介绍
使用 Azure Synapse Analytics 中用于 Apache Spark 的 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池连接器,可以有效地在 Apache Spark 运行时和专用 SQL 池之间传输大型数据集。 连接器是作为默认库连同 Azure Synapse工作区一起提供的。 该连接器使用 Scala 语言实现。 该连接器支持 Scala 和 Python。 若要将连接器与其他笔记本语言选项配合使用,请使用 Spark magic 命令 %%spark。
在高级别,该连接器提供以下功能:
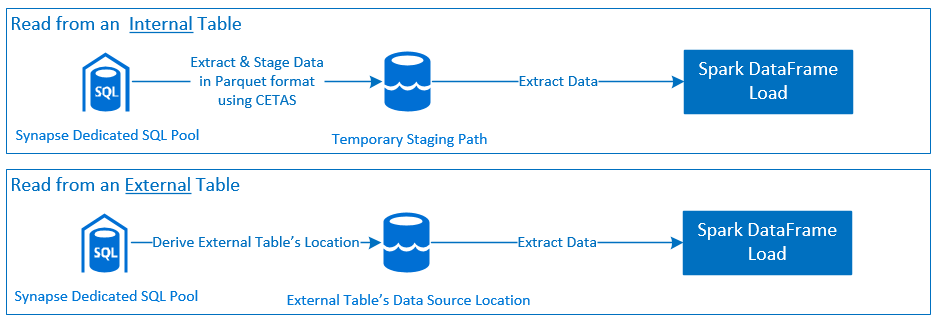
- 从 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池进行读取:
- 从 Synapse 专用 SQL 池表(内部和外部)和视图中读取大型数据集。
- 全面支持谓词下推,其中,数据帧筛选器将映射到相应的 SQL 谓词下推。
- 支持列修剪。
- 支持查询下推。
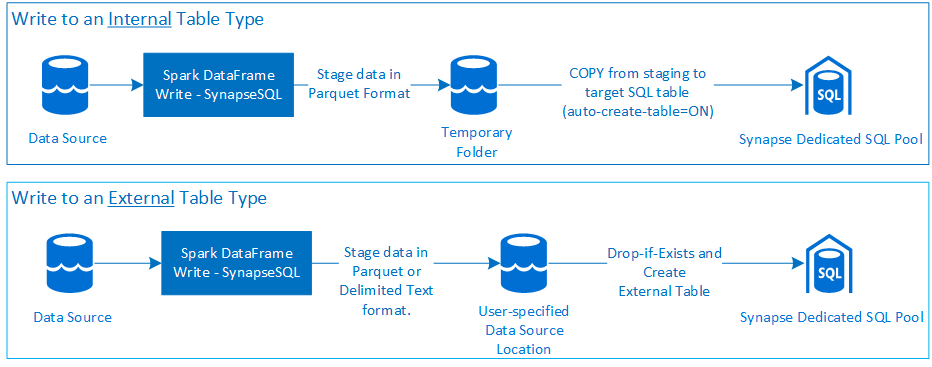
- 写入到 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池:
- 将大量数据引入到内部和外部表类型。
- 支持以下数据帧保存模式首选项:
AppendErrorIfExistsIgnoreOverwrite
- 写入外部表类型支持 Parquet 和带分隔符的文本文件格式(例如 CSV)。
- 为了将数据写入内部表,连接器现在使用 COPY 语句而不是 CETAS/CTAS 方法。
- 优化端到端写入吞吐量性能的增强功能。
- 引入了一个可选的回调句柄(Scala 函数参数),客户端可使用该句柄接收写入后指标。
- 几个示例包括记录数、完成特定操作的持续时间和失败原因。
协同协调方法
读取
写入
先决条件
本部分讨论先决条件(例如设置必需的 Azure 资源)和配置这些资源的步骤。
Azure 资源
查看并设置以下依赖 Azure 资源:
- Azure Data Lake Storage - 用作 Azure Synapse 工作区的主存储帐户。
- Azure Synapse 工作区 - 创建笔记本、生成并部署基于数据帧的入口-出口工作流。
- 专用 SQL 池(以前称为 SQL DW)- 提供企业数据仓库功能。
- Azure Synapse 无服务器 Spark 池 - 将作业作为 Spark 应用程序执行的 Spark 运行时。
准备数据库
连接到 Synapse 专用 SQL 池数据库,并运行以下设置语句:
创建一个数据库用户,该用户映射到用于登录到 Azure Synapse 工作区的 Microsoft Entra 用户标识。
CREATE USER [username@domain.com] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;创建将在其中定义表的架构,以便连接器可以成功写入和读取相应的表。
CREATE SCHEMA [<schema_name>];
身份验证
基于 Microsoft Entra ID 的身份验证
基于 Microsoft Entra ID 的身份验证是一种集成身份验证方法。 用户需要成功登录到 Azure Synapse Analytics 工作区。
基本身份验证
基本身份验证方法要求用户配置 username 和 password 选项。 请参阅配置选项部分,了解相关配置参数,以便从 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池中的表读取数据,以及向这些表写入数据。
授权
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
可以通过两种方式向 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 存储帐户授予访问权限:
- 基于角色的访问控制角色 - 存储 Blob 数据参与者角色
- 通过分配
Storage Blob Data Contributor Role,可向用户授予 Azure 存储 Blob 容器的读取、写入和删除权限。 - RBAC 在容器级别提供粗略控制方法。
- 通过分配
-
访问控制列表 (ACL)
- ACL 方法允许对给定文件夹下的特定路径和/或文件进行精细控制。
- 如果已使用 RBAC 方法授予用户权限,则不会强制执行 ACL 检查。
- 有两种广泛的 ACL 权限类型:
- 访问权限(应用于特定级别或对象)。
- 默认权限(创建时自动应用于所有子对象)。
- 权限类型包括:
-
Execute允许遍历文件夹层次结构或在其中导航。 -
Read允许读取。 -
Write允许写入。
-
- 务必配置 ACL,以便连接器可以成功对存储位置进行读写。
注释
若要使用 Synapse 工作区管道运行笔记本,还必须向 Synapse 工作区默认托管标识授予上面列出的访问权限。 工作区的默认托管标识名称与工作区的名称相同。
若要将 Synapse 工作区与受保护的存储帐户配合使用,必须从笔记本配置托管专用终结点。 必须通过
Private endpoint connections窗格中 ADLS Gen2 存储帐户的Networking部分批准该托管专用终结点。
Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池
若要能够与 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池成功地进行交互,必须进行以下授权,除非你是一位也在专用 SQL 终结点上配置为 Active Directory Admin 的用户:
读取方案
使用系统存储过程
db_exporter授予用户sp_addrolemember。EXEC sp_addrolemember 'db_exporter', [<your_domain_user>@<your_domain_name>.com];
编写情境
- 连接器使用 COPY 命令将暂存数据写入内部表的托管位置。
配置此处所述的所需权限。
下面是同样的快速访问代码片段:
--Make sure your user has the permissions to CREATE tables in the [dbo] schema GRANT CREATE TABLE TO [<your_domain_user>@<your_domain_name>.com]; GRANT ALTER ON SCHEMA::<target_database_schema_name> TO [<your_domain_user>@<your_domain_name>.com]; --Make sure your user has ADMINISTER DATABASE BULK OPERATIONS permissions GRANT ADMINISTER DATABASE BULK OPERATIONS TO [<your_domain_user>@<your_domain_name>.com]; --Make sure your user has INSERT permissions on the target table GRANT INSERT ON <your_table> TO [<your_domain_user>@<your_domain_name>.com]
- 连接器使用 COPY 命令将暂存数据写入内部表的托管位置。
API 文档
用于 Apache Spark 的 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池连接器 - API 文档。
配置选项
连接器需要某些配置参数才能成功启动和协调读取或写入操作。 对象定义 com.microsoft.spark.sqlanalytics.utils.Constants 为每个参数键提供标准化常量的列表。
下面是基于使用方案的配置选项列表:
- 使用基于 Microsoft Entra ID 的身份验证进行读取
- 凭据是自动映射的,用户不需要提供特定配置选项。
-
synapsesql方法上的包含三个部分的表名称参数需要从 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池中的相应表读取。
- 使用基本身份验证进行读取
- Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 终结点
-
Constants.SERVER-Synapse 专用 SQL 池终结点(服务器 FQDN) -
Constants.USER- SQL 用户名。 -
Constants.PASSWORD- SQL 用户密码。
-
- Azure Data Lake Storage (Gen 2) 终结点 - 暂存文件夹
-
Constants.DATA_SOURCE- 在数据源位置参数中设置的存储路径用于数据暂存。
-
- Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 终结点
- 使用基于 Microsoft Entra ID 的身份验证进行写入
- Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 终结点
- 默认情况下,连接器使用
synapsesql方法的三部分表名称参数中设置的数据库名称来推断 Synapse 专用 SQL 终结点。 - 或者,用户可以使用
Constants.SERVER选项来指定 SQL 终结点。 确保终结点托管采用相关架构的相应数据库。
- 默认情况下,连接器使用
- Azure Data Lake Storage (Gen 2) 终结点 - 暂存文件夹
- 对于内部表类型:
- 配置
Constants.TEMP_FOLDER或Constants.DATA_SOURCE选项。 - 如果用户选择提供
