Get started creating an internal load balancer using the Azure classic CLI
Azure Internal Load Balancer (ILB) provides network load balancing between virtual machines that reside inside a cloud service or a virtual network with a regional scope.
For information about the use and configuration of virtual networks with a regional scope, see Regional virtual networks. Existing virtual networks that have been configured for an affinity group cannot use ILB.
Important
Azure has two different deployment models for creating and working with resources: Resource Manager and classic. This article covers using the classic deployment model. Microsoft recommends that most new deployments use the Resource Manager model. Learn how to perform these steps using the Resource Manager model.
Configuration scenario
In this scenario, we're creating an internal load balancer in a virtual network as shown in the following figure:
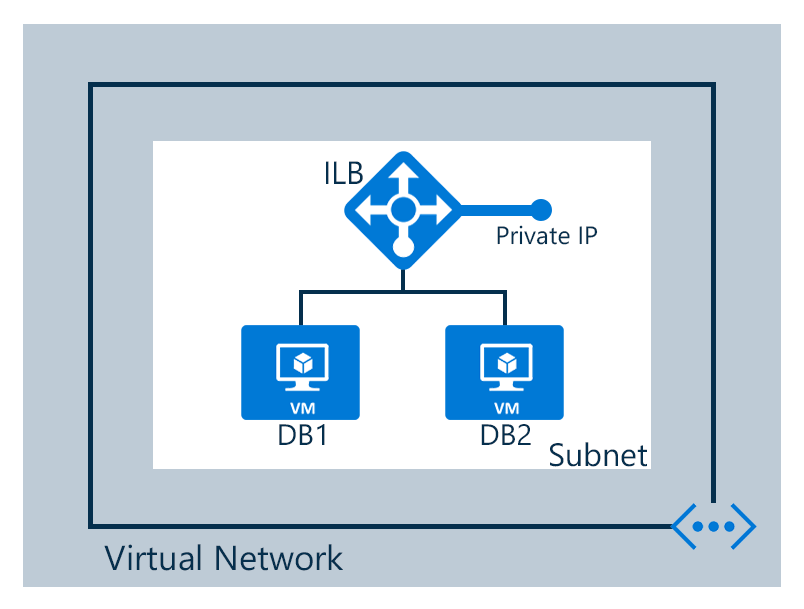
The configuration for our scenario is as follows:
- Two virtual machines named DB1 and DB2
- Endpoints for the internal load balancer
- An internal load balancer
To create an internal load balancer set for virtual machines
To create an internal load balancer set and the servers that sends their traffic to it, you must do the following:
- Create an instance of Internal Load Balancing that is the endpoint of incoming traffic to be load balanced across the servers of a load-balanced set.
- Add endpoints corresponding to the virtual machines that can receive the incoming traffic.
- Configure the servers to send their traffic to the virtual IP (VIP) address of the Internal Load Balancing instance.
Step by step creating an internal load balancer using classic CLI
This guide shows how to create an internal load balancer based on the scenario above.
If you have never used classic CLI, see Install and Configure the Azure CLI and follow the instructions up to the point where you select your Azure account and subscription.
Run the azure config mode command to switch to classic mode, as shown below.
azure config mode asmExpected output:
info: New mode is asm
Create endpoint and load balancer set
The scenario assumes the virtual machines "DB1" and "DB2" in a cloud service called "mytestcloud". Both virtual machines are using a virtual network called my "testvnet" with subnet "subnet-1".
This guide creates an internal load balancer set using port 1433 as private port and 1433 as local port.
This is a common scenario where you have SQL virtual machines on the back end using an internal load balancer to guarantee the database servers won't be exposed directly using a public IP address.
Step 1
Create an internal load balancer set using azure network service internal-load-balancer add.
azure service internal-load-balancer add --serviceName mytestcloud --internalLBName ilbset --subnet-name subnet-1 --static-virtualnetwork-ipaddress 192.168.2.7
Check out azure service internal-load-balancer --help for more information.
You can check the internal load balancer properties using the command azure service internal-load-balancer list cloud service name.
