Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can enable Azure Arc-enabled servers for one or more Windows or Linux machines in your environment by performing a set of steps manually. Or you can use an automated method by running a template script that we provide. This script automates the download and installation of both agents.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a trial subscription before you begin.
Prerequisites
This method requires that you have administrator permissions on the machine to install and configure the agent. On Linux, use the root account, and on Windows, you must be a member of the Local Administrators group.
Before you get started, review the Connected Machine agent prerequisites and verify that your subscription and resources meet the requirements. For information about supported regions and other related considerations, see supported Azure regions.
Note
Follow best security practices and avoid using an Azure account with Owner access to onboard servers. Instead, use an account that only has the Azure Connected Machine Onboarding or Azure Connected Machine Resource Administrator role assignment. To learn more, see Azure Identity Management and access control security best practices.
Generate the installation script from the Azure portal
Use the Azure portal to create a script that automates the agent download and installation and establishes the connection with Azure Arc. To complete the process, perform the following steps:
At the top of the Azure portal, search for and select Azure Arc.
In the service menu, expand Infrastructure, then select Machines.
On the Azure Arc | Machines page, select + Add at the upper left.
On the Basics page, provide the following:
Select the Subscription and Resource group for the machines.
Under Region, select the Azure region to store the servers' metadata.
Under Operating system, select the operating system that the script is configured to run on.
Under Connectivity method:
- Select either Public endpoint or Private endpoint. If you select Private endpoint, you can either select an existing private link scope or create a new one.
- If you want to use a Proxy server URL, enter the proxy server IP address or the name and port number that the machine uses in the format
http://<proxyURL>:<proxyport>.
Under Authentication, select Authenticate machines manually, then select Next.
Under Tags, review the default Physical location tags suggested and enter a value, or specify one or more Custom tags to support your standards.
Select Next.
Under Download and run script, review the summary information. If you need to make changes, select Previous and make necessary edits.
Select Download, then select Close.
For Windows, you're prompted to save OnboardingScript.ps1, and for Linux OnboardingScript.sh to your computer.
Install the agent on Windows
You can install the Connected Machine agent manually by running the Windows Installer package AzureConnectedMachineAgent.msi. You can download the latest version of the Windows agent Windows Installer package from the Microsoft Download Center.
Note
- To install or uninstall the agent, you must have Administrator permissions.
- You must first download and copy the installer package to a folder on the target server, or from a shared network folder. If you run the installer package without any options, it starts a setup wizard that you can follow to install the agent interactively.
If the machine needs to communicate through a proxy server to the service, after you install the agent you need to run a command described in the following steps. This command sets the proxy server system environment variable https_proxy. When this configuration is used, the agent communicates through the proxy server using the HTTP protocol.
If you're unfamiliar with the command-line options for Windows Installer packages, review Msiexec standard command-line options and Msiexec command-line options.
For example, run the installation program with the /? parameter to review the help and quick reference option.
msiexec.exe /i AzureConnectedMachineAgent.msi /?
To install the agent silently and create a setup log file in the
C:\Support\Logsfolder, run the following command.msiexec.exe /i AzureConnectedMachineAgent.msi /qn /l*v "C:\Support\Logs\Azcmagentsetup.log"If the agent fails to start after setup is finished, check the logs for detailed error information. The log directory is %ProgramData%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\log.
If the machine needs to communicate through a proxy server, set the proxy server environment variable by running the following command. Replace
{proxy-url}with your proxy server address (for example,proxy.example.com) and{proxy-port}with the port number (for example,8080).[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("https_proxy", "http://{proxy-url}:{proxy-port}", "Machine") $env:https_proxy = [System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("https_proxy","Machine") # For the changes to take effect, the agent service needs to be restarted after the proxy environment variable is set. Restart-Service -Name HIMDSNote
The agent doesn't support setting proxy authentication.
For more information, see Agent-specific proxy configuration.
After installing the agent, configure it to communicate with the Azure Arc service.
Parameters
--resource-group(string, example:myResourceGroup)--tenant-id(string, example:aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee)--subscription-id(string, example:aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e)--location(string, example:chinaeast2)--cloud(string, example:AzureCloud)--proxy(string, example:http://proxy.example.com:8080)
& "$env:ProgramFiles\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\azcmagent.exe" connect ` --resource-group "myResourceGroup" ` --tenant-id "aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee" ` --location "chinaeast2" ` --subscription-id "aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e"
Install the agent on Linux
The Connected Machine agent for Linux is provided in the preferred package format for the distribution (.RPM or .DEB) hosted in the Microsoft package repository. The shell script bundle Install_linux_azcmagent.sh performs the following actions:
Configures the host machine to download the agent package from packages.microsoft.com.
Installs the Hybrid Resource Provider package.
Optionally, you can configure the agent with your proxy information by including the --proxy "{proxy-url}:{proxy-port}" parameter. When this configuration is used, the agent communicates through the proxy server using the HTTP protocol.
The script also contains logic to identify the supported and unsupported distributions, and it verifies the permissions that are required to perform the installation.
To download and install the agent, run the following commands:
# Download the installation package. wget https://aka.ms/azcmagent -O ~/Install_linux_azcmagent.sh # Install the Azure Connected Machine agent. bash ~/Install_linux_azcmagent.shIf your machine needs to communicate through a proxy server to connect to the internet, include the
--proxyparameter, for example:# Download the installation package. wget https://aka.ms/azcmagent -O ~/Install_linux_azcmagent.sh # Install the Azure Connected Machine agent. bash ~/Install_linux_azcmagent.sh --proxy "proxy.contoso.com:8080"After installing the agent, configure it to communicate with the Azure Arc service:
Parameters
--resource-group(string, example:myResourceGroup)--tenant-id(string, example:aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee)--subscription-id(string, example:aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e)--location(string, example:chinaeast2)--cloud(string, example:AzureCloud)--proxy(string, example:http://proxy.example.com:8080)
azcmagent connect \ --resource-group "myResourceGroup" \ --tenant-id "aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee" \ --location "chinaeast2" \ --subscription-id "aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e" \ --cloud "AzureCloud"
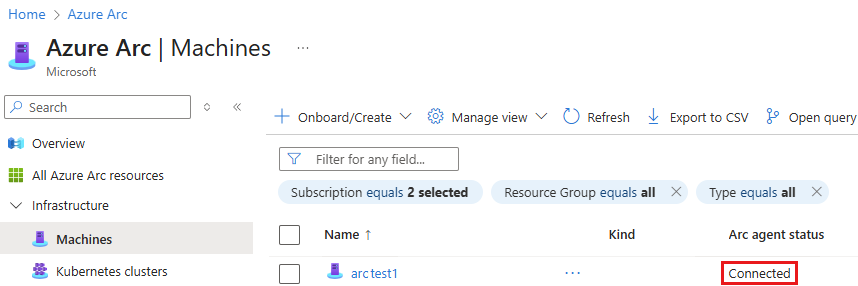
Verify the connection with Azure Arc
After you install the agent and configure it to connect to Azure Arc-enabled servers, go to the Azure portal to verify that the server successfully connected.
Next steps
Troubleshooting information can be found in the Troubleshoot Connected Machine agent guide.
Review the Planning and deployment guide to plan for deploying Azure Arc-enabled servers at any scale and implement centralized management and monitoring.
You can manage your machines using Azure Policy for tasks such as virtual machine (VM) guest configuration. Azure Policy also helps verify that machines are reporting to the expected Log Analytics workspace.