Constants.DATA_SOURCE选项,则使用数据源中的location值派生暂存文件夹。 - 如果提供这两个选项,则使用
Constants.TEMP_FOLDER选项值。 - 如果没有暂存文件夹选项,连接器将基于运行时配置
spark.sqlanalyticsconnector.stagingdir.prefix派生一个暂存文件夹。
- 配置
- 对于外部表类型:
-
Constants.DATA_SOURCE是必需的配置选项。 - 连接器使用数据源位置参数中设置的存储路径,与
location方法的synapsesql参数相结合,从而派生出保存外部表数据的绝对路径。 - 如果未指定
location方法的synapsesql参数,则连接器将位置值派生为<base_path>/dbName/schemaName/tableName。
-
- 对于内部表类型:
- Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 终结点
- 使用基本身份验证进行写入
- Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 终结点
-
Constants.SERVER- Synapse 专用 SQL 池终结点(服务器 FQDN)。 -
Constants.USER- SQL 用户名。 -
Constants.PASSWORD- SQL 用户密码。 -
Constants.STAGING_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_KEY,与托管Constants.TEMP_FOLDERS(仅限内部表类型)或Constants.DATA_SOURCE的存储帐户相关联。
-
- Azure Data Lake Storage (Gen 2) 终结点 - 暂存文件夹
- SQL 基本身份验证凭据不适用于访问存储终结点。
- 因此,请确保按照 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 部分中所述分配相关的存储访问权限。
- Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 终结点
代码模板
本部分提供参考代码模板来介绍如何使用和调用用于 Apache Spark 的 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池连接器。
从 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池进行读取
读取请求 - synapsesql 方法签名
使用基于 Microsoft Entra ID 的身份验证从表中读取
//Use case is to read data from an internal table in Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool DB
//Azure Active Directory based authentication approach is preferred here.
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import com.microsoft.spark.sqlanalytics.utils.Constants
import org.apache.spark.sql.SqlAnalyticsConnector._
//Read from existing internal table
val dfToReadFromTable:DataFrame = spark.read.
//If `Constants.SERVER` is not provided, the `<database_name>` from the three-part table name argument
//to `synapsesql` method is used to infer the Synapse Dedicated SQL End Point.
option(Constants.SERVER, "<sql-server-name>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn").
//Defaults to storage path defined in the runtime configurations
option(Constants.TEMP_FOLDER, "abfss://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<some_base_path_for_temporary_staging_folders>").
//Three-part table name from where data will be read.
synapsesql("<database_name>.<schema_name>.<table_name>").
