Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article shows you how to view observability metrics and improve observability for AKS clusters with KMS etcd encryption.
Prerequisites
- An AKS cluster with KMS etcd encryption enabled. For more information, see Add Key Management Service (KMS) etcd encryption to an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster.
- You must enable diagnostic settings for the key vault to check the encryption logs.
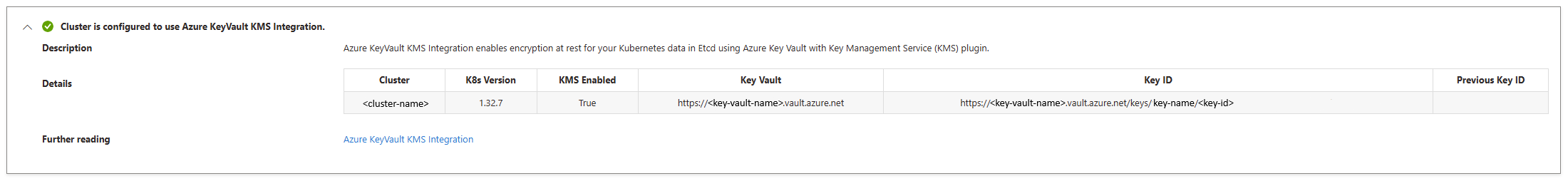
Check the KMS config
Get the KMS config using the
az aks showcommand.az aks show --name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --query "securityProfile.azureKeyVaultKms"The output looks similar to the following example output:
... "securityProfile": { "azureKeyVaultKms": { "enabled": true, "keyId": "https://<key-vault-name>.vault.azure.cn/keys/<key-name>/<key-id>", "keyVaultNetworkAccess": "Public", "keyVaultResourceId": <key-vault-resource-id> ...
Diagnose and solve problems
Because the KMS plugin is a sidecar of kube-apiserver pod, you can't access it directly. To improve the observability of KMS, you can check the KMS status using the Azure portal.
- In the Azure portal, navigate to your AKS cluster.
- From the service menu, select Diagnose and solve problems.
- In the search bar, search for KMS and select Azure KeyVault KMS Integration Issues.
Example problem
Let's say you see the following issue: KeyExpired: Operation encrypt isn't allowed on an expired key.
Because the AKS KMS plugin currently only allows bring your own (BYO) key vault and key, it's your responsibility to manage the key lifecycle. If the key is expired, the KMS plugin fails to decrypt the existing secrets. To resolve this issue, you need to extend the key expiration date to make KMS work and rotate the key version.
Next steps
For more information on using KMS with AKS, see the following articles: