How to use Docker Machine to create hosts in Azure
This article details how to use Docker Machine to create hosts in Azure. The docker-machine command creates a Linux virtual machine (VM) in Azure then installs Docker. You can then manage your Docker hosts in Azure using the same local tools and workflows. To use docker-machine in Windows 10, you must use Linux bash.
Create VMs with Docker Machine
First, obtain your Azure subscription ID with az account show as follows:
sub=$(az account show --query "id" -o tsv)
You create Docker host VMs in Azure with docker-machine create by specifying azure as the driver. For more information, see the Docker Azure Driver documentation
The following example creates a VM named myVM, based on "Standard D2 v2" plan, creates a user account named azureuser, and opens port 80 on the host VM. Follow any prompts to log in to your Azure account and grant Docker Machine permissions to create and manage resources.
docker-machine create -d azure \
--azure-subscription-id $sub \
--azure-ssh-user azureuser \
--azure-open-port 80 \
--azure-size "Standard_DS2_v2" \
myvm
The output looks similar to the following example:
Creating CA: /Users/user/.docker/machine/certs/ca.pem
Creating client certificate: /Users/user/.docker/machine/certs/cert.pem
Running pre-create checks...
(myvm) Completed machine pre-create checks.
Creating machine...
(myvm) Querying existing resource group. name="docker-machine"
(myvm) Creating resource group. name="docker-machine" location="westus"
(myvm) Configuring availability set. name="docker-machine"
(myvm) Configuring network security group. name="myvm-firewall" location="westus"
(myvm) Querying if virtual network already exists. rg="docker-machine" location="westus" name="docker-machine-vnet"
(myvm) Creating virtual network. name="docker-machine-vnet" rg="docker-machine" location="westus"
(myvm) Configuring subnet. name="docker-machine" vnet="docker-machine-vnet" cidr="192.168.0.0/16"
(myvm) Creating public IP address. name="myvm-ip" static=false
(myvm) Creating network interface. name="myvm-nic"
(myvm) Creating storage account. sku=Standard_LRS name="vhdski0hvfazyd8mn991cg50" location="westus"
(myvm) Creating virtual machine. location="westus" size="Standard_A2" username="azureuser" osImage="canonical:UbuntuServer:16.04.0-LTS:latest" name="myvm
Waiting for machine to be running, this may take a few minutes...
Detecting operating system of created instance...
Waiting for SSH to be available...
Detecting the provisioner...
Provisioning with ubuntu(systemd)...
Installing Docker...
Copying certs to the local machine directory...
Copying certs to the remote machine...
Setting Docker configuration on the remote daemon...
Checking connection to Docker...
Docker is up and running!
To see how to connect your Docker Client to the Docker Engine running on this virtual machine, run: docker-machine env myvm
Configure your Docker shell
To connect to your Docker host in Azure, define the appropriate connection settings. As noted at the end of the output, view the connection information for your Docker host as follows:
docker-machine env myvm
The output is similar to the following example:
export DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY="1"
export DOCKER_HOST="tcp://40.68.254.142:2376"
export DOCKER_CERT_PATH="/Users/user/.docker/machine/machines/machine"
export DOCKER_MACHINE_NAME="machine"
# Run this command to configure your shell:
# eval $(docker-machine env myvm)
To define the connection settings, you can either run the suggested configuration command (eval $(docker-machine env myvm)), or you can set the environment variables manually.
Run a container
To see a container in action, lets run a basic NGINX webserver. Create a container with docker run and expose port 80 for web traffic as follows:
docker run -d -p 80:80 --restart=always nginx
The output is similar to the following example:
Unable to find image 'nginx:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/nginx
ff3d52d8f55f: Pull complete
226f4ec56ba3: Pull complete
53d7dd52b97d: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:41ad9967ea448d7c2b203c699b429abe1ed5af331cd92533900c6d77490e0268
Status: Downloaded newer image for nginx:latest
675e6056cb81167fe38ab98bf397164b01b998346d24e567f9eb7a7e94fba14a
View running containers with docker ps. The following example output shows the NGINX container running with port 80 exposed:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
d5b78f27b335 nginx "nginx -g 'daemon off" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, 443/tcp festive_mirzakhani
Test the container
Obtain the public IP address of Docker host as follows:
docker-machine ip myvm
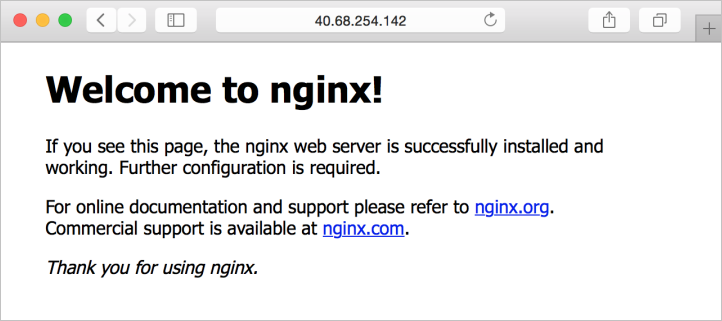
To see the container in action, open a web browser and enter the public IP address noted in the output of the preceding command:
Next steps
For examples on using Docker Compose, see Get started with Docker and Compose in Azure.