MLflow 支持 Amazon Bedrock 的自动追踪,Amazon Bedrock 是 AWS 上的一项完全托管服务,提供由领先的 AI 提供商(如 Anthropic、Cohere、Meta、Mistral AI 等)提供的高性能基础。 通过调用 mlflow.bedrock.autolog 函数为 Amazon Bedrock 启用自动跟踪,MLflow 将捕获 LLM 调用的跟踪并将其记录到活动的 MLflow 试验。
MLflow 跟踪自动捕获有关 Amazon Bedrock 调用的以下信息:
- 提示和完成响应
- 潜伏期
- 模型名称
- 其他元数据(如温度、max_tokens)(如果指定)。
- 在响应中返回时进行函数调用
- 引发的任何异常
注释
在无服务器计算群集上,不会自动启用自动记录。 必须显式调用 mlflow.bedrock.autolog() 才能为此集成启用自动跟踪。
先决条件
若要将 MLflow 跟踪与 Amazon Bedrock 配合使用,需要安装 MLflow 和 AWS SDK for Python (Boto3)。
开发
对于开发环境,请安装包含 Databricks 附加程序和 boto3 的完整 MLflow 软件包:
pip install --upgrade "mlflow[databricks]>=3.1" boto3
完整 mlflow[databricks] 包包括用于 Databricks 的本地开发和试验的所有功能。
生产
对于生产部署,请安装 mlflow-tracing 和 boto3:
pip install --upgrade mlflow-tracing boto3
包 mlflow-tracing 已针对生产用途进行优化。
注释
强烈建议使用 MLflow 3 以获得与 Amazon Bedrock 的最佳追踪体验。
在运行以下示例之前,需要配置环境:
对于不使用 Databricks 笔记本的用户:设置 Databricks 环境变量:
export DATABRICKS_HOST="https://your-workspace.cloud.databricks.com"
export DATABRICKS_TOKEN="your-personal-access-token"
对于 Databricks 笔记本中的用户:这些凭据会自动为您设置。
AWS 凭据:确保配置用于 Bedrock 访问的 AWS 凭据。 对于生产用途,请考虑使用 IAM 角色、AWS 机密管理器或 Databricks 机密 ,而不是环境变量(例如,使用 AWS CLI、IAM 角色或环境变量)。
受支持的 API
MLflow 支持以下 Amazon Bedrock API 的自动跟踪:
基本示例
import boto3
import mlflow
import os
# Ensure your AWS credentials are configured in your environment
# (e.g., using AWS CLI `aws configure`, or by setting
# AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, AWS_SESSION_TOKEN, AWS_DEFAULT_REGION)
# Enable auto-tracing for Amazon Bedrock
mlflow.bedrock.autolog()
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/bedrock-tracing-demo")
# Create a boto3 client for invoking the Bedrock API
bedrock = boto3.client(
service_name="bedrock-runtime",
region_name="<REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_AWS_REGION>",
)
# MLflow will log a trace for Bedrock API call
response = bedrock.converse(
modelId="anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Describe the purpose of a 'hello world' program in one line.",
}
],
inferenceConfig={
"maxTokens": 512,
"temperature": 0.1,
"topP": 0.9,
},
)
与实验关联的跟踪记录可以在 MLflow UI 中看到。
原始输入和输出
默认情况下,MLflow 为选项卡中的输入和输出消息 Chat 呈现丰富的类似聊天的 UI。若要查看原始输入和输出有效负载(包括配置参数),请单击 Inputs / Outputs UI 中的选项卡。
注释
Chat面板仅支持converse和converse_stream API。 对于其他 API,MLflow 仅显示 Inputs / Outputs 选项卡。
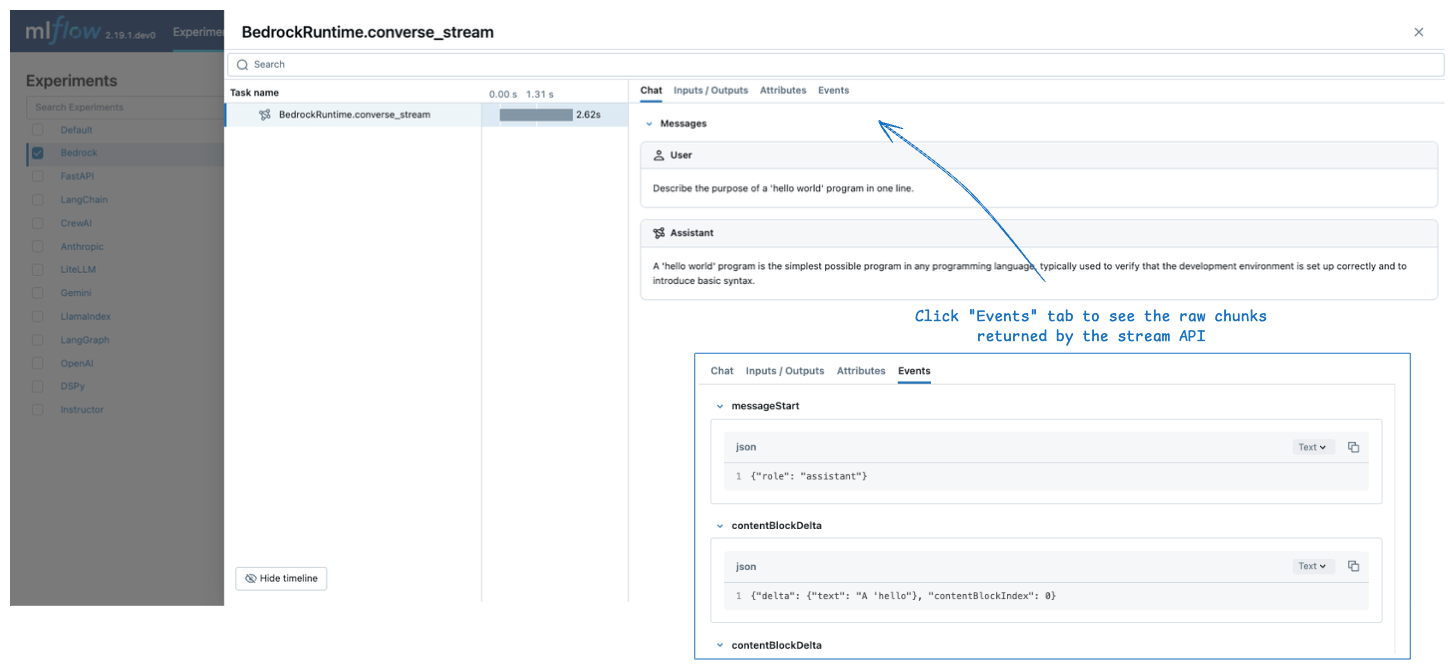
流媒体
MLflow 支持跟踪对 Amazon Bedrock APIs 的流调用。 生成的跟踪显示在 Chat 选项卡中的聚合输出消息,而各个分块显示在 Events 选项卡中。
response = bedrock.converse_stream(
modelId="anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"text": "Describe the purpose of a 'hello world' program in one line."}
],
}
],
inferenceConfig={
"maxTokens": 300,
"temperature": 0.1,
"topP": 0.9,
},
)
for chunk in response["stream"]:
print(chunk)
警告
在返回流式处理响应时,MLflow 不会立即创建跨度。 相反,当流式传输数据块被消耗时,会创建一个范围,例如,上述代码片段中的 for 循环。
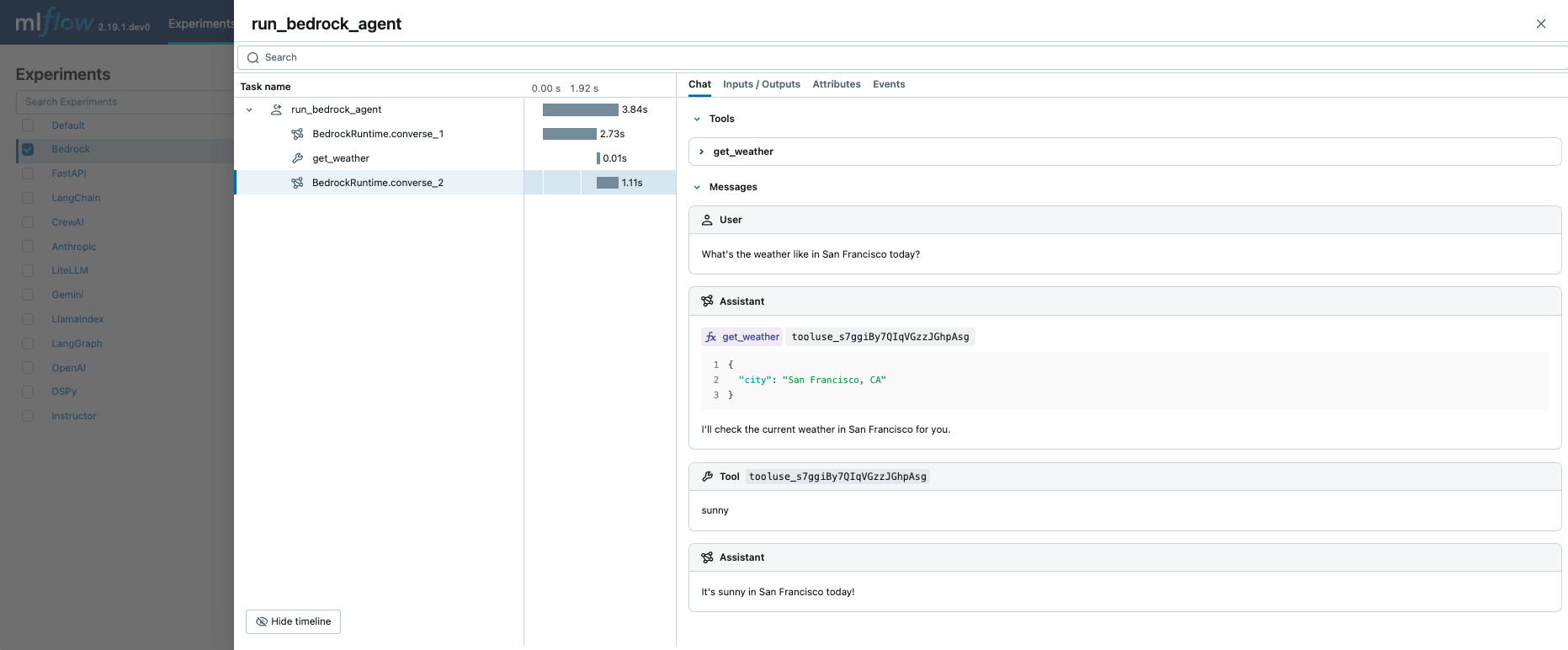
函数调用代理
MLflow 跟踪功能在调用 Amazon Bedrock API 接口时自动捕获函数调用元数据。 响应中的函数定义和指令将在跟踪 UI 上的选项卡中突出显示 Chat 。
将此功能与手动跟踪功能相结合,可以定义函数调用代理(ReAct)并跟踪其执行。 整个代理实现看起来可能很复杂,但跟踪部分非常简单:(1)将 @mlflow.trace 修饰器添加到用于跟踪的函数,并且(2)使用 mlflow.bedrock.autolog() 为 Amazon Bedrock 启用自动跟踪。 MLflow 将处理复杂性,例如解析调用链和记录执行元数据。
import boto3
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
import os
# Ensure your AWS credentials are configured in your environment
# Enable auto-tracing for Amazon Bedrock
mlflow.bedrock.autolog()
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/bedrock-agent-demo")
# Create a boto3 client for invoking the Bedrock API
bedrock = boto3.client(
service_name="bedrock-runtime",
region_name="<REPLACE_WITH_YOUR_AWS_REGION>",
)
model_id = "anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0"
# Define the tool function. Decorate it with `@mlflow.trace` to create a span for its execution.
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.TOOL)
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