Here follows an example of the output:
azure service internal-load-balancer list my-testcloud
info: Executing command service internal-load-balancer list
+ Getting cloud service deployment
data: Name Type SubnetName StaticVirtualNetworkIPAddress
data: ------ ------- ---------- -----------------------------
data: ilbset Private subnet-1 192.168.2.7
info: service internal-load-balancer list command OK
Step 2
You configure the internal load balancer set when you add the first endpoint. You can associate the endpoint, virtual machine, and probe port to the internal load balancer set in this step.
azure vm endpoint create db1 1433 --local-port 1433 --protocol tcp --probe-port 1433 --probe-protocol tcp --probe-interval 300 --probe-timeout 600 --internal-load-balancer-name ilbset
Step 3
Verify the load balancer configuration using azure vm show virtual machine name
azure vm show DB1
The output is as follows:
azure vm show DB1
info: Executing command vm show
+ Getting virtual machines
data: DNSName "mytestcloud.cloudapp.net"
data: Location "East US 2"
data: VMName "DB1"
data: IPAddress "192.168.2.4"
data: InstanceStatus "ReadyRole"
data: InstanceSize "Standard_D1"
data: Image "a699494373c04fc0bc8f2bb1389d6106__Windows-Server-2012-R2-20151022-en.us-127GB.vhd"
data: OSDisk hostCaching "ReadWrite"
data: OSDisk name "db1-DB1-0-201511120457370846"
data: OSDisk mediaLink "https://XXXX.blob.core.windows.net/vhd"
data: OSDisk sourceImageName "a699494373c04fc0bc8f2bb1389d6106__Windows-Server-2012-R2-20151022-en.us-127GB.vhd"
data: OSDisk operatingSystem "Windows"
data: OSDisk iOType "Standard"
data: ReservedIPName ""
data: VirtualIPAddresses 0 address "137.116.64.107"
data: VirtualIPAddresses 0 name "db1ContractContract"
data: VirtualIPAddresses 0 isDnsProgrammed true
data: VirtualIPAddresses 1 address "192.168.2.7"
data: VirtualIPAddresses 1 name "ilbset"
data: Network Endpoints 0 localPort 5986
data: Network Endpoints 0 name "PowerShell"
data: Network Endpoints 0 port 5986
data: Network Endpoints 0 protocol "tcp"
data: Network Endpoints 0 virtualIPAddress "137.116.64.107"
data: Network Endpoints 0 enableDirectServerReturn false
data: Network Endpoints 1 localPort 3389
data: Network Endpoints 1 name "Remote Desktop"
data: Network Endpoints 1 port 60173
data: Network Endpoints 1 protocol "tcp"
data: Network Endpoints 1 virtualIPAddress "137.116.64.107"
data: Network Endpoints 1 enableDirectServerReturn false
data: Network Endpoints 2 localPort 1433
data: Network Endpoints 2 name "tcp-1433-1433"
data: Network Endpoints 2 port 1433
data: Network Endpoints 2 loadBalancerProbe port 1433
data: Network Endpoints 2 loadBalancerProbe protocol "tcp"
data: Network Endpoints 2 loadBalancerProbe intervalInSeconds 300
data: Network Endpoints 2 loadBalancerProbe timeoutInSeconds 600
data: Network Endpoints 2 protocol "tcp"
data: Network Endpoints 2 virtualIPAddress "192.168.2.7"
data: Network Endpoints 2 enableDirectServerReturn false
data: Network Endpoints 2 loadBalancerName "ilbset"
info: vm show command OK
Create a remote desktop endpoint for a virtual machine
You can create a remote desktop endpoint to forward network traffic from a public port to a local port for a specific virtual machine using azure vm endpoint create.
azure vm endpoint create web1 54580 -k 3389
Remove virtual machine from load balancer
You can remove a virtual machine from an internal load balancer set by deleting the associated endpoint. Once the endpoint is removed, the virtual machine won't belong to the load balancer set anymore.
Using the example above, you can remove the endpoint created for virtual machine "DB1" from internal load balancer "ilbset" by using the command azure vm endpoint delete.
azure vm endpoint delete DB1 tcp-1433-1433
Check out azure vm endpoint --help for more information.
Next steps
Configure a load balancer distribution mode using source IP affinity