//Column-pruning i.e., query select column values.
select("<some_column_1>", "<some_column_5>", "<some_column_n>").
//Push-down filter criteria that gets translated to SQL Push-down Predicates.
filter(col("Title").startsWith("E")).
//Fetch a sample of 10 records
limit(10)
//Show contents of the dataframe
dfToReadFromTable.show()
使用基于 Microsoft Entra ID 的身份验证从查询中读取
注释
从查询中读取时的限制:
- 不能同时指定表名和查询。
- 仅允许使用 SELECT 查询。 不允许使用 DDL 和 DML SQL。
- 指定查询时,数据帧上的选择和筛选选项不会向下推送到 SQL 专用池。
- 从查询中读取仅在 Spark 3 中可用。
//Use case is to read data from an internal table in Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool DB
//Azure Active Directory based authentication approach is preferred here.
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import com.microsoft.spark.sqlanalytics.utils.Constants
import org.apache.spark.sql.SqlAnalyticsConnector._
// Read from a query
// Query can be provided either as an argument to synapsesql or as a Constant - Constants.QUERY
val dfToReadFromQueryAsOption:DataFrame = spark.read.
// Name of the SQL Dedicated Pool or database where to run the query
// Database can be specified as a Spark Config - spark.sqlanalyticsconnector.dw.database or as a Constant - Constants.DATABASE
option(Constants.DATABASE, "<database_name>").
//If `Constants.SERVER` is not provided, the `<database_name>` from the three-part table name argument
//to `synapsesql` method is used to infer the Synapse Dedicated SQL End Point.
option(Constants.SERVER, "<sql-server-name>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn").
//Defaults to storage path defined in the runtime configurations
option(Constants.TEMP_FOLDER, "abfss://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<some_base_path_for_temporary_staging_folders>")
//query from which data will be read
.option(Constants.QUERY, "select <column_name>, count(*) as cnt from <schema_name>.<table_name> group by <column_name>")
synapsesql()
val dfToReadFromQueryAsArgument:DataFrame = spark.read.
// Name of the SQL Dedicated Pool or database where to run the query
// Database can be specified as a Spark Config - spark.sqlanalyticsconnector.dw.database or as a Constant - Constants.DATABASE
option(Constants.DATABASE, "<database_name>")
//If `Constants.SERVER` is not provided, the `<database_name>` from the three-part table name argument
//to `synapsesql` method is used to infer the Synapse Dedicated SQL End Point.
option(Constants.SERVER, "<sql-server-name>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn").
//Defaults to storage path defined in the runtime configurations
option(Constants.TEMP_FOLDER, "abfss://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<some_base_path_for_temporary_staging_folders>")
//query from which data will be read
.synapsesql("select <column_name>, count(*) as counts from <schema_name>.<table_name> group by <column_name>")
//Show contents of the dataframe
dfToReadFromQueryAsOption.show()
dfToReadFromQueryAsArgument.show()
使用基本身份验证从数据表中读取
//Use case is to read data from an internal table in Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool DB
//Azure Active Directory based authentication approach is preferred here.
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import com.microsoft.spark.sqlanalytics.utils.Constants
import org.apache.spark.sql.SqlAnalyticsConnector._
//Read from existing internal table
val dfToReadFromTable:DataFrame = spark.read.
//If `Constants.SERVER` is not provided, the `<database_name>` from the three-part table name argument
//to `synapsesql` method is used to infer the Synapse Dedicated SQL End Point.
option(Constants.SERVER, "<sql-server-name>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn").
//Set database user name
option(Constants.USER, "<user_name>").
//Set user's password to the database
option(Constants.PASSWORD, "<user_password>").
//Set name of the data source definition that is defined with database scoped credentials.
//Data extracted from the table will be staged to the storage path defined on the data source's location setting.
option(Constants.DATA_SOURCE, "<data_source_name>").
//Three-part table name from where data will be read.
synapsesql("<database_name>.<schema_name>.<table_name>").
