Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Document translation is a cloud-based feature of the Azure Translator service that asynchronously translates whole documents in supported languages and various file formats. In this quickstart, learn to use Document translation with a programming language of your choice to translate a source document into a target language while preserving structure and text formatting.
Important
- Document translation is currently supported in the Azure Translator (single-service) resource only, and is not included in the Azure AI services (multi-service) resource.
- Document translation is supported in paid tiers. The Language Studio supports the S1 or D3 instance tiers. We suggest that you select Standard S1 to try Document translation. See Azure AI services pricing—Translator.
- Document translation public preview releases provide early access to features that are in active development. Features, approaches, and processes can change, before General Availability (GA) release, based on user feedback.
- The public preview version of Document translation client libraries default to REST API version 2024-05-01.
Prerequisites
To get started, you need:
An active Azure account. If you don't have one, you can create a Trial.
A single-service Azure Translator resource (not a multi-service Azure AI services resource). If you're planning on using the Document translation feature with managed identity authorization, choose a geographic region such as China North. Select the Standard S1 Standard Service Plan or C2, C3, C4, or D3 Volume Discount Plans.
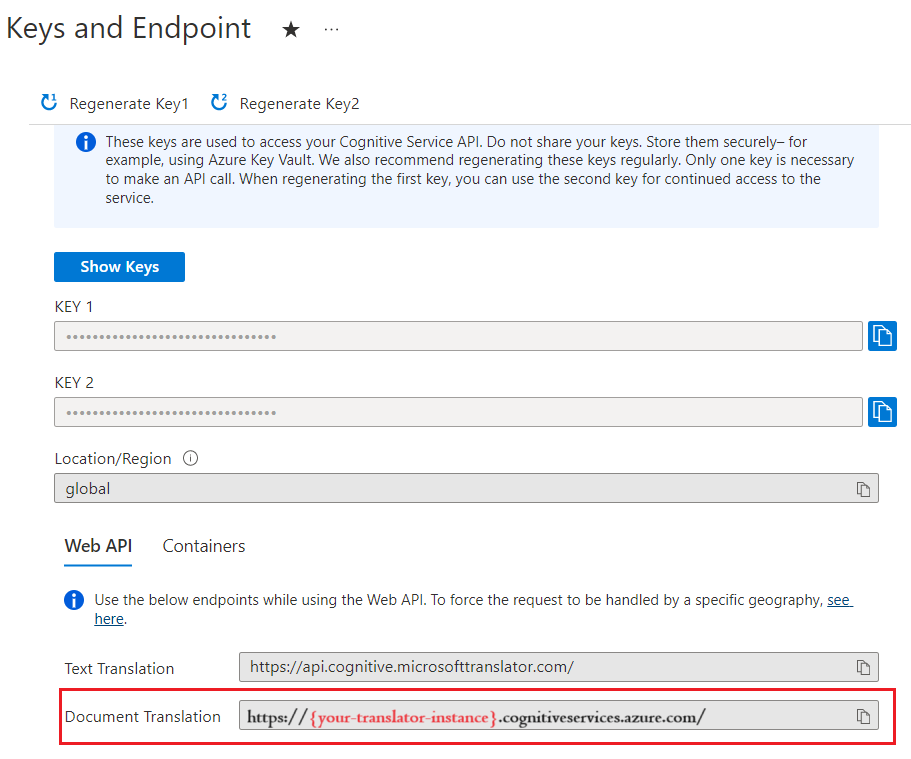
After your resource deploys, select Go to resource and retrieve your key and endpoint.
You need the key and endpoint from the resource to connect your application to the Azure Translator. You paste your key and endpoint into the code later in the quickstart. You can find these values on the Azure portal Keys and Endpoint page.
An Azure Blob Storage account. You'll create containers in your Azure Blob Storage account for your source and target files:
- Source container. This container is where you upload your files for translation (required).
- Target container. This container is where your translated files are stored (required).
Storage container authorization
You can choose one of the following options to authorize access to your Azure Translator resource.
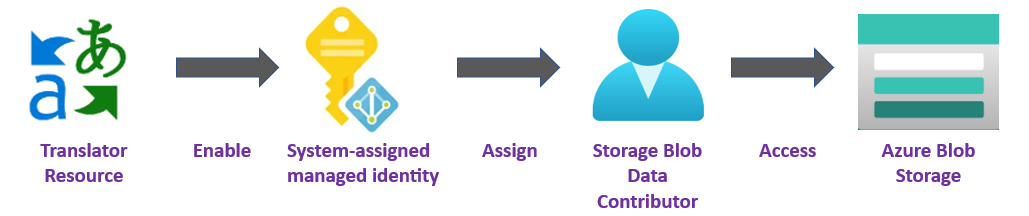
✔️ Managed Identity. A managed identity is a service principal that creates a Microsoft Entra identity and specific permissions for an Azure managed resource. Managed identities enable you to run your Azure Translator application without having to embed credentials in your code. Managed identities are a safer way to grant access to storage data and replace the requirement for you to include shared access signature tokens (SAS) with your source and target URLs.
