 JSON 格式。
初始管道
这是逐步从云存储导入事件注册原始数据的管道程序代码。
Python
from pyspark import pipelines as dp
source_root_path = spark.conf.get("registration_events_source_root_path")
begin_year = spark.conf.get("begin_year")
incremental_load_path = f"{source_root_path}/*/*/*"
# create a streaming table and the default flow to ingest streaming events
@dp.table(name="registration_events_raw", comment="Raw registration events")
def ingest():
return (
spark
.readStream
.format("cloudFiles")
.option("cloudFiles.format", "json")
.option("cloudFiles.inferColumnTypes", "true")
.option("cloudFiles.maxFilesPerTrigger", 100)
.option("cloudFiles.schemaEvolutionMode", "addNewColumns")
.option("modifiedAfter", "2025-01-01T00:00:00.000+00:00")
.load(incremental_load_path)
.where(f"year(timestamp) >= {begin_year}") # safeguard to not process data before begin_year
)
SQL
-- create a streaming table and the default flow to ingest streaming events
CREATE OR REFRESH STREAMING LIVE TABLE registration_events_raw AS
SELECT * FROM read_files(
"/Volumes/gc/demo/apps_raw/event_registration/*/*/*",
format => "json",
inferColumnTypes => true,
maxFilesPerTrigger => 100,
schemaEvolutionMode => "addNewColumns",
modifiedAfter => "2024-12-31T23:59:59.999+00:00"
)
WHERE year(timestamp) >= '2025'; -- safeguard to not process data before begin_year
在这里,我们使用 modifiedAfter 自动加载程序选项来确保未处理云存储路径中的所有数据。 增量处理在该边界处被切断。
小窍门
其他数据源(例如 Kafka、Kinesis 和 Azure 事件中心)具有等效的读取器选项来实现相同的行为。
回填前 3 年的数据
现在,需要添加一个或多个流来回填以前的数据。 在此示例中,执行以下步骤:
- 使用
append once流。 这会执行一次性回填,并且不会在此一次性回填后继续运行。 代码保留在管道中,如果管道已完全刷新,则重新运行回填。 - 创建三个回填流,每个流对应一年(在此示例中,数据按年份在路径中拆分)。 对于 Python,我们将流创建参数化,但在 SQL 中,我们为每个流重复三次代码。
如果您正在处理自己的项目,并且不使用无服务器计算,则可能需要更新流水线的最大工作线程。 增加最大工作者可确保有资源来处理历史数据,同时继续在预期服务级别协议内处理当前流数据。
小窍门
如果使用具有增强的自动缩放(默认值)的无服务器计算,则当负载增加时,群集会自动增加大小。
Python
from pyspark import pipelines as dp
source_root_path = spark.conf.get("registration_events_source_root_path")
begin_year = spark.conf.get("begin_year")
backfill_years = spark.conf.get("backfill_years") # e.g. "2024,2023,2022"
incremental_load_path = f"{source_root_path}/*/*/*"
# meta programming to create append once flow for a given year (called later)
def setup_backfill_flow(year):
backfill_path = f"{source_root_path}/year={year}/*/*"
@dp.append_flow(
target="registration_events_raw",
once=True,
name=f"flow_registration_events_raw_backfill_{year}",
comment=f"Backfill {year} Raw registration events")
def backfill():
return (
spark
.read
.format("json")
.option("inferSchema", "true")
.load(backfill_path)
)
# create the streaming table
dp.create_streaming_table(name="registration_events_raw", comment="Raw registration events")
# append the original incremental, streaming flow
@dp.append_flow(
target="registration_events_raw",
name="flow_registration_events_raw_incremental",
comment="Raw registration events")
def ingest():
return (
spark
.readStream
.format("cloudFiles")
.option("cloudFiles.format", "json")
.option("cloudFiles.inferColumnTypes", "true")
.option("cloudFiles.maxFilesPerTrigger", 100)
.option("cloudFiles.schemaEvolutionMode", "addNewColumns")
.option("modifiedAfter", "2024-12-31T23:59:59.999+00:00")
.load(incremental_load_path)
.where(f"year(timestamp) >= {begin_year}")
)
# parallelize one time multi years backfill for faster processing
# split backfill_years into array
for year in backfill_years.split(","):
setup_backfill_flow(year) # call the previously defined append_flow for each year
SQL
-- create the streaming table
CREATE OR REFRESH STREAMING TABLE registration_events_raw;
-- append the original incremental, streaming flow
CREATE FLOW
registration_events_raw_incremental
AS INSERT INTO
registration_events_raw BY NAME
SELECT * FROM STREAM read_files(
"/Volumes/gc/demo/apps_raw/event_registration/*/*/*",
format => "json",
inferColumnTypes => true,
maxFilesPerTrigger => 100,
schemaEvolutionMode => "addNewColumns",
modifiedAfter => "2024-12-31T23:59:59.999+00:00"
)
WHERE year(timestamp) >= '2025';
-- one time backfill 2024
CREATE FLOW
registration_events_raw_backfill_2024
AS INSERT INTO ONCE
registration_events_raw BY NAME
SELECT * FROM read_files(
"/Volumes/gc/demo/apps_raw/event_registration/year=2024/*/*",
format => "json",
inferColumnTypes => true
);
-- one time backfill 2023
CREATE FLOW
registration_events_raw_backfill_2023
AS INSERT INTO ONCE
registration_events_raw BY NAME
SELECT * FROM read_files(
"/Volumes/gc/demo/apps_raw/event_registration/year=2023/*/*",
format => "json",
inferColumnTypes => true
);
-- one time backfill 2022
CREATE FLOW
registration_events_raw_backfill_2022
AS INSERT INTO ONCE
registration_events_raw BY NAME
SELECT * FROM read_files(
"/Volumes/gc/demo/apps_raw/event_registration/year=2022/*/*",
format => "json",
inferColumnTypes => true
);
此实现重点介绍了几个重要的模式。
关注点分离
- 增量处理与回填操作相互独立。
- 每个流都有自己的配置和优化设置。
- 增量和回填操作之间有明显的区别。
受控执行
- 使用
ONCE选项可确保每个回填准确运行一次。 - 回填流保留在管道图中,但在完成后会处于空闲状态。 它已准备好在完全刷新时自动使用。
- 在管道定义中有回填操作的明确审计记录。
处理优化
- 可以将大型回填拆分为多个较小的回填,以便更快地处理或控制处理。
- 使用增强的自动缩放根据当前群集负载动态缩放群集大小。
架构演变
- 使用
schemaEvolutionMode="addNewColumns"优雅地处理架构更改。 - 跨历史数据和当前数据具有一致的模式推断。
- 对较新的数据中的新列进行安全处理。