""" "Get the current weather in a given location"""
return "sunny" if city == "San Francisco, CA" else "unknown"
# Define the tool configuration passed to Bedrock
tools = [
{
"toolSpec": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"inputSchema": {
"json": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g., San Francisco, CA",
},
},
"required": ["city"],
}
},
}
}
]
tool_functions = {"get_weather": get_weather}
# Define a simple tool calling agent
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.AGENT)
def run_tool_agent(question: str) -> str:
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": [{"text": question}]}]
# Invoke the model with the given question and available tools
response = bedrock.converse(
modelId=model_id,
messages=messages,
toolConfig={"tools": tools},
)
assistant_message = response["output"]["message"]
messages.append(assistant_message)
# If the model requests tool call(s), invoke the function with the specified arguments
tool_use = next(
(c["toolUse"] for c in assistant_message["content"] if "toolUse" in c), None
)
if tool_use:
tool_func = tool_functions[tool_use["name"]]
tool_result = tool_func(**tool_use["input"])
messages.append(
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"toolResult": {
"toolUseId": tool_use["toolUseId"],
"content": [{"text": tool_result}],
}
}
],
}
)
# Send the tool results to the model and get a new response
response = bedrock.converse(
modelId=model_id,
messages=messages,
toolConfig={"tools": tools},
)
return response["output"]["message"]["content"][0]["text"]
# Run the tool calling agent
question = "What's the weather like in San Francisco today?"
answer = run_tool_agent(question)
执行上述代码将创建一个包含所有 LLM 调用和工具调用的单个跟踪。

警告
对于生产环境,请始终使用 AI 网关或 Databricks 机密,而不是硬编码值,以实现安全的 API 密钥管理。
禁用自动跟踪
可以通过调用 mlflow.bedrock.autolog(disable=True) 或 mlflow.autolog(disable=True) 来全局禁用 Amazon Bedrock 的自动跟踪。