To learn more, see Managed identities for Document translation.
✔️ Shared Access Signature (SAS). A shared access signature is a URL that grants restricted access for a specified period of time to your Translator. To use this method, you need to create Shared Access Signature (SAS) tokens for your source and target containers. The sourceUrl and targetUrl must include a Shared Access Signature (SAS) token, appended as a query string. The token can be assigned to your container or specific blobs.
- Your source container or blob must designate read and list access.
- Your target container or blob must designate write and list access.
To learn more, see Create SAS tokens.

Build your application
There are several tools available for creating, building, and running Translator C#/.NET applications. Here, we guide you through using either the command-line interface (CLI) or Visual Studio. Select one of following tabs to get started:
Set up your project
In a console window (such as cmd, PowerShell, or Bash), use the dotnet new command to create a new console app with the name batch-document-translation. This command creates a simple "Hello World" C# project with a single source file: Program.cs.
dotnet new console -n batch-document-translation
Change your directory to the newly created app folder. Build your application with the following command:
dotnet build
The build output should contain no warnings or errors.
...
Build succeeded.
0 Warning(s)
0 Error(s)
...
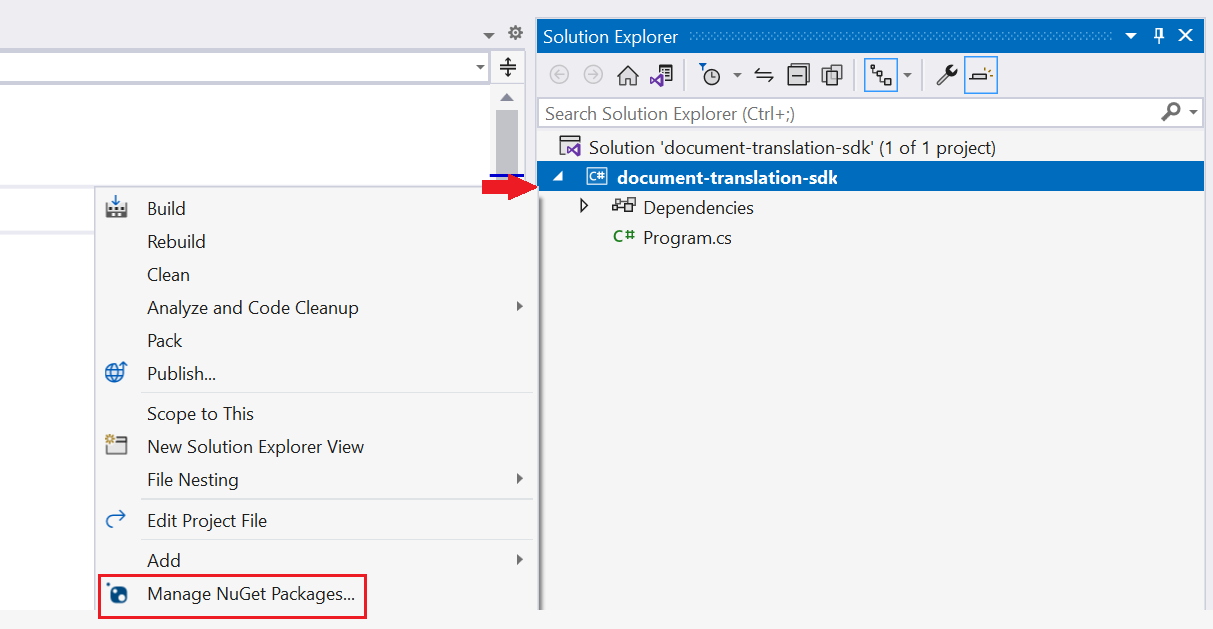
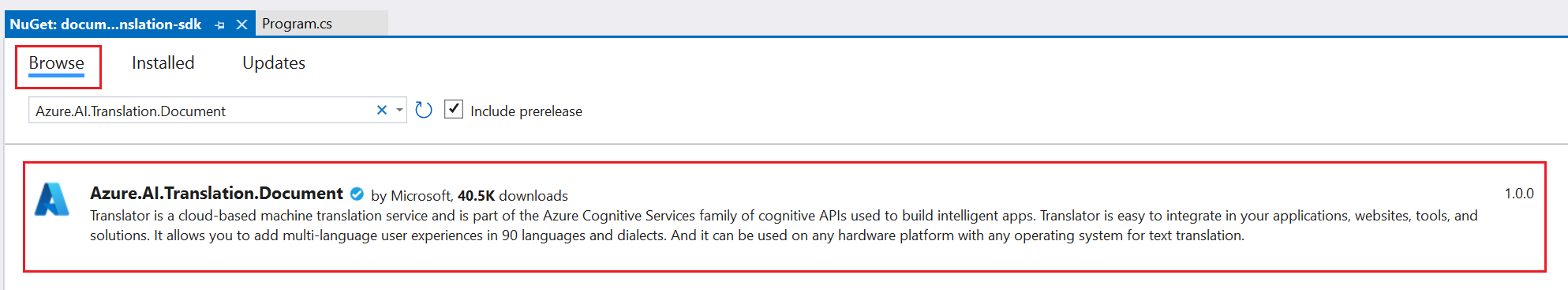
Install the client library
Within the application directory, install the Document translation client library for .NET:
dotnet add package Azure.AI.Translation.Document --version 2.0.0-beta
Translate documents asynchronously
For this project, you need a source document uploaded to your source container. You can download our document translation sample document for this quickstart. The source language is English.
