Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn how to use an Azure Managed Redis cache with the Python language and connect using Microsoft Entra ID.
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription - create one for free
- Install Python 3.7+ language environment
- Add these imports from to your project and to your development environment
redis- The Redis Python clientredis-entraid- Redis Microsoft Entra ID authentication extensionazure-identity- Azure authentication library
Create an Azure Managed Redis instance
First, create a cache. You can create a cache using Azure Managed Redis or Azure Cache for Redis using the Azure portal. In this Quickstart, we use Azure Managed Redis.
When you create the cache, Microsoft Entra ID is enabled by default making it secure from the start. Your cache must also use a public endpoint for this QuickStart.
To create a cache with the portal, follow one of these procedures:
Optionally, you can create a cache using Azure CLI, PowerShell, whichever you prefer.
Code to connect to a Redis cache
In the first part of the code sample, set your connection to the cache.
- Ports for Azure Managed Redis and Enterprise caches: 10000
- Ports for Azure Cache for Redis instances: 6380
import redis
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from redis_entraid.cred_provider import create_from_default_azure_credential
redis_host = "<host-url>"
redis_port = 10000 # Managed Redis default port
credential_provider = create_from_default_azure_credential(
("https://redis.azure.com/.default",),
)
r = redis.Redis(
host=redis_host,
port=redis_port,
ssl=True,
decode_responses=True,
credential_provider=credential_provider
)
Before you can run this code, you must add yourself as a Redis user to the cache.
You must also authorize your connection to Azure from the command line using the Azure command line or Azure developer command line (azd).
You should also add users or a System principal to your cache. Add anyone who might run the program as a user on the Redis cache.
The result looks like this:
PING: True
GET: Hello from Azure Managed Redis!
Here, you can see this code sample in its entirety. The code contains some error checking omitted from the earlier code explanations for simplicity. The final step is closing the connection to the cache.
import redis
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from redis_entraid.cred_provider import create_from_default_azure_credential
redis_host = "<host-url>"
redis_port = 10000 # Managed Redis default port
credential_provider = create_from_default_azure_credential(
("https://redis.azure.com/.default",),
)
try:
r = redis.Redis(
host=redis_host,
port=redis_port,
ssl=True,
decode_responses=True,
credential_provider=credential_provider,
socket_timeout=10,
socket_connect_timeout=10
)
print("PING:", r.ping())
r.set("Message", "Hello from Azure Managed Redis!")
print("GET:", r.get("Message"))
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
finally:
if 'r' in locals():
r.close()
Clean up resources
If you want to continue to use the resources you created in this article, keep the resource group.
Otherwise, if you're finished with the resources, you can delete the Azure resource group that you created to avoid charges.
Important
Deleting a resource group is irreversible. When you delete a resource group, all the resources in it are permanently deleted. Make sure that you do not accidentally delete the wrong resource group or resources. If you created the resources inside an existing resource group that contains resources you want to keep, you can delete each resource individually instead of deleting the resource group.
To delete a resource group
Sign in to the Azure portal, and then select Resource groups.
Select the resource group you want to delete.
If there are many resource groups, use the Filter for any field... box, type the name of your resource group you created for this article. Select the resource group in the results list.
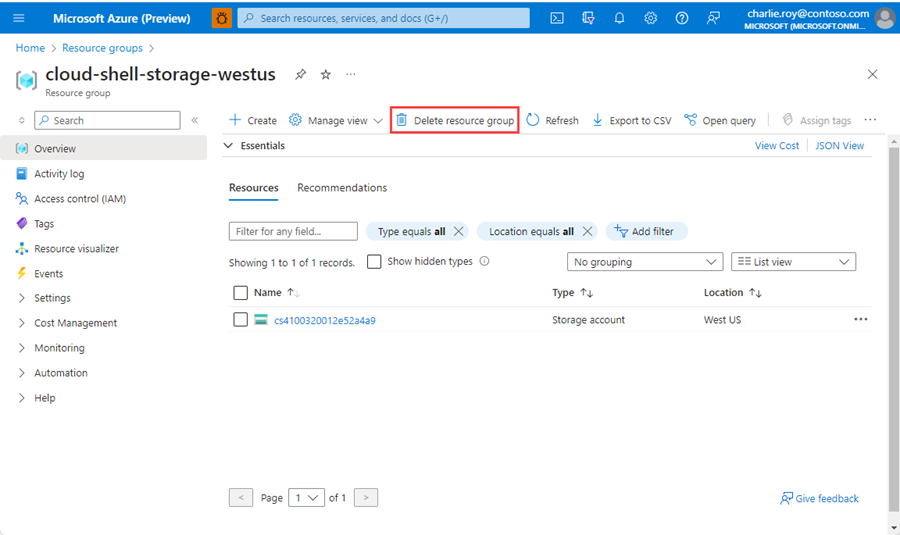
Select Delete resource group.
You're asked to confirm the deletion of the resource group. Type the name of your resource group to confirm, and then select Delete.
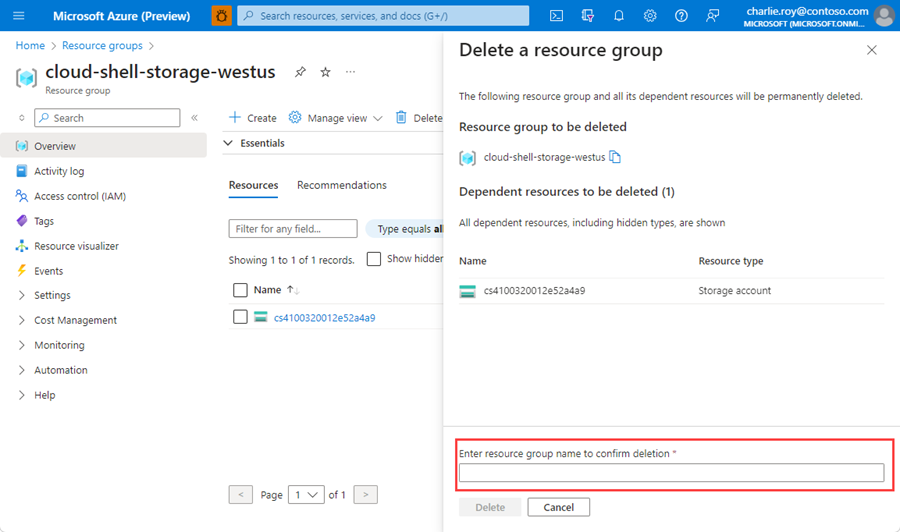
After a few moments, the resource group and all of its resources are deleted.