//Column-pruning i.e., query select column values.
select("<some_column_1>", "<some_column_5>", "<some_column_n>").
//Push-down filter criteria that gets translated to SQL Push-down Predicates.
filter(col("Title").startsWith("E")).
//Fetch a sample of 10 records
limit(10)
//Show contents of the dataframe
dfToReadFromTable.show()
使用基本身份验证从查询中读取
//Use case is to read data from an internal table in Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool DB
//Azure Active Directory based authentication approach is preferred here.
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import com.microsoft.spark.sqlanalytics.utils.Constants
import org.apache.spark.sql.SqlAnalyticsConnector._
// Name of the SQL Dedicated Pool or database where to run the query
// Database can be specified as a Spark Config or as a Constant - Constants.DATABASE
spark.conf.set("spark.sqlanalyticsconnector.dw.database", "<database_name>")
// Read from a query
// Query can be provided either as an argument to synapsesql or as a Constant - Constants.QUERY
val dfToReadFromQueryAsOption:DataFrame = spark.read.
//Name of the SQL Dedicated Pool or database where to run the query
//Database can be specified as a Spark Config - spark.sqlanalyticsconnector.dw.database or as a Constant - Constants.DATABASE
option(Constants.DATABASE, "<database_name>").
//If `Constants.SERVER` is not provided, the `<database_name>` from the three-part table name argument
//to `synapsesql` method is used to infer the Synapse Dedicated SQL End Point.
option(Constants.SERVER, "<sql-server-name>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn").
//Set database user name
option(Constants.USER, "<user_name>").
//Set user's password to the database
option(Constants.PASSWORD, "<user_password>").
//Set name of the data source definition that is defined with database scoped credentials.
//Data extracted from the SQL query will be staged to the storage path defined on the data source's location setting.
option(Constants.DATA_SOURCE, "<data_source_name>").
//Query where data will be read.
option(Constants.QUERY, "select <column_name>, count(*) as counts from <schema_name>.<table_name> group by <column_name>" ).
synapsesql()
val dfToReadFromQueryAsArgument:DataFrame = spark.read.
//Name of the SQL Dedicated Pool or database where to run the query
//Database can be specified as a Spark Config - spark.sqlanalyticsconnector.dw.database or as a Constant - Constants.DATABASE
option(Constants.DATABASE, "<database_name>").
//If `Constants.SERVER` is not provided, the `<database_name>` from the three-part table name argument
//to `synapsesql` method is used to infer the Synapse Dedicated SQL End Point.
option(Constants.SERVER, "<sql-server-name>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn").
//Set database user name
option(Constants.USER, "<user_name>").
//Set user's password to the database
option(Constants.PASSWORD, "<user_password>").
//Set name of the data source definition that is defined with database scoped credentials.
//Data extracted from the SQL query will be staged to the storage path defined on the data source's location setting.
option(Constants.DATA_SOURCE, "<data_source_name>").
//Query where data will be read.
synapsesql("select <column_name>, count(*) as counts from <schema_name>.<table_name> group by <column_name>")
//Show contents of the dataframe
dfToReadFromQueryAsOption.show()
dfToReadFromQueryAsArgument.show()
写入到 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池
写入请求 - synapsesql 方法签名
synapsesql(tableName:String,
tableType:String = Constants.INTERNAL,
location:Option[String] = None,
callBackHandle=Option[(Map[String, Any], Option[Throwable])=>Unit]):Unit
使用基于 Microsoft Entra ID 的身份验证进行写入
下面是一个全面的代码模板,它介绍了如何将连接器用于写入方案:
//Add required imports
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import org.apache.spark.sql.SaveMode
import com.microsoft.spark.sqlanalytics.utils.Constants
import org.apache.spark.sql.SqlAnalyticsConnector._
//Define read options for example, if reading from CSV source, configure header and delimiter options.
val pathToInputSource="abfss://<storage_container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<some_folder>/<some_dataset>.csv"
//Define read configuration for the input CSV
val dfReadOptions:Map[String, String] = Map("header" -> "true", "delimiter" -> ",")
//Initialize DataFrame that reads CSV data from a given source
val readDF:DataFrame=spark.
read.
options(dfReadOptions).
csv(pathToInputSource).
limit(1000) //Reads first 1000 rows from the source CSV input.
//Setup and trigger the read DataFrame for write to Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool.
//Fully qualified SQL Server DNS name can be obtained using one of the following methods:
// 1. Synapse Workspace - Manage Pane - SQL Pools - <Properties view of the corresponding Dedicated SQL Pool>
// 2. From Azure portal, follow the bread-crumbs for <Portal_Home> -> <Resource_Group> -> <Dedicated SQL Pool> and then go to Connection Strings/JDBC tab.
//If `Constants.SERVER` is not provided, the value will be inferred by using the `database_name` in the three-part table name argument to the `synapsesql` method.
//Like-wise, if `Constants.TEMP_FOLDER` is not provided, the connector will use the runtime staging directory config (see section on Configuration Options for details).
val writeOptionsWithAADAuth:Map[String, String] = Map(Constants.SERVER -> "<dedicated-pool-sql-server-name>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn",
Constants.TEMP_FOLDER -> "abfss://<storage_container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<some_temp_folder>")
//Setup optional callback/feedback function that can receive post write metrics of the job performed.
var errorDuringWrite:Option[Throwable] = None
val callBackFunctionToReceivePostWriteMetrics: (Map[String, Any], Option[Throwable]) => Unit =
(feedback: Map[String, Any], errorState: Option[Throwable]) => {
println(s"Feedback map - ${feedback.map{case(key, value) => s"$key -> $value"}.mkString("{",",\n","}")}")
errorDuringWrite = errorState
}
//Configure and submit the request to write to Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool (note - default SaveMode is set to ErrorIfExists)
//Sample below is using AAD-based authentication approach; See further examples to leverage SQL Basic auth.
readDF.
write.
//Configure required configurations.
options(writeOptionsWithAADAuth).
//Choose a save mode that is apt for your use case.
mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).
synapsesql(tableName = "<database_name>.<schema_name>.<table_name>",
//For external table type value is Constants.EXTERNAL
tableType = Constants.INTERNAL,
//Optional parameter that is used to specify external table's base folder; defaults to `database_name/schema_name/table_name`
location = None,
//Optional parameter to receive a callback.
callBackHandle = Some(callBackFunctionToReceivePostWriteMetrics))
//If write request has failed, raise an error and fail the Cell's execution.
if(errorDuringWrite.isDefined) throw errorDuringWrite.get
使用基本身份验证进行写入
以下代码片段替换了使用基于 Microsoft Entra ID 的身份验证进行写入部分中所述的写入定义,以使用 SQL 基本身份验证方法提交写入请求:
//Define write options to use SQL basic authentication
val writeOptionsWithBasicAuth:Map[String, String] = Map(Constants.SERVER -> "<dedicated-pool-sql-server-name>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn",
//Set database user name
Constants.USER -> "<user_name>",
//Set database user's password
Constants.PASSWORD -> "<user_password>",
//Required only when writing to an external table. For write to internal table, this can be used instead of TEMP_FOLDER option.
Constants.DATA_SOURCE -> "<Name of the datasource as defined in the target database>"
//To be used only when writing to internal tables. Storage path will be used for data staging.
Constants.TEMP_FOLDER -> "abfss://<storage_container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<some_temp_folder>")
//Configure and submit the request to write to Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool.
readDF.
write.
options(writeOptionsWithBasicAuth).