From the project directory, open the Program.cs file in your preferred editor or IDE. Delete the existing code, including the line
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!").In the application's Program.cs , create variables for your key and custom endpoint. For more information, see Retrieve your key and custom domain endpoint.
private static readonly string endpoint = "<your-document-translation-endpoint>"; private static readonly string key = "<your-key>";Call the
StartTranslationAsyncmethod to Start a translation operation for one or more documents in a single blob container.To call
StartTranslationAsync, you need to initialize aDocumentTranslationInputobject that contains thesourceUri,targetUri, andtargetLanguageCodeparameters:For Managed Identity authorization create these variables:
sourceUri. The URL for the source container containing documents to be translated.
targetUri The URL for the target container to which the translated documents are written.
targetLanguageCode. The language code for the translated documents. You can find language codes on our Language support page.
To find your source and target URLs, navigate to your storage account in the Azure portal. In the left sidebar, under Data storage , select Containers, and follow these steps to retrieve your source documents and target container
URLS.Source Target 1. Select the checkbox next to the source container 1. Select the checkbox next to the target container. 2. From the main window area, select a file or documents for translation. 2. Select the ellipses located at the right, then choose Properties. 3. The source URL is located at the top of the Properties list. 3. The target URL is located at the top of the Properties list.
For Shared Access Signature (SAS) authorization create these variables
- sourceUri. The SAS URI, with a SAS token appended as a query string, for the source container containing documents to be translated.
- targetUri The SAS URI, with a SAS token appended as a query string, for the target container to which the translated documents are written.
- targetLanguageCode. The language code for the translated documents. You can find language codes on our Language support page.
Important
Remember to remove the key from your code when you're done, and never post it publicly. For production, use a secure way of storing and accessing your credentials like Azure Key Vault. For more information, see Azure AI services security.
Asynchronous translation code sample
Enter the following code sample into your application's Program.cs file:
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.Translation.Document;
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Text;
class Program {
// create variables for your custom endpoint and resource key
private static readonly string endpoint = "<your-document-translation-endpoint>";
private static readonly string key = "<your-key>";
static async Task Main(string[] args) {
// create variables for your sourceUrl, targetUrl, and targetLanguageCode
Uri sourceUri = new Uri("<sourceUrl>");
Uri targetUri = new Uri("<targetUrl>");
string targetLanguage = "<targetLanguageCode>"
// initialize a new instance of the DocumentTranslationClient object to interact with the Document translation feature
DocumentTranslationClient client = new DocumentTranslationClient(new Uri(endpoint), new AzureKeyCredential(key));
// initialize a new instance of the `DocumentTranslationInput` object to provide the location of input for the translation operation
DocumentTranslationInput input = new DocumentTranslationInput(sourceUri, targetUri, targetLanguage);
// initialize a new instance of the DocumentTranslationOperation class to track the status of the translation operation
DocumentTranslationOperation operation = await client.StartTranslationAsync(input);
await operation.WaitForCompletionAsync();
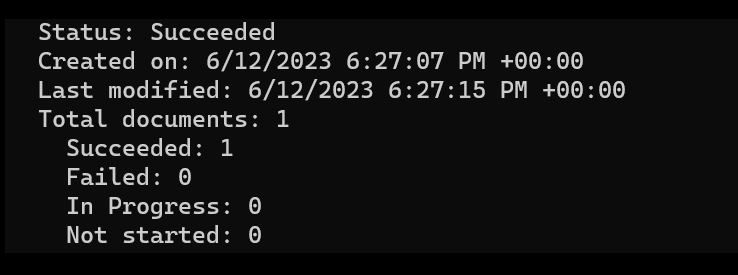
Console.WriteLine($" Status: {operation.Status}");
Console.WriteLine($" Created on: {operation.CreatedOn}");
Console.WriteLine($" Last modified: {operation.LastModified}");
Console.WriteLine($" Total documents: {operation.DocumentsTotal}");
Console.WriteLine($" Succeeded: {operation.DocumentsSucceeded}");
Console.WriteLine($" Failed: {operation.DocumentsFailed}");
Console.WriteLine($" In Progress: {operation.DocumentsInProgress}");
Console.WriteLine($" Not started: {operation.DocumentsNotStarted}");
await foreach(DocumentStatusResult document in operation.Value) {
Console.WriteLine($"Document with Id: {document.Id}");
Console.WriteLine($" Status:{document.Status}");
if (document.Status == DocumentTranslationStatus.Succeeded) {
Console.WriteLine($" Translated Document Uri: {document.TranslatedDocumentUri}");
Console.WriteLine($" Translated to language: {document.TranslatedToLanguageCode}.");
Console.WriteLine($" Document source Uri: {document.SourceDocumentUri}");
} else {
Console.WriteLine($" Error Code: {document.Error.Code}");
Console.WriteLine($" Message: {document.Error.Message}");
}
}
}
}
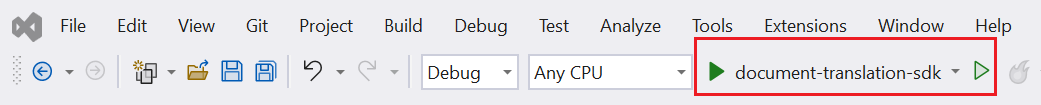
Run your application
Once you add the code sample to your application, run your application from the project directory by typing the following command in your terminal:
dotnet run
Here's a snippet of the expected output:
Synchronous translation code sample
You can download our document translation sample document for this quickstart. The source language is English.
using Azure;
using Azure.AI.Translation.Document;
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Text;
class Program {
string endpoint = "{your-document-translation-endpoint}";
string apiKey = "{your-api-key}";
SingleDocumentTranslationClient client = new SingleDocumentTranslationClient(new Uri(endpoint), new AzureKeyCredential(apiKey));
try
{
string filePath = @"C:\{folder}\document.txt"
using Stream fileStream = File.OpenRead(filePath);
// MultipartFormFileData (string name, System.IO.Stream content, string contentType);
var sourceDocument = new MultipartFormFileData(Path.GetFileName(filePath), fileStream, "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document");
DocumentTranslateContent content = new DocumentTranslateContent(sourceDocument);
// DocumentTranslate (string targetLanguage, Azure.AI.Translation.Document.DocumentTranslateContent documentTranslateContent, string sourceLanguage = default, string category = default, bool? allowFallback = default, System.Threading.CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
var response = client.DocumentTranslate("de", content);
Console.WriteLine($"Request string for translation: {requestString}");
Console.WriteLine($"Response string after translation: {responseString}");
}
catch (RequestFailedException exception) {
Console.WriteLine($"Error Code: {exception.ErrorCode}");
Console.WriteLine($"Message: {exception.Message}");
}
}
That's it! You just created a program to translate documents in a storage container using the .NET client library.
Set up your project
Make sure that the latest version of Python is installed.
Install the client library
Install the latest version of the Document translation client library:
pip install azure-ai-translation-document==1.0.0
Translate batch files
For this project, you need a source document uploaded to your source container. You can download our document translation sample document for this quickstart. The source language is English.
In your Python application file, create variables for your resource key and custom endpoint. For more information, see Retrieve your key and custom domain endpoint.
key = "{your-api-key}"
endpoint = "{your-document-translation-endpoint}"
Initialize a
DocumentTranslationClientobject that contains yourendpointandkeyparameters.Call the
begin_translationmethod and pass in thesourceUri,targetUri, andtargetLanguageCodeparameters.For Managed Identity authorization create these variables:
sourceUri. The URL for the source container containing documents to be translated.
targetUri The URL for the target container to which the translated documents are written.
targetLanguageCode. The language code for the translated documents. You can find language codes on our Language support page.
To find your source and target URLs, navigate to your storage account in the Azure portal. In the left sidebar, under Data storage , select Containers, and follow these steps to retrieve your source documents and target container
URLS.Source Target 1. Select the checkbox next to the source container 1. Select the checkbox next to the target container. 2. From the main window area, select a file or documents for translation. 2. Select the ellipses located at the right, then choose Properties. 3. The source URL is located at the top of the Properties list. 3. The target URL is located at the top of the Properties list.
For Shared Access Signature (SAS) authorization create these variables
- sourceUri. The SAS URI, with a SAS token appended as a query string, for the source container containing documents to be translated.
- targetUri The SAS URI, with a SAS token appended as a query string, for the target container to which the translated documents are written.
- targetLanguageCode. The language code for the translated documents. You can find language codes on our Language support page.
Asynchronous translation code sample
Important
Remember to remove the key from your code when you're done, and never post it publicly. For production, use a secure way of storing and accessing your credentials like Azure Key Vault. For more information, see Azure AI services security.
Enter the following code sample into your Python application:
# import libraries
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.translation.document import DocumentTranslationClient
# create variables for your resource key, custom endpoint, sourceUrl, targetUrl, and targetLanguage
key = '{your-api-key}'
endpoint = '{your-document-translation-endpoint}'
sourceUri = '<your-container-sourceUrl>'
targetUri = '<your-container-targetUrl>'
targetLanguage = '<target-language-code>'
# initialize a new instance of the DocumentTranslationClient object to interact with the asynchronous Document translation feature
client = DocumentTranslationClient(endpoint, AzureKeyCredential(key))
# include source and target locations and target language code for the begin translation operation
poller = client.begin_translation(sourceUri, targetUri, targetLanguage)
result = poller.result()
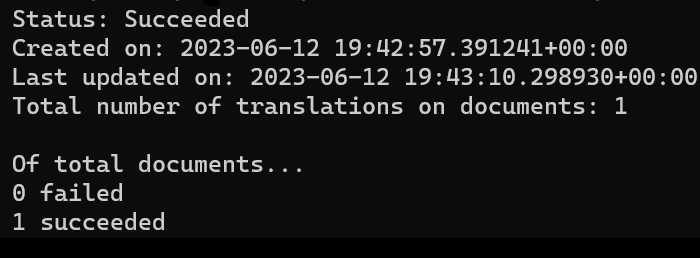
print('Status: {}'.format(poller.status()))
print('Created on: {}'.format(poller.details.created_on))
print('Last updated on: {}'.format(poller.details.last_updated_on))
print(
'Total number of translations on documents: {}'.format(
poller.details.documents_total_count
)
)
print('\nOf total documents...')
print('{} failed'.format(poller.details.documents_failed_count))
print('{} succeeded'.format(poller.details.documents_succeeded_count))
for document in result:
print('Document ID: {}'.format(document.id))
print('Document status: {}'.format(document.status))
if document.status == 'Succeeded':
print('Source document location: {}'.format(document.source_document_url))
print(
'Translated document location: {}'.format(document.translated_document_url)
)
print('Translated to language: {}\n'.format(document.translated_to))
else:
print(
'Error Code: {}, Message: {}\n'.format(
document.error.code, document.error.message
)
)
Run your application
Once you add the code sample to your application type the following command in your terminal:
python asynchronous-sdk.py
Here's a snippet of the expected output:
Synchronous translation code sample
You can download our document translation sample document for this quickstart. The source language is English.
import os
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.ai.translation.document import SingleDocumentTranslationClient
from azure.ai.translation.document.models import DocumentTranslateContent
def sample_single_document_translation():
# create variables for your resource api key, document translation endpoint, and target language
key = "<your-api-key>"
endpoint = "<your-document-translation-endpoint>"
target_language = "{target-language-code}"
# initialize a new instance of the SingleDocumentTranslationClient object to interact with the synchronous Document translation feature
client = SingleDocumentTranslationClient(endpoint, AzureKeyCredential(key))
# absolute path to your document
file_path = "C:/{your-file-path}/document-translation-sample.docx"
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path)
file_type = (
"application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document"
)
print(f"File for translation: {file_name}")
with open(file_path, "rb") as file:
file_contents = file.read()
document_content = (file_name, file_contents, file_type)
document_translate_content = DocumentTranslateContent(document=document_content)
response_stream = client.document_translate(
body=document_translate_content, target_language=target_language
)
# Save the response_stream to a file
output_file_path = "./translated-document.docx"
with open(output_file_path, "wb") as output_file:
output_file.write(response_stream)
print(f"Translated document saved to: {output_file_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
sample_single_document_translation()
That's it! You just created a program to translate documents asynchronously and synchronously using the Python client library.