//Choose a save mode that is apt for your use case.
mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).
synapsesql(tableName = "<database_name>.<schema_name>.<table_name>",
//For external table type value is Constants.EXTERNAL
tableType = Constants.INTERNAL,
//Not required for writing to an internal table
location = None,
//Optional parameter.
callBackHandle = Some(callBackFunctionToReceivePostWriteMetrics))
在基本身份验证方法中,若要从源存储路径读取数据,需要其他配置选项。 以下代码片段提供了使用服务主体凭据从 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 数据源进行读取的示例:
//Specify options that Spark runtime must support when interfacing and consuming source data
val storageAccountName="<storageAccountName>"
val storageContainerName="<storageContainerName>"
val subscriptionId="<AzureSubscriptionID>"
val spnClientId="<ServicePrincipalClientID>"
val spnSecretKeyUsedAsAuthCred="<spn_secret_key_value>"
val dfReadOptions:Map[String, String]=Map("header"->"true",
"delimiter"->",",
"fs.defaultFS" -> s"abfss://$storageContainerName@$storageAccountName.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn",
s"fs.azure.account.auth.type.$storageAccountName.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn" -> "OAuth",
s"fs.azure.account.oauth.provider.type.$storageAccountName.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn" ->
"org.apache.hadoop.fs.azurebfs.oauth2.ClientCredsTokenProvider",
"fs.azure.account.oauth2.client.id" -> s"$spnClientId",
"fs.azure.account.oauth2.client.secret" -> s"$spnSecretKeyUsedAsAuthCred",
"fs.azure.account.oauth2.client.endpoint" -> s"https://login.partner.microsoftonline.cn/$subscriptionId/oauth2/token",
"fs.AbstractFileSystem.abfss.impl" -> "org.apache.hadoop.fs.azurebfs.Abfs",
"fs.abfss.impl" -> "org.apache.hadoop.fs.azurebfs.SecureAzureBlobFileSystem")
//Initialize the Storage Path string, where source data is maintained/kept.
val pathToInputSource=s"abfss://$storageContainerName@$storageAccountName.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/<base_path_for_source_data>/<specific_file (or) collection_of_files>"
//Define data frame to interface with the data source
val df:DataFrame = spark.
read.
options(dfReadOptions).
csv(pathToInputSource).
limit(100)
支持的数据帧保存模式
将源数据写入到 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池中的目标表时,支持以下保存模式:
- ErrorIfExists(默认保存模式)
- 如果目标表存在,则中止写入,并向被调用方返回异常。 否则,将会使用暂存文件夹中的数据创建新表。
- 忽略
- 如果目标表存在,则写入操作将忽略写入请求而不返回错误。 否则,将会使用暂存文件夹中的数据创建新表。
- 覆盖
- 如果目标表存在,则目标中的现有数据将替换为临时文件夹中的数据。 否则,将会使用暂存文件夹中的数据创建新表。
- 追加
- 如果目标表存在,则会向其追加新的数据。 否则,将会使用暂存文件夹中的数据创建新表。
写入请求回调句柄
新的写入路径 API 变更引入了一项实验性功能,可为客户端提供写入后指标的键值映射。 指标的键在新对象定义 Constants.FeedbackConstants 中定义。 指标可以通过传入回调句柄 (Scala Function) 作为 JSON 字符串进行检索。 下面是函数签名:
//Function signature is expected to have two arguments - a `scala.collection.immutable.Map[String, Any]` and an Option[Throwable]
//Post-write if there's a reference of this handle passed to the `synapsesql` signature, it will be invoked by the closing process.
//These arguments will have valid objects in either Success or Failure case. In case of Failure the second argument will be a `Some(Throwable)`.
(Map[String, Any], Option[Throwable]) => Unit
下面是一些值得注意的指标(以驼峰命名法形式显示):
WriteFailureCauseDataStagingSparkJobDurationInMillisecondsNumberOfRecordsStagedForSQLCommitSQLStatementExecutionDurationInMillisecondsrows_processed
下面是包含写入后指标的示例 JSON 字符串:
{
SparkApplicationId -> <spark_yarn_application_id>,
SQLStatementExecutionDurationInMilliseconds -> 10113,
WriteRequestReceivedAtEPOCH -> 1647523790633,
WriteRequestProcessedAtEPOCH -> 1647523808379,
StagingDataFileSystemCheckDurationInMilliseconds -> 60,
command -> "COPY INTO [schema_name].[table_name] ...",
NumberOfRecordsStagedForSQLCommit -> 100,
DataStagingSparkJobEndedAtEPOCH -> 1647523797245,
SchemaInferenceAssertionCompletedAtEPOCH -> 1647523790920,
DataStagingSparkJobDurationInMilliseconds -> 5252,
rows_processed -> 100,
SaveModeApplied -> TRUNCATE_COPY,
DurationInMillisecondsToValidateFileFormat -> 75,
status -> Completed,
SparkApplicationName -> <spark_application_name>,
ThreePartFullyQualifiedTargetTableName -> <database_name>.<schema_name>.<table_name>,
request_id -> <query_id_as_retrieved_from_synapse_dedicated_sql_db_query_reference>,
StagingFolderConfigurationCheckDurationInMilliseconds -> 2,
JDBCConfigurationsSetupAtEPOCH -> 193,
StagingFolderConfigurationCheckCompletedAtEPOCH -> 1647523791012,
FileFormatValidationsCompletedAtEPOCHTime -> 1647523790995,
SchemaInferenceCheckDurationInMilliseconds -> 91,
SaveModeRequested -> Overwrite,
DataStagingSparkJobStartedAtEPOCH -> 1647523791993,
DurationInMillisecondsTakenToGenerateWriteSQLStatements -> 4
}
更多代码示例
跨单元格使用具体化数据
Spark 数据帧的 createOrReplaceTempView 可用于通过注册临时视图来访问在另一个单元格中提取的数据。
- 在其中提取数据的单元格(比如说,将
Scala作为笔记本语言首选项的单元格)
//Necessary imports
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import org.apache.spark.sql.SaveMode
import com.microsoft.spark.sqlanalytics.utils.Constants
import org.apache.spark.sql.SqlAnalyticsConnector._
//Configure options and read from Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool.
val readDF = spark.read.
//Set Synapse Dedicated SQL End Point name.
option(Constants.SERVER, "<synapse-dedicated-sql-end-point>.sql.azuresynapse.azure.cn").
//Set database user name.
option(Constants.USER, "<user_name>").
//Set database user's password.
option(Constants.PASSWORD, "<user_password>").
//Set name of the data source definition that is defined with database scoped credentials.
option(Constants.DATA_SOURCE,"<data_source_name>").
//Set the three-part table name from which the read must be performed.
synapsesql("<database_name>.<schema_name>.<table_name>").
//Optional - specify number of records the DataFrame would read.
limit(10)
//Register the temporary view (scope - current active Spark Session)
readDF.createOrReplaceTempView("<temporary_view_name>")
- 现在,将笔记本上的语言首选项更改为
PySpark (Python),并从已注册视图<temporary_view_name>中提取数据
spark.sql("select * from <temporary_view_name>").show()
响应处理
调用 synapsesql 会得到两种可能的最终状态 - 成功或失败。 本部分介绍如何处理每个方案的请求响应。
读取请求响应
完成后,读取响应片段显示在单元格的输出中。 当前单元格中的失败还将取消后续单元执行。 Spark 应用程序日志中提供了详细的错误信息。
写入请求响应
默认情况下,写入响应会显示在单元格输出中。 失败时,当前单元格会被标记为失败,后续的单元格执行操作会中止。 另一种方法是将回调句柄选项传递给 synapsesql 方法。 回调句柄将提供对写入响应的编程访问。
其他注意事项
- 从 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池表进行读取时:
- 请考虑对 DataFrame 应用必要的筛选器,以利用连接器的列修剪功能。
- 在构建
TOP(n-rows)查询语句时,读取方案不支持SELECT子句。 限制数据的选项是使用 DataFrame 的 limit(.) 子句。- 请参阅示例 - 跨单元格使用具体化数据部分。
- 写入 Azure Synapse 专用 SQL 池表时:
- 监视 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 利用率趋势,以辨识可能影响读取和写入性能的限制行为。